Pulse - AZ HOSA
advertisement

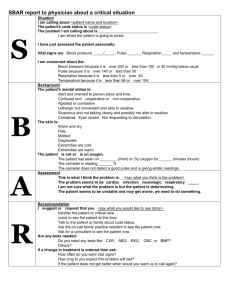
Pulse • Define – The pressure of the blood pushing against the walls of an artery as the heart beats and rests – Felt more easily in arteries that lie close to the skin Pulse Sites • Temporal – forehead • Carotid – neck • Brachial – inner, upper arm • Radial – wrist • Femoral – groin • Popliteal – behind knee • Dorsalis pedis – top of foot Pulse Rate • Define – Number of beats per minute • Variables – Age, sex, body size Pulse Rates • Adults 60-90bpm • Children > 7 70-90bpm • Children 1-7 80-110bpm • Infants 100-160bpm Pulse Terms • Bradycardia – Pulse rate under 60 beats per minute • Tachycardia – Pulse rate greater than 100 beats per minute Characteristics of the Pulse • Rate – beats per minute • Rhythm – regularity or spacing of beats – Regular or irregular – Arrhythmia – irregular heartbeat/pulse • Volume – strength or intensity – Strong, weak, thready, bounding Factors that Increase the Pulse – Exercise – Stimulant drugs – Excitement – Fever – Shock – Nervous tension Factor that Decrease the Pulse – Sleep – Depressant drugs – Heart disease – Coma – Physical training Apical Pulse • Heartbeat taken by listening with a stethoscope over the apex of the heart • The heart sounds are lubb-dupp • Each lubb-dupp is one beat • Used for taking an infant’s pulse because it is so rapid Respirations • Define – Process of taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide • One Respiration includes – 1 inspiration, breathing in – 1 expiration, breathing out Respiration Rates • Adults – 14-18 breaths per minute • Children – 16-25 breath per minute • Infants – 30-50 breaths per minute Respiration Characteristic • Rate – Number of respirations per minute – One respiration is one inspiration and one expiration • Rhythm – Regular or irregular • Character – Deep, shallow, stertorous, moist Abnormal Respiration Terminology • • • • • • Dyspnea – difficulty breathing Apnea – absence of respirations Tachypnea – respiration > 25/min Bradypnea – respirations <10/min Orthopnea – severe dyspnea Cheyne-Stokes – periods of dyspnea followed by periods of apnea. Seen in dying patients • Rales – bubbling respiration caused by moisture in the lungs Procedure for Taking Respirations • Count respirations so patient is unaware • Do not tell patient you are taking their respirations as it is a voluntary and involuntary process • Take the patients pulse and afterwards leave hand in place and lift eyes to count the rise and fall of the patients chest