Autotroph or Heterotroph
advertisement

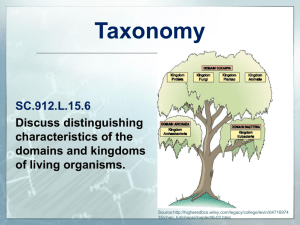
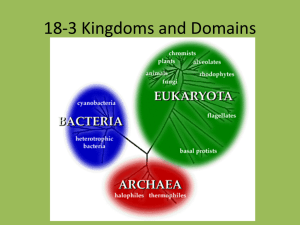
Happy Monday! Bellwork: Fill in the chart correctly on your “Kingdom Chart” you were given on Friday and put on Page 55 of your I.A.N. On your bellwork write “Fill in Kingdom Chart”. Kingdom Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote) Prokaryotic Prokaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular? Unicellular Unicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph? Autotroph or Heterotroph Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall? Yes, with peptidoglycan Yes, without peptidoglycan Example All Habitats E. coli Extreme environments Introduction to Bacteria Essential Question: How do scientists classify the different kinds of Eukarya? Standard: compare characteristics of taxonomic groups including fungi and protist (B8C) Match the following terms. 1. Unicellular A. Made up of 2 or more cells 2. Autotrophic B. Photosynthesizes or makes its own food 3. Multicellular 4. Heterotrophic C. Eats other organisms D. Made up of only 1 cell Match the following terms. 1. Unicellular A. Made up of 2 or more cells 2. Autotrophic B. Photosynthesizes or makes its own food 3. Multicellular 4. Heterotrophic C. Eats other organisms D. Made up of only 1 cell Which kingdom am I? Cases of walking pneumonia are most common in the late summer and fall. But infections can occur with no particular pattern throughout the year. And, even though the disease is contagious, it spreads slowly. The contagious period in most cases lasts less than 10 days. Researchers also think it takes prolonged close contact with an infected person for someone else to develop walking pneumonia; still, there are widespread outbreaks every four to eight years. When those outbreaks occur, walking pneumonia can account for as many as one out of every two cases of pneumonia. Symptoms include: •Cough that may come in violent spasms but produce very little mucus •Mild flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills •Sore throat •Headache •Tiredness •Lingering weakness that may persist after other symptoms go away •Some people with walking pneumonia may also have an ear infection, anemia, or a skin rash. Walking pneumonia is often the result of a lung infection from a bacterial microorganism called Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Halophiles These are salt-loving bacteria that grow in places like the Great Salt Lake of Utah or salt ponds on the edge of San Francisco Bay. Large numbers of certain halophiles can turn these waters a dark pink. Pink halophiles contain a pigment very similar to the rhodopsin in the human retina. They use this visual pigment for a type of photosynthesis that does not produce oxygen. Halophiles are aerobes and perform aerobic respiration. The waters of Lake Owens in California Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Gonorrhea Common symptoms in men include a burning sensation when urinating, or a white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis that usually appears 1 to 14 days after infection. Most women with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. Even when a woman has symptoms, they are often mild and include a painful or burning sensation when urinating, increased vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding between periods. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, even if symptoms are not present or are mild. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a bacterium. Gonorrhea can grow easily in the warm, moist areas of the reproductive tract. The bacterium can also grow in the mouth, throat, eyes, and anus. Thermus aquaticus: Thermophiles These are bacteria from hot springs and other high temperature environments. Some can grow above the boiling temperature of water. They are anaerobes, performing anaerobic respiration. Thermophiles are interesting because they contain genes for heat-stable enzymes that may be of great value in industry and medicine. An example is taq polymerase, the gene for which was isolated from a collection of Thermus aquaticus in a Yellowstone Park hot spring. Taq polymerase is used to make large numbers of copies of DNA sequences in a DNA sample. It is invaluable to medicine, biotechnology, and biological research. Annual sales of taq polymerase are roughly half a billion dollars. Treponema pallidum: Syphilis The appearance of a single sore marks the first (primary) stage of syphilis symptoms. The sore appears at the location where syphilis entered the body. The sore is usually firm, round, and painless. The sore lasts 3 to 6 weeks and heals regardless of whether or not a person is treated. Large, raised, gray or white lesions may develop in warm, moist areas such as the mouth, underarm or groin region. Sometimes rashes associated with secondary syphilis are so faint that they are not noticed. Other symptoms include fever, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, patchy hair loss, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and fatigue. The symptoms of secondary syphilis will go away with or without treatment. Symptoms of the late stage of syphilis include difficulty coordinating muscle movements, paralysis, numbness, gradual blindness, and dementia. In the late stages of syphilis, the disease damages the internal organs, including the brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. This damage can result in death. Domain Eukaryota KINGDOM PROTISTA Domain Eukaryota Kingdom fungi The Faces of Fungi… Mycorrhizae Fun-guy video facts (See what I did there?) • Fungi (introduction) –You should have 3 facts • Cordyceps –You should have 1 fact • Truffles –You should have 6 facts Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. They do not have much in common except that they are relatively simple eukaryotes. They are either unicellular or multicellular without reaching the specialized tissue level of organization. Protists include organisms such as algae, amoebae, protozoans, euglena, and slime molds. Protists live in almost any environment that contains liquid water. Some protists, such as algae, are photosynthetic, so they are autotrophs. Other protists are heterotrophs, obtaining nutrients from their environment. Amoebae engulf, or take into their membrane, other cells. This process is called phagocytosis. Most protists reproduce asexually, through a form of cell division. Other protists engage in a form of sexual reproduction. Some protists are responsible for diseases such as malaria in humans and potato blight in potato plants. Research scientists are experimenting with ways to use protists to wipe out fire ants and other pests. Fungi are a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes such organisms as yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. Many fungi are multicellular, but some are unicellular, such as yeast. Some differences between fungi and other eukaryotes are at the cellular level. Fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin. Fungi are heterotrophs. They take in nutrients by absorbing them from their environment. Fungi reproduction is complex. Many fungi reproduce both asexually and sexually at different stages in their life cycles. Fungal reproduction often involves the production and dispersal of spores. Fungi can be both harmful and helpful. Some fungi grow in or on plants or animals causing disease, such as Dutch Elm Disease or Ringworm. Fungi, such as the mold that the antibiotic penicillin is made from, can help organisms by killing bacteria. Yeast is used in the process of baking bread. Other fungi are used to produce cheese and yogurt. Kingdom Fungi Protista Cell Type? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote) Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicelluar? Unicellular or Unicellular or Multicellular Multicellular Heterotroph Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall? Yes, chitin Some do and some don’t Example Yeast, mold, mushroom Algae, euglena Autotroph or Heterotroph? Fill in the chart using the information from your notes. “Enhance” your chart using the following colors: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote: • • Color eukaryotic boxes blue Color prokaryotic boxes yellow. Unicellular vs Multicellular: • • • Color unicellular boxes purple Color multicellular boxes orange Color the both boxes half purple and half orange. Autotroph or Heterotroph: • • • Color heterotrophic boxes red Color autotrophic boxes green Color the both boxes half red and half green. Cell Wall: • • • Color the yes boxes grey Color the no boxes light blue Color the both boxes half grey and half light blue.