Name________________________ Date________ Block____
advertisement

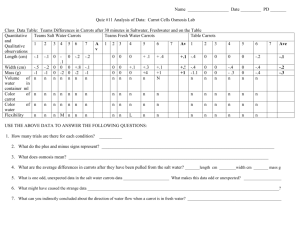
Name________________________ Date________ Block____ LAB: Observing Osmosis in Plants Background Information: When one area has more of a substance than another, that area has a high concentration of substance. When an area has less of a substance than another, it has a low concentration of the substance. In diffusion, substances in an area of higher concentration move to an area of lower concentration. This occurs until the amount of substances on each side of the membrane is equal. This equal distribution of substances is called equilibrium. Diffusion is a form of passive transport. It does not require cells to use energy to move materials. Active transport requires a cell to use energy to move materials. Osmosis is another form of passive transport. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Plant and animal cells react differently to osmosis. When a plant cell undergoes osmosis and water enters the cell, the cell is said to have turgor pressure - the cytoplasm swells with water, but the cell wall keeps the cell from bursting (lysing). When a plant cell undergoes osmosis and water leaves the cell, the cell is said to plasmolyze (shrink/shrivel) - the cytoplasm shrivels from a lack of water and the cell will eventually die. When an animal cell, which does not have a cell wall, undergoes osmosis and water enters the cell, the cell will eventually burst (lyse). When an animal cell undergoes osmosis and water leaves the cell, the cell shrivels and eventually dies from lack of water. Objectives: 1. Observe living plant cells as they respond to environmental changes 2. Make accurate microscope drawings of plant cells undergoing plasmolysis and turgor pressure. 3. Determine movement of water within cells based on observations. Materials: - microscope - slide - cover slip - forceps - eggs - dropper - distilled H2O - 10% salt H2O - paper towel -vinegar - carrots - corn syrup - green colored pencil - Elodea Pre-Lab: Fill out the chart below using your notes and the background information on the front page of this lab. Definition (with examples) Diffusion Equilibrium Passive Transport Active Transport Osmosis Turgor Pressure Plasmolyze Picture Procedures and Observations Part A: Microscopic Observations - Read all instructions before you begin work on this lab. 1. Wet mounts of elodea leaves have been prepared for you. You will be observing an elodea leaf that is in three different solutions: spring water, salt water, and distilled water. Pay special attention to the cell membrane and the position of the chloroplasts. 2. Look at the elodea leaf that is in the spring water (90% water). Draw four cells as they appear under high power. Label the cell wall, chloroplasts, and cytoplasm. Elodea in spring water _______ x 3. Observe the elodea leaf that is in the salt water (80% water). Draw four cells as they appear on high power, and label the cell wall, chloroplasts, and cytoplasm. Elodea in salt water ______ x 4. Observe the elodea leaf that is in the distilled water (100% water). Draw four cells as they appear on high power, and label the cell wall, chloroplasts, and cytoplasm. Elodea in distilled water _____ x Part B: Macroscopic Observations 1. Feel the carrots that have been soaking in fresh water and salt water. Write down what type of solution you think the carrot is in for each solution. Write down your observations about the condition of the carrots in the chart below. Then return the carrot to the jar. Solution Type of solution (Isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic) Observations Carrot in Distilled Water Carrot in Salt Water 2. Observe the eggs that have been soaking in distilled water, vinegar, and corn syrup. Write down what type of solution you think the egg is in for each solution. Write down your observations about the condition of the eggs in the chart below. Solution Egg in corn syrup Egg in vinegar Egg in distilled water Type of solution (Isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic) Observations Analysis- Part A: Microscopic Observations (Elodea) 1. Of the three solutions you observed (spring water, salt walter, distilled water) what solution was an isotonic solution? A hypotonic solution? A hypertonic solution? 2. When placed in a hypertonic solution, what type of molecules left the plant cells? Explain why they left and what observations you made that confirmed this. 3. Could Elodea live in a salt water environment? EXPLAIN your answer! 4. When placed in a hypotonic solution, what type of molecules entered the plant cells? Explain why they entered and what observations you made that confirmed this. 5. What would have happened if the cells you used had been animal cells instead of plant cells? EXPLAIN your answer! Analysis- Part B: Macroscopic Observations (Carrots and eggs) 1. What type of solution were the eggs in that were in vinegar? What directions were the water molecules moving when the eggs were in vinegar? Draw a picture. 2. What type of solution were the carrots and eggs in that were in distilled water? What direction were the water molecules moving when the carrots and eggs were in the distilled water? Draw a picture. 3. What type of solution were the carrots in that were in salt water and the eggs in that were in corn syrup? What direction were the water molecules moving when the carrots and eggs were in these solutions? Draw a picture. 4. This type of diffusion is called ____________________________.