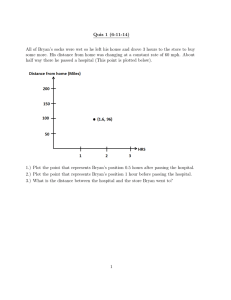
D. Pollock v. Farmer's Loan and Trust Company (1895)
advertisement

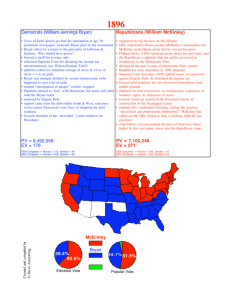
Agrarian Unrest, Depression, and Political Realignment I. Goldbugs and Silver Surfers A. Sutter’s Mill Strike, 1848-1849 B. Western Mining and Challenges to Goldbugs C. “Crime of 1873” D. 1890, 1893, Sherman Silver Purchase Acts E. 1892 Election a. Democrats- Grover Cleveland b. Republicans - Benjamin Harrison c. James Weaver, Populists II. Laissez Faire: Lack of regulation, Supreme Court Activism A. ICC (1887) was paper tiger B. Sherman Antitrust Act (1890), Ineffective C. US v. E. C. Knight Co. (1894) D. Pollock v. Farmer’s Loan and Trust Company (1895) E. J. P. Morgan Loan (1895) Depression III. 1893 Panic A. Deflation, overleveraged investment B. Popular Reaction 1. Pullman Strike (1894) 2. 1894 Congressional Populists, 42% vote increase 3. Jacob Coxey/Coxey’s Army (1895) C. Cleveland Reaction: 1. Police and Military Repression 2. Gold coinage I. 3. “Investor confidence” Populists IV. Populist Visions A. Currency Reform = Social Reform 1. Favors debtors and farmers 2. Economy is policy issue 3. Supply-siders (Drip) v. demand-siders (Percolator) B. Mary Lease A. “Raise less corn, and more hell!” B. “I wish I had said that!” C. Tom Watson, GA, 1896 Dem. VP candidate 1. Race is distraction 1896 Contenders IV. 1896 Election A. Populist Challenge B. Divided Democratic Party at convention C. William Jennings Bryan 1. Bryan enthralls audiences, is 36 2. Nominated as insurgent Democrat 3. Nominated as Populist presidential a. Fusionists D. Bryan Rhetoric 1. Bryan “Burn Down Your Cities” Speech a. No alliances with new urban working class 2. Bryan, “Cross of Gold” V. GOP, Big Business, and Campaign Innovation A. William McKinley and Mark Hanna, Modern campaigning 1. Organization, advertising, and spending B. McKinley and Corporate Spending 1. Passing the hat C. Front Porch campaign of McKinley 1. Folksy 2. Trains to Ohio D. McKinley for the WIN! 1. Bryan wins no new ground for Democrats 2. Goldbug Democrats repulsed; workers and tariff linked by Hanna