absolutism, enlightenment, and revolution vocab
advertisement

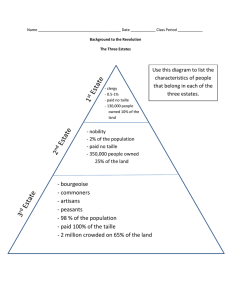
Vocab Absolute monarch: kings or queens who held all of the power within their states’ boundaries. Divine right: idea that God created the monarchy and that the monarch acted as God’s representative on earth. Huguenots: French protestants. Intendents: Government agents used by Louis XIV who collected taxes and administered justice. Edict of Nantes: Declaration made by Henry of Navarre of France allowing Huguenots freedom to worship in France. Scientific Revolution: a major change in European thought, in which the study of the natural world began to be characterized by careful observation and the questioning of accepted beliefs. Geocentric theory: Theory that the earth is the center of the universe. Heliocentric Theory: Idea that the sun is at the center of the solar system. Scientific method: logical procedure for gathering and testing ideas. Enlightenment: intellectual movement that stressed reason and thought and the power of individuals to solve problems. Philosophe: social critics or philosophers from France. Social contract: Idea from Thomas Hobbes that suggested all humas are naturally selfish and wicked and must had over their rights to a strong ruler to create/run their government. Estate: social classes of France. 1st Estate: Church leaders. 2nd estate: rich nobles. 3rd estate: 97% of the people. Tennis Court Oath: a pledge made by the members of France’s National Assembly in 1789, in which they vowed to continue meeting until they had drawn up a new constitution. National Assembly: a French congress established by representatives of the Third Estate to enact laws and reforms in the name of the French people. Estates-General: Gathering of all three estates of France called by the king. Great Fear: a wave of senseless panic that spread through the French countryside after the storming of the Bastille in 1789. Bastille: French prison torn down in the early days of the French Revolution. Jacobins: radical political party during the French Revolution Guillotine: a machine for beheading people, used as a means of execution during the French Revolution. Reign of Terror: period from 17931794 when Maximilien Robespierre ruled France nearly as a dictator and thousands of political figures and ordinary citizens were executed. Napoleonic Code: a comprehensive and uniform system of laws established for France by Napoleon. Battle of Trafalgar: an 1805 naval battle in which Napoleon’s forces were defeated by a British fleet under command of Horatio Nelson. Continental System: Napoleon’s policy of preventing trade between Great Britain and continental Europe intended to destroy Great Britain’s economy. Peninsular War: a conflict in which Spanish rebels, with the aid of British forces, fought to drive Napoleon’s French troops out of Spain. Scorched-earth policy: the practice of buring crops and killing livestock during wartime so that the enemy cannot live off the land.