Earth and Space Science Objective Booklet
advertisement

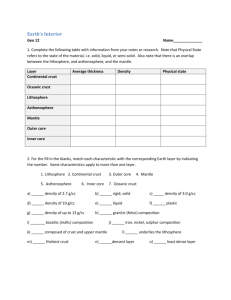
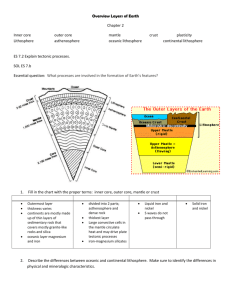
Earth and Space Science Objective Booklet 4a. Compare and contrast the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 1) Illustrate a picture of the Earth and label the crust, lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, and inner core. How thick is each layer? 2) Compare and contrast the composition, density, and location of continental crust and oceanic crust. 3) Compare and contrast the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 4) Explain what is meant by the plastic-like nature of the asthenosphere. 5) What is a plate and what is the theory of plate tectonics? What forces drive the movement of tectonic plates? 6) What occurs at divergent plate boundaries and what do they form? 7) What occurs at convergent plate boundaries and what do they form? (Oceanic/Continental, Continental/Continental, Oceanic/Oceanic) 4b. Describe the cause and effect relationships between the composition of and movement within the Earth’s lithosphere. 1) Compare the modern distribution of continents to the supercontinent Pangaea. 2) What is convection and how does it cause movements of the lithosphere. 3) What is an earthquake and how does it occur? 4) How does density of material affect wave speed? 5) Explain how seismology can be utilized as well as its limitations. 6) Explain how each of the following are formed: a. Mid–ocean ridge c. Island arc b. Rift valley d. Volcano 4c. Examine weather forecasting and describe how meteorologists use atmospheric features and technology to predict the weather. 1) Explain the difference between a land breeze and a sea breeze? 2) What is the Coriolis effect? 3) What are the polar easterlies? 4) What are global winds? 5) What are the westerlies? 6) What is precipitation? List four forms of precipitation. 7) What is air pressure and how do we measure it? 8) What is humidity and how do we measure it? What is air pressure? How does a high-pressure system form and what type of weather does it produce? How does a low-pressure system form and what type of weather does it produce? 9) What is the difference between a cold front, stationary front, occluded front, and a warm front? What type of weather does each one produce? 10) Draw the weather map symbols for a high-pressure system, low-pressure system, precipitation (rain, snow), cold front, warm front, and stationary front. 11) What is a jet stream? 12) Explain what weather satellites are and how they can be utilized to predict the weather. 13) What is a computer model and how can it be utilized to predict weather. 4h. Justify why an imaginary hurricane might or might not hit a particular area, using important technological resources. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) List three websites that can be utilized to track the path of hurricanes. Describe the transition from a depression to a hurricane. What is a hurricane? Explain the difference between latitude and longitude. Outline the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. 4d. Research the importance of the conservation of renewable and nonrenewable resources including (but not limited to) Mississippi, and justify methods that might be useful in decreasing the human impact on global warming. 1) What is the difference between a renewable resource and a nonrenewable resource? Give five examples of each. 2) What is conservation? 3) List three ways to conserve. 4) What is the greenhouse effect? How is it caused naturally? Infer how humans contribute to the greenhouse effect? 5) What is global warming? 6) Explain how the greenhouse effect and global warming are related. 7) What are three effects of global warming. 8) What is overpopulation? How does it decrease the planet’s biodiversity? 9) Draw the water cycle. 10) Draw the Carbon cycle. 11) Draw the oxygen cycle. 12) Draw the nitrogen cycle. 4g. Justify the importance of continued research and use of new technology in the development and commercialization of potentially useful natural products, including, but not limited to research efforts in Mississippi. 1) What is a natural product and give 3 examples? 2) What is a synthetic product? 3) What are advantages and disadvantages of natural vs. synthetic products? 4) List five natural products, their sources and their uses. 5) What companies in Mississippi are involved with research and development of new natural products? 4e Explain how the tilt of Earth’s axis and the position of the Earth in relation to the sun determine climatic zones, seasons, and length of the days. 1) What is the difference between revolution and rotation? 2) Explain how the Earth’s revolution around the Sun and the Earth’s axial tilt cause seasons on Earth. a) Draw the position of the Sun and tilt of the Earth would look if the Northern Hemisphere was having winter. b) Draw the position of the Sun and tilt of the Earth would look if the Northern Hemisphere was having summer. 3) List and explain the different climate zones. How are they divided? 4) What is a solstice? 5) What would happen if the Earth was not tilted on its axis? 6) Relate daylight hours and amounts of direct sunlight to each of the four seasons. 4f. Describe the hierarchical structure (stars, clusters, galaxies, galactic clusters) of the universe and examine the expanding universe to include its age and history, and the modern techniques (e.g., radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and X-ray astronomy) used to measure objects and distances in the universe). 1) Explain how the Universe is organized beginning with stars. 2) What are the three types of galaxies? Describe how each one is arranged and draw a picture of each. 3) What is the difference between a galactic cluster and a globular cluster? 4) What is the unit of distance used to describe distance between stars and how many kilometers is it equivalent to? 5) Describe the widely accepted theory regarding the formation of the universe. 6) What evidence supports this theory of universe formation? 7) Explain three theories regarding the future of the universe. 8) What is illustrated by the red shift? 9) Describe at five different types of telescopes and what form of electromagnetic radiation they utilize.