Osmosis in Elodea Cells: Lab Worksheet
advertisement

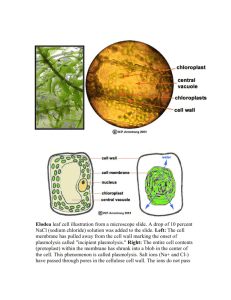
Name ____________________________________________________________ Date ______ Score_______ Lab 4 part 3 - Observing Osmosis in Living Cells The interactions between selectively permeable membranes, water, and solutes are important in cellular and organismal functions. For example, water and nutrients move from plant roots to the leaves and shoots because of differences in water potentials. Based upon what you know and what you have learned about osmosis, diffusion, and water potential in the course of your investigations, think about these questions. 1. What is turgor pressure in a plant cell? 2. What are two different ways a plant could control turgor pressure? 3. Is the definition in item 1 above a sufficient definition for turgor pressure in all cell types? 4. Will water move into or out of a plant cell if the cell has a higher water potential than its surrounding environment? Virtual Observations Start by looking at the image of a single leaf blade from Elodea (a water plant). We have already observed the cells of this plant during the cell lab. The ideal or normal state for Elodea would be a hypotonic environment. Use the color slide images to complete the virtual observations of Elodea cell Plasmolysis. Procedure Image 1: Draw the two Elodea cells in their normal state and describe the appearance of the cells by answering the following questions. Label all visible cell parts. 1a. Where is the cell membrane in relation to the cell wall? Can you see the two structures easily? Why or why not? 1b. What parts of the cell that you see control the water concentration inside the cell? Procedure Image 2: Draw the two Elodea cells in a hypertonic solution and describe the appearance of the cells by answering the following questions. Label all visible cell parts. 2a. Where is the cell membrane in relation to the cell wall? Can you see the two structures easily? Why or why not? 2b. Explain what happened to make the cells look the way they do. Procedure Image 3: Draw the two Elodea cells flooded in fresh water and describe the appearance of the cells by answering the following questions. Label all visible cell parts. 3a. Where is the cell membrane in relation to the cell wall? Can you see the two structures easily? Why or why not? 3b. Describe how the cells adjusted to the new environmental conditions. Application Questions 1. What is plasmolysis? 2. Why did the Elodea cells plasmolyze? 3. In the winter, grass often dies near roads that have been salted to remove ice. What causes this to happen – apply what you have learned from this exercise.