Big 5 Ideas Handout
advertisement

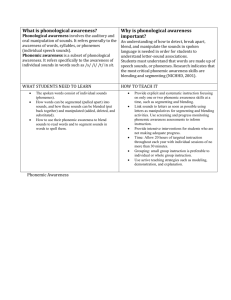
The Big 5 Areas of Reading Professional Development Phonological Awareness What is it? Phonological awareness is being able to recognize and manipulate sounds in words without attaching the letters. It also includes rhyming and recognizing when words share the same sound. What Does it Look Like? Children can show they have phonological awareness skills in several ways, including: • Identifying and making rhymes: “The pig has a (wig).” “Pat the (cat).” “The bunny is (funny).” • Identifying and working with syllables in spoken words: “I can clap the parts in my name: An – drew.” • Identifying and working with parts of words: “The first part of sip is s-.” “The last part of win is –in.” • Identifying and working with individual sounds in words: “The sounds in sun are s- u- n-.” Assess Your Student By … Administering the DIBELS assessment in which the student is asked to: Identify the initial sound in a word Produce all the sounds in 3-4 sound words Phonics What is it? Phonics teaches students that letters stand for particular sounds. Students are taught to use these sounds to make words. There are different ways to teach phonics. For example, some will teach phonics by teaching individual sounds (s-a-m), and some will teach phonics by teaching word chunks (s-am). What Does it Look Like? Children can show they have phonics skills in several ways, including: • Identifying letter sounds “Look at this letter S. What sound? /s/” • Breaking down new words. “Read this word MAP. /m/ /a/ /p/. What word? /map/.” Assess Your Student By … Administering the Dibels assessment, which tests the student’s knowledge of letter/sound correspondence as well as their ability to blend letters into words. Fluency What is it? Fluency is the ability to read a text accurately, effortlessly, and with good expression. This is important because time is not spent trying to figure out the words, but in focusing on the meaning of what is being read. Studies have demonstrated a close relationship between fluency and reading comprehension. What Does it Look Like? Children can show their reading is fluent by: • Reading effortlessly and with expression • Reading sounds naturally, as if they are speaking Assess Your Student By… As students become readers, fluency is assessed through a variety of oral reading assessments that evaluate speed, expression, smoothness, and effortless decoding. Our district currently uses both the DIBELS Next and AIMSweb assessments. Vocabulary What is it? Comprehension is the essential outcome in reading and cannot be understood without a strong vocabulary base. Vocabulary includes understanding what words mean when we see them in written materials, like books, or understanding words that people use in conversation. What Does it Look Like? Children can show they have strong vocabulary skills by: Recognizing that a new word being read is one they have heard and understood before: - Sounding out a new word (d- i- g-) and recalling they have heard and understood that word before. When misreading an unfamiliar word the student knows to adjust the pronunciation so that it makes sense in the context of the text being read. Understanding what an author is communicating by knowing the meanings of a lot of words. Assess How Your Child is Doing By … Although there is no formal vocabulary assessment used by our district, students are exposed daily to words through classroom literacy activities, repeated readings of stories, discussions, and many opportunities to hear quality literature through teacher read alouds. Comprehension What is it? Comprehension is the reason for reading. Comprehending what is read means that the child understands what he or she has read and is able to communicate it to others. What Does it Look Like? Children can show they have strong comprehension skills in several ways, including: • Setting a purpose for reading such as: • finding an answer to a question • figuring out how to put something together • completing homework assignments • experiencing the pleasure of great literature • Monitoring what they are reading and slowing down when the material gets difficult. • Answering questions about what has been read. • Summarizing what has been read. • Predicting what will happen next in the story. Assess How Your Child is Doing By … In addition to the retelling component of DIBELS Next and the Maze of AIMSweb, teachers informally evaluate comprehension through classroom and small group discussions. As students begin to read, assessments are administered to evaluate student use of comprehension strategies while reading and to determine instructional reading levels. References ¤Center for the Improvement of Early Reading Achievement. (2003). Put Reading First: The Research Building Blocks for Teaching Children to Read Kindergarten through Grade 3. Jessup, MD: National Institute for Literacy. ¤Learning Point Associates. (2004). A Closer Look at the Five Essential Components of Effective Reading Instruction: A Review of Scientifically Based Reading Research for Teachers. Naperville, IL: Learning Point Associates. ¤National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2000). Report of the National Reading Panel. Teaching children to read: an evidencebased assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction. Retrieved November, 4, 2011, from http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/nrp/smallbook.htm. Additional Resources ¤Florida Center for Reading Research www.fcrr.org ¤Reading Resource www.readingresource.net ¤Reading Rockets http://www.pbs.org/launchingreaders/rootsofreading/