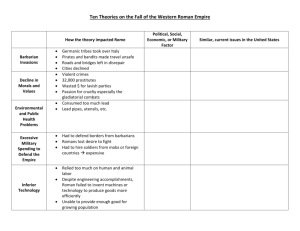
Review

Review
Hint game
Patriarchal
• Men as hunters
• Men as traders and warriors
• Men as head of family
• Societal Structure
River Valleys
• Yellow
• Indus
• Nile
• Where we find the earliest agricultural societies
Mesopotamia
• Sumer
• Babylonians
• In present day Iraq
• “ between the rivers ”
Pastoralism
• Fertile crescent goats
• Typically nomadic
• Horse peoples on the Asian steppe
City-state
• Sumer
• Sparta
• Maya
• Political structure: independent cities that had their own legal and social structure
Bronze Age
• Minoans
• Hittites
• Shang
• Ancient Egypt
• Age that predated the Iron Age
Hammurabi
• Ancient King of the Amorites (Babylonian
Empire)
• Law codes based on class
• Carthage
• Sea People
• Alphabet
Phoenicians
Nubians
• Connected Egypt to interior of Africa
• Ruled Egypt in 9 th C… the “ Black
Pharaohs of Egypt ”
• Lived south of Egypt and had key cities such as Meroe
• People of the bow
Minoans
• Inhabited the Aegean
• Bronze Age civ
• Flush toilets
• Probably ruled over the Mycenaean's from their capitol of Knossos on Crete
Diffusion
• Spread of ideas
• Spread of diseases
• Spread of… well, everything
• Ex: Bantu language and culture spread from W. Africa to all reaches of sub-
Saharan Africa
Iron Age
• Assyrians
• First to initiate were the Hittites
• An age that first started with the
Mycenaens
• Democratized metallurgy… but an age
Alexander the Great
• Macedonian
• Father was Phillip II
• Educated by Aristotle
• Conquered Persia, but died and opened the door for the Maurya Empire (Chandragupta
Maurya may have met him)
• Hellenized Persia
• Started the Greek Hellenistic Age
Hellenism
• Greek colonization of Persia and the
Mediterranean
• Ex: Rome adopts Greek mythology
• Ex: Greek influences in the Middle East
• “ Like Greece ”
Classical Empires
• Before 600BCE
• Empires with strong militaries and centralized governments
• All pressured and defeated bypeoples from the Asian Steppe
• Han, Rome, Maurya and Gupta
Rome
• Kingdom, Republic, Empire
• Italy
• City-state that grows to conquer most of
Western Europe and the Mediterranean
• Split in two
• Defeated by barbarians
Punic Wars
• Rome vs Phoenicians…
• Phoenician Carthage, that is
• 2 nd one found Romans running from
Hannibal and his elephants
• Third war Rome devastated Carthage
Augustus
• Adopted heir of Julius Caesar
• Octavian
• First emperor of Rome
• More stringent laws and focus on family values (Pater-familias)
• Ushers in the Pax Romana
Pax Romana
• Ushered in by Augustus
• Roman Peace
• Empire had expanded enough to create buffer states that provided security for citizens and merchants
Athens
• Greek city-state
• Socrates, Plato, Aristotle
• Early democracy
• Defeated the Persians at Marathon
• Eventually Persians burn this city to the ground… but then rebuild it.
Marathon
• Persian vs. Greek
• Athenian victory
• Angers Persia
• Darius, then Xerxes forms a Massive army in an attempt to defeat the Greeks
Maurya Empire
• Founder may have met Alexander
• Power Vacuum left by Alexander may have led to the rise of this empire
Celts
• First peoples to settle Europe
• Settled a land called Gual
• Eventually will make their way North to
Ireland
Dynastic Cycle
• Continuation of norms in China
• From Shang to Zhou to Qin to Han to Sui to Tang to Song…
• Probably the main reason that the fall of
Western Europe was so much worse on the region than the fall of the Han in China
• Round and round she goes…
Zhou
• Dynasty constantly at war
• Spring and Autumn period (don ’ t be fooled, kingdoms were warring)
• Warring States period (kingdoms banded together to form states and kept on fighting)
• Confucius, Laozi, and Legalism, Oh my!
Qin
• United China (of course it all falls apart a few more times)
• Shi Huangdi (self-proclaimed first emperor of China)
• Dynasty that followed Zhou
Han
• Strong centralized government
• Bureaucrats placed in high positions
• Strong military to defend their northern frontiers
• Founded by Liu Bang
• Dynasty that followed the Qin
• Pressure from Xiongnu (called Huns by some) led to their downfall
Vedic Age
• Indo-Europeans made their way into northern India and started this period
• Time of the Vedas (Rig Veda)
• Sanskrit developed from combining Aryan and Dravidian languages
• Beginning of Hinduism and birth of the
Caste system
Caste System
• India
• Reinforced by Hinduism… especially reincarnation
• Rejected by Buddhism
• Class system
Constantinople
• Earlier known as Byzantium
• City on the Bosporus
• First Roman Christian City
• Justinian had the Hagia Sophia (Church of
Holy Wisdom)
• Taken by the Ottomans and renamed
Istanbul
• Founded by Constantine
Diaspora
• Jews forced to leave (Northern Kingdom,
Israel, destroyed by Assyrians in 722BCE,
Southern Kingdom, Judah, destroyed by
Babylonians in 586BCE).
• Merchants travel abroad to make their fortunes in the Indian Ocean
• Africans brought to the New World and to areas of the Middle East
• Means dispersion
Gupta
• Classical Empire
• India
• Theater State
• Defeated by White Huns
The Huns
• From the Asian Steppe
• Pastoral nomads
• Pushed German tribes into Europe
• Attila
Germanization
• During and after the fall of Rome
• People groups entering Europe at the end of the Classical Age
• Changed the culture and structure of
Europe: from Latin to German
Olmec
• Americas (Mesoamerica)
• Mother Culture
• Big Heads
• Were-jaguars and sacrifices
Dao
• Belief system in China
• The Way
• Harmony between humanity and nature
• Founded by Laozi
Apostle Paul
• Roman Citizen
• Spread Christianity
• Successfully set up churches in cosmopolitan Rome
Legalism
• Another response to the constant fighting during the Zhou
• Ideas embraced by the Qin
• Men need strict laws and strict leaders to function well in society
Judaism
• Belief system with origin in the Middle East
• Dualism
• Covenant between Hebrew people and
God
• Abraham is the patriarch
Confucianism
• China
• Response to Warring States Period
• Social Harmony
• Created strict social hierarchy
• Examination system was based on these ideals
Hinduism
• India
• Polytheism
• Aryan origins
• Based on a mix of Aryan and Dravidian beliefs along with the Vedas
• Spread through India, into Sri Lanka and to S.E. Asia
Buddhism
• Indian Origin
• Response to Caste System and reincarnation
• Rejected by India
• Spread along the silk routes to SE Asia and E. Asia
• Rejected by the Tang Dynasty
• Founder: Siddhartha Gautama
Christianity
• Middle Eastern Origin
• During the Roman Empire
• Paul and others spread this belief system through the Eastern Mediterranean
• Branches: Roman Catholicism, Eastern
Orthodox and later Protestantism