Neurological Exam Overview for Neurology
advertisement

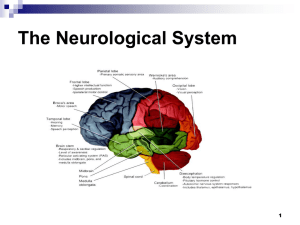
Neurological Examination Indiana University Department of Neurology Overview Learn / do in organized sequence General Vital signs: wt, pulse , BP, temp ( respirations) Skin for café au lait, meningococcal purpura, splinter hemorrhages Measure OFC ( head size) in kids Listen for bruits in neck ( carotid or vertebral arteries) Neurological exam Mental status Cranial nerves Motor exam Cerebellar Sensory Station & Gait Mental Status Level of consciousness Orientation Alert Sleepy but awakens to verbal prompting ( Lethargic) Unresponsive to painful stimuli ( Comatose) To person, place, time, situation Speech & Language Normal Dysarthric (slurred, nasal) Use of language in symbolic sense Fluency, comprehension, repetition Aphasia: expressive (Broca)/ receptive (Wernicke) Mental Status Parietal Functions Spatial orientation ( R /L) Construction Calculation Stereognosis Gnosis (awareness) agnosagnosia CN I Olfactory nerve Check each nostril individually with patient’s eyes closed Use coffee, mint, vanilla, clove Not ammonia (checks V2) Anosmia in head trauma frontal lobe tumor Parkinson’s & Alzheimer’s Optic System: Overview Functions: Data acquisition & transmission Camera control Eye lids Eye movements Focus CN II Optic nerve Visual acuity Visual fields Pupillary light reflex CN 2 Afferent CN 3 Efferent Funduscopic exam Visual acuity Visual acuity Corrected (with glasses) OS left OD right Ask patient to start at top read down the chart VA is last line read correctly Visual fields Pt looks at your forehead Check each eye alone Keep equidistance between you and patient Count fingers in the 4 visual field quadrants Bring in your finger inward from beyond your periphery to define pts field Pupillary light reflex Direct and consensual Observe pupil size ( mm) Shine light into eye from off center Observe for pupillary constriction in stimulated & opposite eye Accomodation As pt looks at close target; eyes converge and pupils constrict Relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) Light in abnl eye after good eye shows pupil dilation rather than constriction Present with optic nerve lesions Relative afferent pupillary defect Fundoscopy (ophthalmoscope) Optic disk ( optic nerve head) Retinal vessels Retina CN II Optic Nerve Normal Papilledema CN III (oculomotor), IV (trochlear), VI (abducens) Are the eyes conjugate Puplliary function Evaluate motility Horizontal Vertical Oblique Disorders Nerve ( nucleus) Intra-nuclear Supra-nuclear Extraocular muscles and their actions •CN III (Oculomotor nerve) •Superior rectus: •elevation when the eye is aBducted •Inferior rectus: •depression when the eye is aBducted •Medial rectus: aDduction •Inferior oblique: •elevation when the eye is aDducted •CN IV (Trochlear nerve) •Superior oblique: •depression when the eye is aDducted •CN VI (Abducens nerve) •Lateral rectus: aBduction CN III—lesion causes eye motility problems, ptosis and mydriasis (enlarged pupil) Third nerve palsy Eye is “down and out” Pupil abnormal Compression by uncal herniation or P-com aneurysm Pupil normal Nerve infarction Left IV nerve palsy Left hypertropia Right head tilt….What about the doll’s eyes? INO (Internuclear ophthalmoplegia) Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus ( MLF) Lesion CN V Trigeminal Sensory to face and anterior scalp Blink reflex Motor to muscles of mastication (masseter/temporalis) Test 3 divisions with cotton & pin Jaw jerk reflex CN VII -Facial nerve Squeeze eyelids closed (like soap in eyes) Raise eyebrows Smile / pucker Sneer (platysma) Taste Facial Nerve VII relaxed Facial Nerve VII contraction Corneal reflex afferent 5; efferent 7 CN VIII Vestibulo-cochlear Two divisions: Vestibular: head motion sensing Vertigo / nystagmus / veering gait Cochlear: Auditory acuity finger rustle / ticking watch Rinne test: use tuning fork & compare perception of sound via bone and air. In a normal ear air conduction > than bone conduction. Weber test: tuning fork on the patients forehead. Normal: patient hears sound equally in both ears. . CN IX Glossopharyngeal & X Vagus Palatal elevation Gag reflex (sensory & motor) Laryngeal function CN XI -- Spinal Accessory SCM--Right SCM turns head to the left Trapezius Raise shoulders CN XII Hypoglossal Inspect bulk of tongue Protrude tongue midline vs deviation to one side Ask to press tongue against inside of cheek Tongue deviates to the weak side Motor Exam Inspection atrophy, Involuntary movements hypertrophy, fasciculation tremor, chorea, dystonia, myoclonus, myotonia Muscle Tone (resistance to passive movement) Hypotonia (floppy) Hypertonia Spasticity Clasp-knife Rigidity (Lead pipe) Strength (grade 0 to 5) 0/5 no contraction, 3/5 overcomes gravity, 5/5 normal Muscle stretch reflexes (0-4+) r” Plantar response: flexor or extensor (Babinski) Upper versus Lower motor neuron lesions Sign Atrophy Weakness Fasciculations Muscle tone Reflexes UMN +/yes no inc inc LMN yes yes yes dec dec Motor Exam Atrophy of intrinsic hand muscles Calf muscle hypertrophy Check strength proximal to distal shoulder abduction (deltoid) elbow flexion/extension wrist flexion/extension finger flexion/extension finger abduction/adduction hip flexion, abduction/adduction knee extension/flexion ankle extension (dorsiflexion) / plantar flexion toe extensors / flexors/ abductors Muscle stretch reflexes Reflex Biceps Brachioradialis Triceps Knee ( quadriceps) Ankle ( gastroc/soleus) Masseter Nerve root C5 & 6 C5 C7 L3 & 4 S1 CN V Muscle stretch reflexes (MSR) Usually graded 0 to 4 + 0 no response 1+ present but slight in magnitude 2+ present, easily observable 3+ present, “don’t stand in front of pt” 4+ present, recurrent contractions (clonus) Testing for ankle clonus (4+) Plantar reflex Toe flexion is normal. Toe extension is abnormal ( Babinski sign) Superficial Abdominal Reflex Stroke anterior abdominal skin toward umbilicus Rectus muscles Contract in quadrant stimulated Other superficial reflexes Tremor types Resting tremor : present when limb is relaxed or not in active use Parkinson’s & related disorders Action / postural tremor :present when body part is in sustained posture ( holding phone, newspaper) Physiological, familial Intention tremor: present when limb actively / quickly being moved (eating, pointing, applying makeup) Cerebellar lesions Cerebellar Functions Nystagmus (jerky eye movments) Dysarthria (scanning / ataxic speech) Finger-nose-finger Rapid alternating movements (hands) Heel -knee -shin Tandem gait ( heel to toe walking) Cerebellar testing requires cooperative patient Cerebellar: finger-nose finger Patient extends finger out to your finger Then moves finger back to nose The back to your finger Repeat with your finger in different position Cerebellar: finger to nose Pattern of dysfunction: Actions break into jerky steps Target may be missed (dysmetria) Guy in movie Airplane with the “drinking problem” Cerebellar: heel to shin testing Patient flexes hip to place heel to knee Runs heel smoothly down the crest of tibial ( shin) to ankle Abnormal: heel oscillates above knee & slips off shin Sensory Examination Sensory Modalities: Light touch* Vibration* (dorsal column) Pin* (spinothalamic) Temperature (spinothalamic) Position (dorsal column) * = most commonly performed in routine examinations Sensory Examination Light touch Use cotton ball Patient closes eyes Present stimulus & ask for response Move from abnormal area to normal Sensory Examination Vibration Tuning fork ( 128 Hz preferred) Apply stimulus to toe or finger Yes / No response or have patient tell when vibration stops If abnormal distally move proximally: ankle knee wrist elbow Significance of deficits which split the forehead or chest Sensory Examination Pin ( pain) sensation Use safety pin or broken cotton swap stick Ask patient to distinguish pin from opposite end of safety pin ( or your finger tip) Identify abnormal areas and then find normal ones: distal / proximal vs dermatomal Sensory Examination Position Sense Use toes & fingers Patient closes eyes Move part from straight (neutral) position into either flexion (down) or extension ( up) Patient reports direction of movement Sensory Examination Temperature Sensation Hot vs Cold Cold used more often Tuning fork often used for this vs tube of cool water Limb must be warm to properly test Start distally & move proximally Good for finding “spinal level” in cord lesions Gait & Station Testing Causal walking & then heel to toe ( tandem) Observe: Stride length Smoothness of movement Symmetry Steadiness during turning Gait & Station Standing (station) Normal foot spread vs wide vs narrow normal width is feet directly under hips Steady vs unsteady Have patient move feet close together Have patient close eyes Worsening with eye closure is Rhomberg’s sign (sensory deficit) Common Patterns of Abnormality Foot slap: peroneal palsy / L5 radiculopathy Spastic/scissoring: corticospinal tract lesion Waddling: hip girdle weakness muscle diseases / dystrophy Broad based: sensory or cerebellar Short stepped with reduced arm swing: basal ganglia (parkinsons) Non-organic patterns