A&P I Tutorial 2015 Exam 3A Name 1) Joints can be classified
advertisement

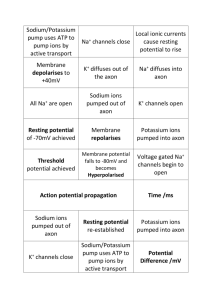
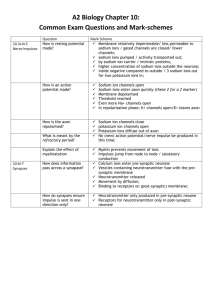
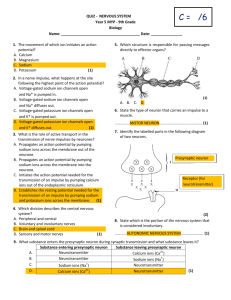
A&P I Tutorial 2015 Exam 3A Name _________________________________________ 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2) An immovable joint is a(n) A) synarthrosis. B) diarthrosis. C) amphiarthrosis. D) syndesmosis. E) symphysis. 3) Which of the following occurs when the articular cartilage is damaged? A) The matrix begins to break down. B) The exposed surface appears rough. C) Friction in the joint increases. D) Normal synovial joint function is unable to continue. E) All of the answers are correct. 1 Figure 9-1 A Simplified Sectional View of the Knee Joint Use Figure 9-1 to answer the following questions: 4) Which structure acts as a cushion and consists of fibrous cartilage? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 5) Identify the structure at label "1." A) meniscus B) bursa C) articular cartilage D) synovial membrane E) joint cavity 2 6) Identify the structure labeled "2." A) serous membrane B) synovial membrane C) joint capsule D) periosteum E) intracapsular ligament 7) What type of tissue occurs at the structure labeled "3"? A) fibrocartilage B) synovial membrane C) articular cartilage D) bone tissue E) dense connective tissue 8) Identify the structure labeled "5." A) serous membrane B) synovial membrane C) joint capsule D) periosteum E) intracapsular ligament 9) The knuckle joint is classified as a ________ joint. A) condylar B) hinge C) glide D) saddle E) pivot 10) Which of the following movements is a good example of flexion? A) opening the mouth B) turning the hand palm upward C) extreme bending of the head backwards D) moving the hand toward the shoulder E) spreading the fingers 11) All of the following movements occur at the intervertebral joints except A) flexion. B) rotation. C) dorsiflexion. D) lateral flexion. E) extension. 12) A herniated disc occurs when the A) nucleus pulposus breaks through the anulus fibrosus. B) disc slips out from between the adjacent vertebrae. C) adjacent bones fuse. D) knee is hyperextended. E) inner core of the disc is squeezed to one side. 13) The elbow joint is extremely stable because A) the ulna and humerus interlock. B) the articular capsule is thin. C) the capsule lacks ligaments. D) several muscles support the joint capsule. E) the joint lacks bursae. 3 14) Contraction of the muscle that is attached to the radial tuberosity results in A) flexion of the forearm. B) extension of the forearm. C) abduction of the forearm. D) adduction of the forearm. E) rotation of the shoulder. 55) Which of the following ligaments is not associated with the hip joint? A) iliofemoral ligament B) pubofemoral ligament C) ischiofemoral ligament D) ligamentum teres E) anterior cruciate ligament 16) In the knee joint, the medial and lateral menisci A) are cartilages that bind the knee to the tibia. B) act as cushions between the articulating surfaces. C) take the place of bursae. D) are found between the patella and femur. E) are prominent fat pads to protect the articulating bones. 17) Muscle tissue, one of the four basic tissue groups, consists chiefly of cells that are highly specialized for A) conduction. B) contraction. C) peristalsis. D) cushioning. E) secretion. 18) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature D) guard body entrances and exits E) All of the answers are correct. 19) At each end of the muscle, the collagen fibers of the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium, come together to form a A) tendon. B) satellite cell. C) ligament. D) tenosynovium. E) sheath. 20) In a sarcomere, the central portion of thick filaments are linked laterally by proteins of the A) Z line. B) M line. C) H band. D) A band. E) I band. 4 21) Which of the following statements about the microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle fibers is false? A) Tubular extensions of the sarcolemma penetrate the fiber transversely. B) Cross striations result from the lateral alignment of thick and thin filaments. C) Each fiber has many nuclei to ensure adequate muscle protein production. D) The net-like sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounds each myofilament. E) All of the answers are true; there are no false answers. Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following questions: 22) Identify the structure labeled "1." A) mitochondria B) glycogen C) ATP D) myofibril E) synaptic vesicle 23) Which of the following are found in the structure labeled "3"? A) actin B) myosin C) titin D) tropomyosin E) All of the answers are correct. 5 24) What physiological process occurs in the structure labeled "7"? A) release of neurotransmitter B) conduction of the action potential into the cell interior C) activity of acetylcholinesterase D) release of protein and calcium ions into the muscle fiber E) opening of sodium channels and subsequent influx of sodium Answer: B Learning Outcome: 10-3 Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension 25) What is released from the structure labeled "9"? A) sarcoplasm B) acetylcholine C) protein D) calcium ions E) acetylcholinesterase 26) In response to action potentials arriving along the transverse tubules, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases A) acetylcholine. B) sodium ions. C) potassium ions. D) calcium ions. E) hydrogen ions. 27) After death, muscle fibers run out of ATP and calcium begins to leak from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm. This results in a condition known as A) tetany. B) treppe. C) depolarization. D) rigor mortis. E) oxygen debt. 28) The rapid rise and fall in force produced by a muscle fiber after a single action potential is a(n) A) tetanus. B) unfused tetanus. C) twitch. D) motor end plate potential. E) muscle action potential. Answer: C Learning Outcome: 10-5 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 29) A weight-lifter strains to lift a heavy weight and there is no movement of the person's arms holding on to the weight. This type of contraction is called a(n) ________ contraction. A) isometric B) tetanus C) isotonic D) treppe E) concentric 6 30) During the recovery period the body's need for oxygen is increased because A) muscle cells are producing ATP anaerobically. B) creatine phosphate stimulates mitochondrial activity. C) additional oxygen is required to restore energy reserves. D) the liver requires more oxygen to produce lactic acid. E) the muscles produce much less ATP. 31) The type of muscle fiber that is most resistant to fatigue is the ________ fiber. A) fast B) slow C) intermediate D) anaerobic E) high-density 32) Which of the following is not a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory information C) coordinate voluntary and involuntary activities D) direct long-term functions, such as growth E) control peripheral effectors 33) The ________ nervous system controls the skeletal muscles. A) sympathetic B) parasympathetic C) afferent D) somatic E) autonomic 34) Which of the following is not a recognized structural classification for neurons? A) anaxonic B) bipolar C) multipolar D) pseudopolar E) unipolar 35) How does blocking retrograde axoplasmic transport in an axon affect the activity of a neuron? A) The neuron becomes unable to produce neurotransmitters. B) The neuron becomes unable to produce action potentials. C) The soma becomes unable to export products to the synaptic terminals. D) The soma becomes unable to respond to changes in the distal end of the axon. E) The neuron becomes unable to depolarize when stimulated. 36) Deteriorating changes in the distal segment of an axon as a result of a break between it and the soma is called ________ degeneration. A) neural B) central C) peripheral D) Wallerian E) conduction 37) Which of the following is a type of glial cell found in the peripheral nervous system? A) astrocytes B) satellite cells C) oligodendrocytes D) microglia E) ependymal cells 7 38) At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron, its sodium-potassium exchange pump transports A) 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. B) 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. D) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. E) 3 extracellular sodium ions for 2 intracellular potassium ions. 39) Opening of sodium channels in the axon membrane causes A) depolarization. B) repolarization. C) hyperpolarization. D) increased negative charge inside the membrane. E) inhibition. 40) Integral membrane proteins that connect electrical synapses are called A) connexons. B) receptors. C) desmosomes. D) sodium channels. E) synapsins. 41) The following are the main steps in the generation of an action potential. 1. Sodium channels are inactivated. 2. Voltage-gated potassium channels open and potassium moves out of the cell, initiating repolarization. 3. Sodium channels regain their normal properties. 4. A graded depolarization brings an area of an excitable membrane to threshold. 5. A temporary hyperpolarization occurs. 6. Sodium channel activation occurs. 7. Sodium ions enter the cell and depolarization occurs. What is the proper sequence of these events? A) 4, 6, 7, 3, 2, 5, 1 B) 4, 6, 7, 1, 2, 3, 5 C) 6, 7, 4, 1, 2, 3, 5 D) 2, 4, 6, 7, 1, 3, 5 E) 4, 2, 5, 6, 7, 3, 1 42) Which of the following is true about threshold for an action potential? A) It is more positive than the resting potential. B) Voltage-gated potassium channels begin to close. C) Voltage-gated potassium channels begin to open. D) The membrane begins to hyperpolarize. E) Threshold for a typical neuron is approximately -30 mV. 43) Which of the following does not influence the time necessary for a nerve impulse to be transmitted? A) length of the axon B) presence or absence of a myelin sheath C) diameter of the axon D) presence or absence of nodes E) whether or not the impulse begins in the CNS 8 44) A neuron that receives neurotransmitter from another neuron is called A) the presynaptic neuron. B) the motor neuron. C) an oligodendrocyte. D) a satellite cell. E) the postsynaptic neuron. 45) The ion that triggers the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft is A) sodium. B) potassium. C) calcium. D) chloride. E) magnesium. 46) The ________ nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) autonomic B) peripheral C) central D) efferent E) afferent 47) The part of the peripheral nervous system that carries sensory information to the CNS is designated A) motor. B) afferent. C) efferent. D) autonomic. E) somatic. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 12-1 Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge 48) The axoplasm of the axon contains which of the following? A) neurotubules B) mitochondria C) vesicles D) neurofibrils E) All of the answers are correct. 9 Match to Figure above 49. pectoralis major 50. deltoid 51. trapezius 52. latissimus dorsi 10 Match to figure above 53. brachioradialis 54. palmaris longus 55. extensor digitorum 11 12 Match to the figure above 56. gastrocnemius 57. soleus 58. rectus abdominis 59. external oblique 60. biceps brachii Extra Credit (1 point each) 1) Syndesmosis is to ligament as symphysis is to A) fibrous cartilage. B) dense regular connective tissue. C) periodontal ligament. D) rigid cartilaginous bridge. E) completely fused. 2) A general term for pain and stiffness that affects the skeletal or muscular system is A) rheumatism. B) atherosclerosis. C) bursitis. D) bunions. E) arthritis. 3) Put the following structures in order from superficial to deep. 1. muscle fiber 2. perimysium 3. myofibril 4. fascicle 5. endomysium 6. epimysium A) 1, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6 B) 6, 2, 5, 4, 1, 3 C) 6, 2, 4, 5, 1, 3 D) 1, 3, 5, 6, 4, 2 E) 2, 3, 1, 4, 6, 5 4) Which of the following statements is/are false regarding human muscles? A) Most have both slow and fast fibers. B) Slow fibers are abundant in the muscles of the hand. C) Eye muscles are composed entirely of fast fibers. D) Slow fibers are abundant in the back muscles. E) All of the answers are correct; none of them are true regarding human muscles. 5) Most CNS neurons lack centrioles. This observation explains A) why CNS neurons grow such long axons. B) why CNS neurons cannot divide to regenerate damaged tissue. C) the ability of neurons to generate an action potential. D) the ability of neurons to communicate with each other. E) the ability of neurons to produce a resting potential. 13