Big Business - US & Global history Ms. Aronova
advertisement

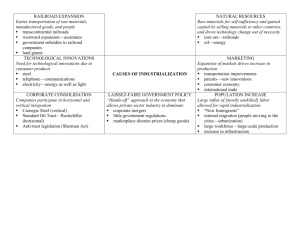
Aim: How did the Industrial Revolution transform American business? Do Now: List 2 modern day inventions you could not live without and explain why. HW: Big Business Emerges Worksheet Rise of American Industry 1865-1920 • Post-Civil War: US developed a prosperous, new economy based on the mass production of goods. • Economic development expanded in the North, but weakened in the South. • Entrepreneurs became wealthy and powerful. • Government began to regulate business. • Labor Unions formed to improve working conditions. Rise of Industry in the US Packet • Directions: • 1. Read and do Free Enterprise System together as a class. • 2. Steps on the Road to becoming Industrial Giant individually. • 3. Share before/after civil war picture of business Aim: To what extent were big business leaders considered robber barons during the Industrial Revolution? Do Now: How did the Industrial Revolution impact the American lifestyle? Give 2 examples. HW: Great Business Leaders: Heroes or Villains? Handout. Business Practices • Monopoly: When 1 company controls the supply or trade of a commodity or service • Laissez faire capitalism: little to no government interference in the economy Business Practices • Vertical Integration: Process in which a company buys out its suppliers • Horizontal Integration: Process in which companies producing similar product merge. – Merge: A combination of two companies into one. Vertical Integration Horizontal Integration/Consolidation • T-Mobile & Metro PCS join to form one cell phone company. Bessemer Process • Turns iron into steel by oxidizing the metal. • Steel will be used for railroads and skyscrapers. Andrew Carnegie • Scottish immigrant who makes fortune in railroad industry. • Became leader of steel industry. • Forced workers to put in long hours at low wages. • Donated money to education and medical research later in life. John D. Rockefeller • Formed Standard Oil Co. • Controlled most of oil refinery business • Forced railroad companies to give him special low rates for shipping oil • Used horizontal integration • Donated money to education and science later in life. Cornelius Vanderbilt • Most powerful railroad baron. • Son of poor farmer, earned his first fortune in steamship lines. • Then bought up railroad lines in NY and expanded to Great Lakes region. • Donated money to education and science. JP Morgan • Consolidated steel industry and railroad industry • One of most famous financiers in business history Henry Ford • Invented Model T, a car afforded by the middle class. • Used assembly line which made workers expendable. Assembly Line Aim: How did the US government attempt to regulate business? Do Now: Should the government be allowed to have control over the economy? Explain. HW: Prepare for Open Notebook Exam tomorrow. Business Regulation • Wabash v. Illinois (1886) Supreme Court Case: – Issue: Whether a state government has the power to regulate railroad prices on that portion of an interstate journey that lies within its borders. – Outcome: Only Congress, not individual states, have the power to regulate interstate commerce. Interstate Commerce Act (1887) • Required that railroads charge fair rates to their customers and make those rates public. • Also created the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC). Sherman Antitrust Act (1880) • Authorized federal action against any "combination in the form of trusts or otherwise, or conspiracy, in restraint of trade." • Any attempt to monopolize trade or commerce is made illegal. Big Business DBQ Packet • Robber Baron v Captain of Industry