Section 2-4: Reasoning in Algebra
advertisement

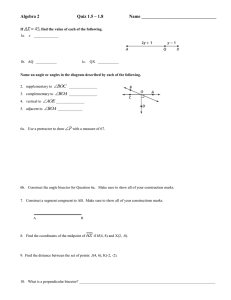
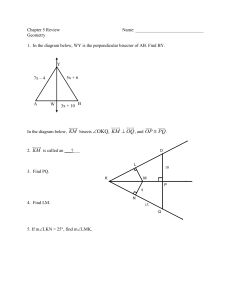
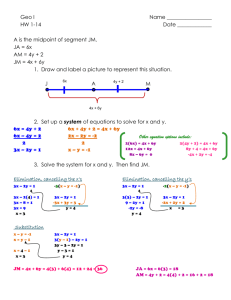
Section 2-4: Reasoning in Algebra Goal 2.01: Use logic and deductive reasoning to draw conclusions and solve problems. Turn in Homework • Lesson Quiz 2-3 Essential Question How are properties of equality used in Algebraic and Geometric Proofs? Addition Property of Equality If a = b and c = d, then a + c = b + d. subtraction property of equality If a = b and c = d, then a – c = b – d. multiplication property of equality If a = b then ac = bc. division property of equality If a = b and c ≠ 0, then a = b . c c substitution property If a = b then either a or b may be substituted for the other in any equation or inequality. reflexive (identity) Property a=a DE = DE 1=1 Symmetric Property If a = b then b = a. Distributive Property a ( b + c ) = ab + ac a ( b – c) = ab - ac Transitive Property If a = b and b = c, then a = c. If DE = FG and FG = JK, then DE = JK. If 1 = 2 and 2= 3, then 1 = 3. Midpoint Theorem If M is the midpoint of AB, then AM = ½ AB and MB = ½ AB, also 2 AM = AB and 2MB = AB. Angle Bisector Theorem If BX is the bisector of ABC, then 2 m ABX = m ABC and m ABX = m ABC. 2 m XBC = m ABC and m XBC = m ABC. Review: Definition of midpoint Definition of angle bisector Angle Addiction Postulate Segment Addition Postulate • Compare the definition of midpoint to the Midpoint Theorem? • Compare the definition of the angle bisector and the Angle Bisector Theorem? Examples • Worksheet Labeled: Justify the Statements examples • Together: p 92 (5 – 24 all) Group Work Practice 2-4 2 – 14 evens Individual Work Practice 2-4: 1 – 13 odds Assess Lesson Quiz 2 – 4: for a grade Homework Worksheet back on Front: Labeled: Properties of Algebra Justify the Statement Homework