Voltaic Cells
advertisement

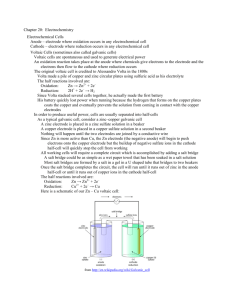
Honors Chemistry Name: ____________________________________ Date: _____________ Mods: ________ Batteries & Redox Reactions 20.3 - Voltaic Cells A voltaic cell, or ________________ cell, is an electrochemical cell that derives electrical energy from spontaneous redox reactions. A battery is a type of device consisting of two or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy Components of a Voltaic Cell: o Cathode Half-Cell: contains the cathode (positive terminal) of the cell; ___________________ occurs at the cathode (Red Cat) this half-cell includes an aqueous solution made with _________ of the cathode o Anode Half-Cell: contains the anode (negative terminal) of the cell; ____________________ occurs at the anode (An Ox) this half-cell includes an aqueous solution made with _________ of the anode o Salt Bridge: Contains ________________ which allow “spectator” ions (which do not take part in the actual redox reaction) to move between the anode-half cell and the cathodehalf cell; the purpose of the salt bridge is for ions to pass from one cell to the other as e- are transferred in order to maintain charge ______________ in each half-cell the negative ions in the salt bridge will migrate into the _______________ half-cell where e- are lost, while positive ions migrate to the ________________ half-cell. The salt bridge is necessary because once even one electron flows from the one half-cell to the other, the charges in each beaker would become unbalanced and the flow of electrons would stop. o Wire/Switch: The wire/switch connects the anode and the cathode to one another When the wire is connected (or the switch is turned on) the circuit is complete and electrons can flow from the ________________ to the ________________. The current that flows through this wire can be measured by a voltmeter Diagram 1: Voltaic Cell BEFORE the Redox Reaction Occurs 1) Label which electrode acts as the cathode and which acts as the anode in Diagram 1. o Use the activity series to determine which metal is more likely to be oxidized; this metal will act as the ___________ while the other metal will act as the ___________. 2) Represent this voltaic cell in cell notation. 3) There appears to be two Zn2+ and two Cu2+ ions present in each half-cell before the redox reaction starts. How does the number of NO3– ions in each half-cell relate to this? Diagram 2: Voltaic Cell AFTER the Redox Reaction Occurs 1) In Diagram 2, draw in arrows (<< or >>) to depict the direction in which electrons flow after the wire is connected and the redox reaction takes place 2) Compare the solutions in Diagram 1 to Diagram 2. What happened to the number of aqueous Zn2+ and Cu2+ ions present in the half-cell solutions before the wire is connected compared to after wire is connected? 3) Explain how the anode half-cell in Diagram 2 remains electrically neutral (no charge) after the wire is connected, electrons are lost, and the number of Zn2+ ions changes. 4) Explain how the cathode half-cell in Diagram 2 remains electrically neutral (no charge) after the wire is connected, electrons are gained, and the number of Cu2+ ions changes. 5) After the wires are connected and the oxidation and reduction reactions are allowed to occur, what happens to the masses of the Zn electrode (anode) and the Cu electrode (cathode)? Label this mass change in Diagram 2. a. Explain, in terms of Zn atoms and Zn2+ ions, what happened to the mass of the Zn electrode (anode). b. Write out the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the anode. c. Explain, in terms of Cu atoms and Cu2+ ions, what happened to the mass of the Cu electrode (cathode). d. Write out the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the cathode. Voltaic Cells – Practice WS 1) a. Draw an unconnected voltaic cell (similar to the one in Diagram 1) using iron metal and silver metal as the electrodes. The solutions present in each half-cell should include silver ions (Ag+) iron ions (Fe3+) and nitrate ions (NO3–). Use a salt bridge identical to Diagram 1. b. Use the activity series of metals to determine which metal in you voltaic cell above will act as the anode and which will act as the cathode. e. Represent this voltaic cell in cell notation. f. Write the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the cathode. g. Write the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the anode. h. Draw arrows (<< or >>) on your diagram to indicate the direction of electron flow through the voltaic cell once the wire is connected. 2) The Diagram below depicts a voltaic cell with generic electrodes “A” and “B”. Answer the following question regarding this voltaic cell. a. Write the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the cathode. (Again, use the generic A’s or B’s to write this reaction) b. Write the balanced half-reaction which occurs at the anode. (Again, use the generic A’s or B’s to write this reaction) c. Which electrode (A or B) is positively charged? _________ d. Which ions from the salt bridge (K+ or Cl–) will flow into the anode half-cell to maintain neutrality of the half-cell. _________ e. Which electrode decreases in mass during the redox reaction? Which electrode increases in mass during the redox reaction? f. Which metal (A or B) would be considered the more reactive metal? How do you know? (Hint: Think about the activity series and how it related to redox reactions). 3) Given the cell notation below and using the activity series, determine which electrode will act as the cathode and which will act as the anode and then write the balanced oxidation-half and reduction-half reactions. Au (s) | Au3+ (aq) ǁ Cathode = ______________ Co (s) | Co2+ (aq) Anode = ______________ Oxidation-Half Reaction: Oxidation-Half Reaction: 4) A student makes voltaic cell using electrodes of cadmium metal and platinum metal. After preparing each half-cell and connecting the wire between the two electrodes, it was discovered that the mass of the platinum electrode increased. a. Since cadmium is not listed on your activity series, use the observations from the voltaic cell and state which electrode is the cathode and which is the anode. b. In which direction will the electrons flow when this voltaic cell is in operation? c. Write the cell notation to represent this voltaic cell. Assume that cadmium forms the Cd2+ ion in solution (You can the most common charge of platinum ions on the activity series)