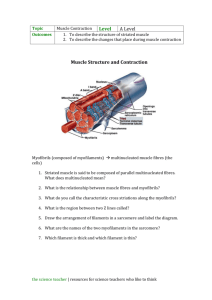
Muscle Contraction: Anatomy & Physiology Worksheet
advertisement

Name: Date: per: Internet Activity: Muscle Contraction Part 1 Click on the following website. Click on the animation tab and click on the narrated version of the animation. Click play and be sure to answer the questions below as you go along. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp47/4702001.html 1. What is the repeating contractile unit in muscle fibers called? 2. Each actin filament is connected a ___________________. 3. During a contraction, _____________________ shorten. 4. During a contraction, the actin and myosin filaments remain the same size. They simple slide past each other, changing their ___________________ positions as the muscle contracts and relaxes. 5. A contraction is triggered when an ________________________ in a neuron reaches the neuromuscular junction. 6. Depolarization of the axon terminal causes the release of the neurotransmitter _____________________________ into the ______________________________. 7. The neurotransmitters trigger the muscle fibers to fire an _______________________of its own. This electrical signal propagates along the muscles _____________________________ and the _____________________________. 8. The SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum) stores __________________________. 9. Draw a picture of a thick and thin filament. Be sure to label each below. 10. Which filament contains the myosin head? 11. After the sarcoplasmic reticulum has released calcium, the calcium molecules bind to the thick/thin (circle one) filaments and exposes the ____________________________ site. 12. When a myosin head binds to actin it forms a ________________________. 13. The myosin head pivots, forcing the actin and myosin filaments to slide past each other. This movement represents the ______________________________ of muscle contraction. 14. Before the myosin heads can release and perform additional power strokes, they must first bind to _____________. 15. Soon after the action potential ceases, the ____________________________________ pumps the calcium that it had released back into its interior. 16. After calcium leaves, the tropomyosin molecules again hide the ___________________________ sites. Once you are finished with these questions, complete the quiz (click on the upper right tab). Part 2 Go to the following website and click play. There is no sound on this animation. Pay attention, there are small quizzes throughout this animation. http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_res ources/animations/muscles/muscles.html 1. The _____________________ is the specialized plasma membrane of the muscle cell. 2. The ________________________________ surrounds the sarcomeres. 3. The bands that mark the sarcomere’s borders are known as the ___________________. 4. The distance between the ends of the thin filaments are called the _____________________. 5. The H zone __________________ during contraction. 6. Chemically, muscle contraction is driven by __________ hydrolysis and triggered by the release of __________________ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 7. If no calcium is available, the myosin heads will _______ bind to the ____________. 8. List the six steps of muscle contraction in the correct order. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Part 3 Go to the following website. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter10/animation__action_potential s_and_muscle_contraction.html Look at the toolbar on the left under “QUIZZES.” Complete the following quizzes: 1. Action Potentials and Muscle Contraction 2. Breakdown of ATP 3. Function of the Neuromuscular Junction (Quiz 1) 4. Myofilament Contraction 5. Sarcomere Contraction Once you click on the link for the quiz, it will automatically play the animation. If not, click play. Watch the animation, then scroll down to the short quiz below. Submit your answers to check them. Record your answers below. Just write the letter of the correct answer. Name: Action Potentials and Muscle Contraction 1. _______ Date: ANSWERS TO QUIZZES Function of the Neuromuscular Joint (Quiz 1) 2. _______ 1. _______ 3. _______ 2. _______ 4. _______ 3. _______ 5. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ Breakdown of ATP 1. _______ per: Myofilament Contraction 2. _______ 1. _______ 3. _______ 2. _______ 4. _______ 3. _______ 5. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ Sarcomere Contraction 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______