Electrochemical+Battery
advertisement

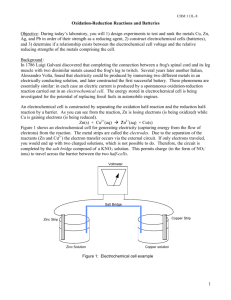
Electrochemical Battery: An electrical battery is a combination of one or more electrochemical cells, used to convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. This happens by the transfer of electrons in one direction. In a battery, oxidation -loss of electrons- occurs at anode and reduction -gaining of electrons- occurs at cathode. Both anode-cathode called as electrode. The electron transfer is done by salt bridge from one to the other solutions,called electrolytes which are solutions of the metal itself. REPORT: Research Question: Which metal(s) provide the best voltage? Materials: metals, salts of that metals, water, beaker, filter paper, KNO3 for salt bridge Procedure: In the experiment, we prepare electrochemical batteries for the metals Cu, Zn, Fe and Pb. We combine all of them and try to compare the voltages between them. Also, we try to observe the effect of concentration of electrolytes on the voltage so, we used 0.1M and 0.5M solutions for all. Datas: For 0,1 M: Cu(+) /Zn(-) Cu(-)/Fe(+) Cu(+)/Pb(-) Zn(-)/Pb(+) Zn/Fe Pb(+)/Fe(-) For 0,5 M: 0.9V 0,1V 0,7V 0,8V 0,1V Cu(+) /Zn(-) Cu(-)/Fe(+) Cu(+)/Pb(-) Zn(-)/Pb(+) Zn/Fe Pb(+)/Fe(-) - 0.45V 0,5V 0,2V 0,3V -V 0,4V :the ion gives electron + :the ion takes the electron Half Reactions: Zn0→Zn2++2e’ 2e’+Cu2+→Cu0 Zn0+2e’+Cu2+↔ Zn2++2e’+ Cu0 Conclusion: At the end of the experiment, we observed the order of activities of metals as: Zn>Fe>Pb>Cu Also we see that the voltage in the cell changes with the change of molarities of the electrolyte solution.