Elodea Cell Plasmolysis: Illustration & Explanation
advertisement
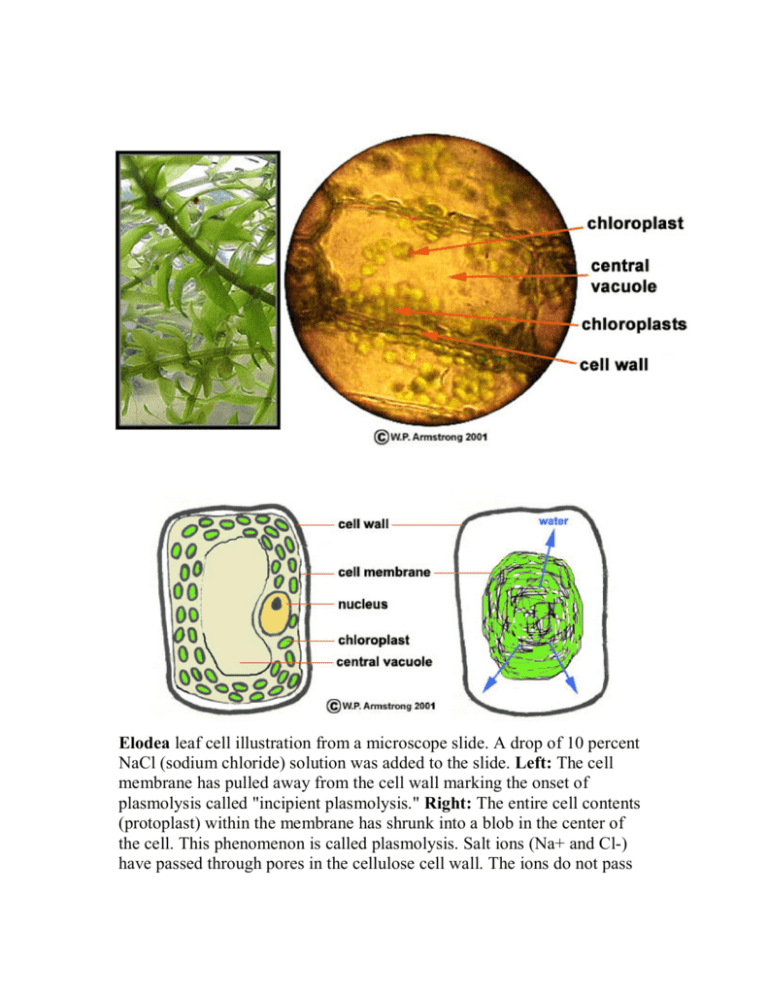
Elodea leaf cell illustration from a microscope slide. A drop of 10 percent NaCl (sodium chloride) solution was added to the slide. Left: The cell membrane has pulled away from the cell wall marking the onset of plasmolysis called "incipient plasmolysis." Right: The entire cell contents (protoplast) within the membrane has shrunk into a blob in the center of the cell. This phenomenon is called plasmolysis. Salt ions (Na+ and Cl-) have passed through pores in the cellulose cell wall. The ions do not pass through the protein-lipid cell membrane because it is impermeable to them. Due to the concentration differential inside and outside of the membrane, water molecules (shown by blue arrows) move out of the cell membrane, thus causing the cell contents to shrink into a blob. This concentration differential does not occur outside the porous, rigid cell wall, therefore its rectangular shape remains intact. Microscopic view of the plasmolyzed cells of an Elodea leaf. A. Cell wall composed of cellulose. B. The contents (protoplast) of a cell that has shrunk into a ball after losing water. C. The faint cell wall of another layer of cells. Since only one layer of cells is in focus due to the depth of field at this magnification, the second layer of cells is blurry and faint. Human Cheek Cell











