Earth*s Energy Sources
advertisement

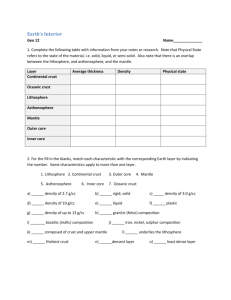
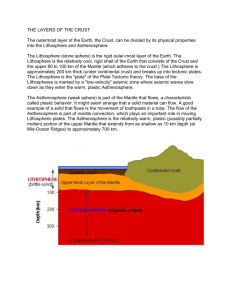
Earth’s Energy Sources Independent Learning Take Charge of Your Learning Learning Activities: By using this sheet every week! YES YES YES YES YES YES 4 1. Read the lesson materials before attending the lessons. 2. Attended the lessons. 3. Reviewed the lesson materials after the lessons and determined whether the learning outcomes have been met. 4. Answered the lesson questions. 5. Completed exam questions. 6. Made notes or read additional material to clarify understanding or extend learning. Each Week: 1. YES or NO if learning activity completed or not. 2. 0 – 5 to show how much you feel you have learnt for that week. 3. Maintain your file as evidence of the learning activities, including notes, answers to set questions, independent learning tasks and any additional reading Temperature Variation within Earth’s Interior Depth (km) Geotherm (°C) Melting point of Peridotite (°C) 0 50 200 500 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 15 1250 1450 1900 2500 3250 4000 4250 4250 4250 1200 1350 1600 2100 3000 3600 3850 4050 4200 4500 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Plot the data onto graph paper, with depth on the vertical axis. Describe how the geotherm varies with depth. Define the geotherm. Locate the Earth’s internal layers on the graph. Describe the physical state of the Earth’s interior in relation to the melting point curve. Calculate the average geothermal gradient for the first 50km into the Earth. Temperature Variation within Earth’s Interior Temperature (°C) Asthenosphere (semi-solid) Depth (km) Mesosphere (solid) Outer Core (liquid) Inner Core (solid) Temperature Variation within Earth’s Interior Temperature (°C) Lithosphere (solid) Asthenosphere (semi-solid) Geotherm Depth (km) Melting curve Mesosphere (solid) Outer Core (liquid) Where does this heat come from? • Radiogenic heat Inner Core (solid) • Primordial heat • Mid-oceanic ridges • Partial melting (twice) • Oceanic trench • Basaltic magma • Oceanic lithosphere • Andesitic magma • Continental lithosphere • Gabbro • Subducting plate • Dolerite dykes • Benioff zone • Basaltic pillow lavas • Oceanic crust • Sediment • Continental crust • Shield volcano • Asthenosphere • Cone-shaped volcano • Moho • Slab pull/ridge push Heat flow (mW /m²) 50 60 70 120 180 70 40 20 40 50 60 75 295 100 70 60 Km 0 10 18 20 23 30 40 45 50 60 70 85 90 93 95 100 Mid-oceanic ridge Volcanic arc Ocean trench Mid-oceanic ridge Volcanic arc Ocean trench