GNP - JLaFemina
advertisement

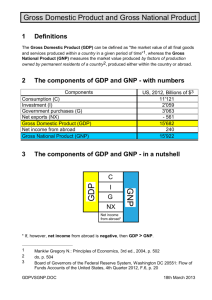
Quick Quiz 1) What is one of the five measures of income? 2) What is another? 3) What is one of the four sectors of the economy? 4) What is another? 5) How is personal income (PI) determined? What is GDP? How does GDP differ from GNP? Today we will be examining the different measures of a nation’s income Measuring a Nation’s Income- GNP The GDP does include production of foreignowned good produced in the US, but EXCLUDE US production outside the US Hence, it is not a proper measure of the total income earned by American citizens! Gross National Product ( GNP) $ value of all final goods, services, and structures produced in one year with labor and property supplied by US Largest measure of economy’s total income Shift from GDP to GNP must: 1. Add all payments that Americans receive from outside the US Subtract all payments made to foreign-owned resources in the US GNP, continued Ex: GDP= $7,872 +payments to Americans=242 -payments to foreigners=270 GNP+$7,844 (similar #s; this is usually true for the US, but not all nations) WHY do you think so? GNP, continued Weakness of GNP: says nothing about the production taking place in the US, just supplied by US Residents- Why is this a weakness? Why is GDP used as the leading indicator of economic health over the GNP? GDP vs. GNP activity Five Measures Biographies -What does the measure show? -What is added or subtracted to find the measure? -To whom would this measure be most valuable? Why? Economic Sectors and Circular Flows The economy is made up of various parts, called sectors. Sectors receive various components of the national income, and the sectors use this income to purchase the total output Consumer Sector (C) Basic unit- Household (all persons who occupy a house, apartment or room) Broader than a FAMILY Unrelated Individual- lives alone or with non relatives Why important to the US Bureau of Census? Consumer sector receives $ after taxes, etc. Investment Sector (I) Proprietorship, partnerships, and corporations. Brings together the factors of production to produce output Income is retained earnings and savings borrowed from the consumer sector Government Sector (G) AKA Public Sector Includes local, state, and federal levels of government Receives income from indirect business taxes, corporate income taxes, Social Security, personal income taxes from the consumer sector Foreign Sector (F) All consumers and producers outside the US Does not have a specific source of income Represents the dollar value of goods sent abroad and the dollar value of goods purchases abroad If the two are reasonably close, the foreign sector will appear to be fairly small, when there are a large number of goods and services being traded Output-Expenditure Model GDP= C+I+G+F Explains and analyzes the performance of the economy. Shows how separate sectors of the economy are interrelated Why are the sectors critical links in economic activity? How are each of the sectors used in determining the performance of the nation’s economy? Write down three questions and the answers about something you learned today. You can write them in any formattrue/false, mc, short answer, etc Homework Write an essay comparing GNP and GDP as measures of economic health and performance. It should be one typed page, double-spaced, tnr, 1inch margins. Price Index What are other ways to measure income besides GDP and GNP? A major problems with GDP- subject to distortions b/c of inflation Inflation can make output appear to grow w/out actually doing so Constructing a Price Index Price Index- a statistical series that can be used to measure changes in prices over time Used to reduce inflation Specific to product or range of items It’s not that difficult to construct a Price Index…so how do we do it? Construction of Price Index 1. Choose a Base Year for comparison 2. Select a MARKET BASKET of goodsmust remain fixed Market Basket= goods representative of the purchases that will be made overtime 3. Prices of each time in market basket are totaled Total=prices of the market basket base year and valued at 100% Major Price Indices 1. Consumer Price Index (CPI) Reports on price changes on 90,000 items in 364 categories Sampled- prices for goods and services taken from 85 geographical areas Complied Monthly by BLS Separate indices for 28 selected areas around the country Major Price Indices, continued 2. Producer Price Index (PPI) Measures price changes received by domestic producers for their own output Samples 3,000 commodities w/based year 1982 Reported Monthly through BLS Broken down into subcategories Major Price Indices, continued 3. Implicit GDP Price Deflator Average level of prices for all goods and services in the economy Computed quarterly Good, long-run indicator of price changes consumers face Not useful for month-to-month changes in inflation Base year 1992 Real vs. Current GDP Current (or nominal) GDP- not adjusted for inflation Real GDP- inflation distortions have been removed Write down three questions and the answers about something you learned today. You can write them in any formattrue/false, mc, short answer, etc Homework Study for Quiz tomorrow, use the websites under Unit IV on the Wiki to track price changes over the last five years for three items that you buy regularly. Chart how your income (allowance/wages) has changed over the five-year period. Type a paragraph reflecting on your results and discuss how you have been affected by inflation.