Assessment-Driven Instruction
advertisement

Assessment-Driven
Instruction
Models of Reading Assessment
Models of Reading Assessment
Deficit Model
Models of Reading Assessment
Deficit Model
Contextual Model
Models of Reading Assessment
Deficit Model
Contextual Model
Stage Models
Models of Reading Assessment
Deficit Model
Contextual Model
Stage Models
Cognitive Model
The Cognitive Model
of
Reading Assessment
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Is the child able to read texts
at his or her grade placement
level with automatic word
recognition and adequate
expression?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child make use of
context to monitor his or her
reading?
Before we go any further, let’s do a
brief sidebar on context. The role of
context in reading has long been a
controversial topic. Two competing
models of the reading process have
described this role very differently. We
will refer to these models as the TopDown and Bottom-Up models. Lets’
take a quick look at each.
Two Models of
Reading
She combed her hair.
She combed her hair.
She combed her hair.
Top-Down Model of Reading
Brain cannot rapidly process print.
Reader predicts the next word.
Reader merely samples the print.
Reader slows down if prediction is wrong.
She combed her
She combed her b
She combed her bangs.
She combed her bangs.
Bottom-Up Model of Reading
Brain processes almost every letter.
Most of this processing is automatic.
Reader does not need to predict words.
Reader uses context for multiple meanings.
Conclusion:
Research has clearly supported the
Bottom-Up Model.
Is the child fluent?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have adequate
sight word knowledge?
the
of
go
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have adequate
knowledge of decoding
strategies?
b
l
m ake
t
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have adequate
phonological awareness?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Is the child able to comprehend
the language of the text?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have an adequate
vocabulary for his or her age
and grade?
wise
blue
equator
weary arrive Pacific
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have the
background knowledge
necessary to understand the
particular passage that he or
she is reading?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Is the child able to use common
text structures to aid in
comprehension?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have adequate
knowledge of the purposes for
reading and possess strategies
available to achieve those
purposes?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Does the child have a set of
strategies that can be used to
achieve different purposes in
reading?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
What does the child view as the
goal of reading in general?
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
Phonological
Awareness
Decoding
Sight Word
Knowledge
Automatic
Word
Recognition
Vocabulary
Background
Knowledge
Knowledge
of Structure
Print
Concepts
General
Purposes
for Reading
Fluency
& Context
Language
Comprehension
Strategic
Knowledge
Specific
Purposes
for Reading
Knowledge
of Strategies
for Reading
Reading
Comprehension
What concepts of print does the
child have?
What is the
Literacy Coach’s
role in reading
assessment?
An LC’s Many Assessment Caps
Tester
Interpreter
Profiler
Cheerleader
Booster
LC as Tester
The LC will be part of the Assessment Team.
The LC may administer diagnostic tests.
LC as Interpreter
The LC may be asked to interpret schoolwide achievement
scores when they arrive.
The LC will need to be able to reach sound conclusions about
trends.
These conclusions will need to communicated with honesty and
tact.
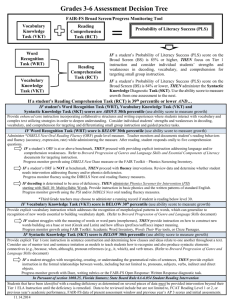
ITBS Percentile Ranks for Grade 3
School
Last Year
This Year
Difference
_______________________________________________________
Morristown
45
41
-4
Harmony
57
62
+5
District
49
51
+2
State
48
50
+2
Three Common Problems of Interpreting
Group Achievement Test Scores
1. Misinterpreting of percentiles
2. Assuming that different groups of
children are equivalent
3. Confusing achievement with norms
ITBS Percentile Ranks for Grade 3
School
Last Year
This Year
Difference
_______________________________________________________
Morristown
45
41
-4
Harmony
57
62
+5
District
49
51
+2
State
48
50
+2
Percentiles and Football
G
50
G
Avoid differences in percentile ranks.
Use NCEs or stanines instead.
How NCEs are made
NCEs “flatten” the normal curve so that
differences are statistically equivalent.
Interpreting Stanines
Above Average
Borderline
Average
Borderline
Below Average
Stanines 7-9
Stanine 6
Stanine 5
Stanine 4
Stanines 1-3
{
9
8
7
6
5
{
4
3
2
1
Three Common Problems of Interpreting
Group Achievement Test Scores
1. Misinterpreting of percentiles
2. Assuming that different groups of
children are equivalent
3. Confusing achievement with norms
Test Scores and Auto Racing
LC as Profiler
The LC should present teachers with classroom
profiles of test results.
Such profiles might use a spreadsheet format.
The point is to influence instruction!
This means:
Discussing options.
Monitoring outcomes.
Sample Excel File
1
A
Student
B
Teacher
C
Grade
D
Terra Nova
Comp NS
E
F
Sep DIBELS Sep DIBELS
ORF Level WC/Minute
2
Doe, Jane
Ellis
3
4
3
Hall, Monte
Ellis
3
5
4
Perez, Juan
Ellis
3
1
5
Rogers, Fred
Ellis
3
5
Low
6
Ruth, Babe
Ellis
3
7
Low
7
Yopp, Hallie
Ellis
3
3
Low
52
Low
60
High
Some
8
61
135
39
G
H
LC as Cheerleader
Look for the silver lining.
Interpret test results intelligently.
Focus on what your teachers are doing right!
Offer constructive suggestions.
Don’t avoid unpleasant truths.
LC as Booster
Understand AYP requirements.
Do your best to make sure classroom
instruction
is data-driven. This is the very
best way to
improve scores.
Cautiously consider additional steps in light of
1.
2.
3.
Ethical issues
Likelihood of effectiveness
Possible threat to professional climate.
How Can DIBELS
Drive Instruction?
?
How do we use DIBELS
to drive instruction at a
grade level?
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
Sample Beginning-of-Year
DIBELS Distribution
Test
K
A
S
1
L
ISF
7
LNF
3 10 87
A
S
2
L
S
L
A
S
L
23 70
5 15 80
PSF
20 26 54
NWF
18
ORF
A
3
20 62
18 20 62 22 22 56
An Action Plan for DIBELS
1. Make a table for fall, including results at the three levels of risk,
for each grade and test.
2. Identify points where large numbers of children are at high and
moderate risk.
3. Discuss the “big picture” with teachers in grade groups.
4. Make clear to everyone that a central goal is to move all children
into the low risk category.
5. Meet with individual teachers to plan for intervention and
progress monitoring.
Beware of comparing
groups from two
different years!
Hamilton Elementary
PreK-5, 622 students
96.9% African American
89.2% Free or Reduced-Price Lunch
27th Percentile Rank in Reading, Grade 3
30th Percentile Rank in Reading, Grade 4
24th Percentile Rank in Reading, Grade 5
16% Annual Teacher Turnover
Serves 3 Housing Projects
Serves 2 Homeless Shelters
Table 1. End-of-Year Kindergarten DIBELS Results over Two Years
_______________________________________________________
Subtest
Year 1
Year 2
___________________
__________________
At
Some
Low
At
Some
Low
_______________________________________________________
LNF
6
11
83
6
17
77
PSF
11
45
45
8
48
44
NWF
7
12
82
5
12
84
_______________________________________________________
Table 2. End-of-Year Grade 1 DIBELS Results over Two Years
_______________________________________________________
Subtest
Year 1
Year 2
___________________
__________________
At
Some
Low
At
Some
Low
_______________________________________________________
PSF
1
12
87
0
15
85
NWF
1
35
63
0
29
71
ORF
9
30
61
4
28
68
_______________________________________________________
Table 3. End-of-Year Grade 2 DIBELS Results over Two Years
_______________________________________________________
Subtest
Year 1
Year 2
___________________
__________________
At
Some
Low
At
Some
Low
_______________________________________________________
ORF
19
24
57
24
34
41
_______________________________________________________
Table 4. End-of-Year Grade 3 DIBELS Results over Two Years
_______________________________________________________
Subtest
Year 1
Year 2
___________________
__________________
At
Some
Low
At
Some
Low
_______________________________________________________
ORF
11
31
58
34
42
24
_______________________________________________________
Table 5. Changes in Percentage of Children at High or Moderate Risk
________________________________________________________
Grade
Subtest
Year 1
Year 2
___________ __________
B
E
B
E
_______________________________________________________
K
LNF
PSF
NWF
7
71
10
17
56
19
27
64
20
23
56
17
1
PSF
NWF
ORF
54
18
21
13
36
39
61
15
18
15
29
32
2
ORF
33
43
62
58
3
ORF
21
42
67
76
_______________________________________________________
It’s better to track cohorts.
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
It’s better to track cohorts.
3
2
1
K
B
M
Year 1
E
B
M
Year 2
E
K
1
2
3
B
M
K
E
B
M
1
E
B
M
2
E
B
M
3
E
Table 6. Long-Term NWF DIBELS Cohort Results for Grades K-1
________________________________________________________
Middle of
End of
Year 1
Year 2
________________________________________________________
Mean Number of Letter Sounds
29.1
66.8
Goal
13
50
Percentage at High or Moderate Risk
10
29
________________________________________________________
B
M
K
E
B
M
1
E
B
M
2
E
B
M
3
E
Table 7. Long-Term ORF DIBELS Cohort Results for Grades 2-3
________________________________________________________
Middle of
End of
Year 1
Year 2
________________________________________________________
Mean WPM Correctly Read
61.7
90.0
Goal
44
110
Percentage at High or Moderate Risk
33
76
________________________________________________________
How do we use DIBELS
to drive instruction in a
classroom?
Start with the
Class Profile!
Class Summary
1st Grade: Beginning Benchmark
Name
LNF
PSF
NWF
SCORE STATUS PCTILESCORE STATUS PCTILESCORE STATUS PCTILE
INTENSIVE
Poe, Edgar Allan
19
HIGH
5
40 ESTAB
65
8
HIGH
13
STRATEGIC
Blass, Bill
31
SOME 27
Borden, Liz
32
SOME 28
Tell, Wm.
40
LOW
Trump, Don
31
44 ESTAB
42 ESTAB
83
22
SOME
72
22
SOME
48
27 EMERG 28
6
HIGH
SOME
27
28 ESTAB
LOW
39
29 EMERG
29
12 SOME
4
40
20
BENCHMARK
Doe, Jane
37
30
36
LOW
72
DIBELS Box-and-Whisker Plot
95th Percentile Rank
80th Percentile Rank
50th Percentile Rank
20th Percentile Rank (May need support)
5th Percentile Rank (May need intensive support)
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Mon 1
Mon 2
Mon 3
Mon 4
Mon 5
Mon 6
Mon 7
Mon 8
Mon 9
Sample Plot for Phoneme Segmentation Fluency
Mon 10
Benchmark range for end of K
Benchmark range for middle of K
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Mon 1
Mon 2
Mon 3
Mon 4
Mon 5
Mon 6
Mon 7
Mon 8
Mon 9
Sample Plot for Phoneme Segmentation Fluency
Mon 10
Benchmark range for end of K
Benchmark range for middle of K
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Mon 1
Mon 2
Mon 3
Mon 4
Mon 5
Mon 6
Mon 7
Mon 8
Mon 9
Sample Plot for Phoneme Segmentation Fluency
Mon 10
A Data-Driven Model
Key Assumptions
1. An SBRR core is in place.
2. The core offers additional materials for
children who are slightly behind.
3. SBRR Intensive Intervention Programs
(outside the core) are available for each of the
5 component areas.
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention
DIBELS Benchmark Test
Low Risk
Some Risk
Core
At Risk
Core +
Core +
Small-Group Intensive
Core Intervention
Intervention
Core
Assessments
Core Intervention
Assessments
Intervention
Assessments
DIBELS Progress Monitoring
Discontinue
Intervention
Yes
Low Risk?
No
Continue
Intervention