notes
advertisement

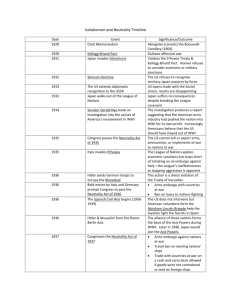
American Neutrality, 1920-1941 I. Roots of Neutrality: Isolationism a. Disillusionment w/ WWI => b. Disillusionment w/ League of Nations => c. Disclosure of War Profiteering i. Nye Committee (1933) => ii. US entry into WWI … iii. Influenced passage of _________________________________ d. Belief in … e. Primary concern of US in 1930s was ____________________________ II. Post WWI American Isolation a. Belief that … b. Efforts by US to avoid future involvement, in wars i. Peace societies => ii. Washington Naval Conference (1922) => iii. Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928) => iv. Recognition of USSR (1933) => v. Good Neighbor Policy (1933) => c. Events of early 1930s showed … i. Japanese invaded _______________________, 1931 ii. Hitler announced … iii. Italian invasion of _____________________, 1935 iv. Spanish Civil War, 1936 => v. ________________________ militarized (1936) vi. Axis Military Pact (1936) => vii. Japan-China clash, 1937 => III. Totalitarian vs. Democracy a. Basic ideals of totalitarian states i. Individual serves … ii. __________________ is supreme iii. State … iv. __________________, force rule b. Basic ideals of democracy i. State serves … ii. __________________ are supreme iii. People … iv. Emphasis on … c. Major totalitarian rulers i. Adolph Hitler => ii. Benito Mussolini => iii. Josef Stalin => iv. Francisco Franco => v. Hideki Tojo = > d. Major democratic leaders i. Franklin Delano Roosevelt => ii. Neville Chamberlain => iii. Eduardo Daladier => IV. American Isolation in action, Post WWI a. Johnson Debt Default Act => b. Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1936, 1937 i. Taken together, they provided that … ii. Neutrality Acts would have … c. FDR’s “Quarantine” speech (1937) => V. Appeasement a. Policy of European countries towards … i. Maintained policy despite … ii. Why?!?!? => b. Examples i. Anschluss (1938) => ii. Hitler’s demand for Sudentenland (1938) => iii. Munich Pact, Sept 1938 1. Nations meeting => 2. France, UK leaders … 3. Chamberlain: “_______________ in our time!” VI. US Response to Appeasement a. Buenos Aires Conference (1936) => b. Canada was brought … c. Declaration of Lima (1938) => VII. European War, 1939 a. Hitler took … b. Italy attacked ___________________, April 1939 c. Germany, USSR, sign … d. Poland attacked by ______________________ & ________________________, Sept. 1 1939 VIII. American Response to European War a. Neutrality Act of 1939 i. “Cash & Carry” on … ii. _____________________ designated as the aggressor b. Declaration of Panama => c. Smith Act (1940) => d. ________________ reinstated, Sept. 1940 e. Lend-Lease Program i. US program to … ii. US shipped a total of _______________________ of war supplies to UK, USSR, France, China iii. In return, US received _______________________ worth of military bases in Newfoundland, Caribbean iv. US received … IX. US Entry into the War a. July 1941: Japan seized ___________________________ b. In response, America … c. Nov. 1941: Japanese peace mission to DC d. Dec. 7 1941: Pearl Harbor attacked => e. War declared on Dec 8, retroactive to Dec. 7 =>