APUSH REVIEW Court Cases
advertisement

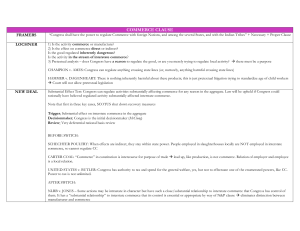
Marbury v. Madison (1803) – Established Judicial Review, the Supreme Court’s right to determine the constitutionality of a law. (“midnight appointments,” forcing Jefferson to deliver his commission, increased the influence of the Supreme Court) Fletcher v. Peck (1810) – Established that states cannot alter contracts. (1st time Supreme Court ruled a state law unconstitutional, although the land was sold illegally, once a contract was made it cannot be revoked) Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) – The sanctity of contracts is reaffirmed. (Dartmouth College, New Hampshire Legislature wants to appoint Trustees altered the school/convert it from a private to public institution, Charter as contract can not be altered) McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) – Establishes the supremacy of Federal law over state law. (Maryland imposed a tax on the Second Bank of the United States, Congress had the right to create the National Bank under the “Commerce Clause,” Maryland had no right to impede Congress tax was struck down) Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) – Congress has the right to regulate interstate commerce. Cherokee Nation v. Georgia (1831) – The Court determined that it could not rule on the case, as the Cherokee tribe was a “denominated domestic dependent nation.” (tribe was not a stateno jurisdiction =no rule on the case) Worcester v. Georgia (1832) – The Federal government, not the states, can make laws with respect to Indian tribes. Charles River Bridge v. Warren Bridge (1837) – Established a policy of relatively narrow interpretation of contracts. The decision favored also technological progress. . Prigg v. Pennsylvania (1842) – Federal law is superior to state law. (establishes that Federal agents were required to enforce the Fugitive Slave Act, undercutting its effectiveness) Commonwealth v. Hunt (1842) – Established the legality of labor unions. Dred Scott v. Sanford (1856) – Determined that descendants of slaves are not US citizens. Bradwell v. Illinois (1873) – The right to practice law is not one of the privileges guaranteed in the 14th Amendment. This ruling effectively validated discrimination against women in hiring decisions. Munn v. Illinois (1877) – States can regulate business when it is in the interest of the public good. Wabash Case (1886) – Only the Federal government can regulate interstate commerce. (creation of the Interstate Commerce Commission) United States v. E.C. Knight Co. (1895) – The Sherman Antitrust Act doesn’t apply to manufacturing companies (only distribution), as they cannot restrict commerce. Pollock v. The Farmers’ Loan and Trust Co. (1895) – Income taxes are unconstitutional, as they are direct taxes that are not correctly divided among the states. (overturned by 16th Amendment which legalized income taxes) Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) – Segregation based on race is legal as long as accommodations are “Separate but Equal.” Williams v. Mississippi (1898) – Established the legality of poll taxes and literacy tests. "Insular Cases" / Downes v. Bidwell (1901) – The Constitution does not necessarily apply in matters concerning US Territories. (Constitution only applies to “integral parts” of the US) Lochner v. New York (1905) – States cannot regulate labor conditions, as such regulation violates a citizen’s right to make contracts. (Initiated Lochner Era Court ruled against Progressive Era laws that sought to regulate working conditions) Muller v. Oregon (1908) – Laws limiting the number of hours women can work are valid, as women require different considerations that men. Hammer v. Dagenhart (1918) – Overturned child labor laws and established that only states have the right to regulate the production of goods. Schenck v. United States (1919) – Speech is not protected by the Constitution when it poses a “Clear and Present Danger” (war) to the welfare of the nation. Schechter Poultry Corp. v. United States (1936) – Established that the National Industrial Recovery Act created during the New Deal was unconstitutional. Korematsu v. United States (1944) – Restrictions on the rights of people of Japanese descent were validated because of the perceived threat to the safety of the United States. Smith v. Allwright (1944) – African Americans are guaranteed the right to vote in primary elections. Sweatt v. Painter (1950) – Determined that segregated law schools could not be “Separate but Equal,” and allowed African Americans to attend such schools with whites. Brown v. Board of Education I (1952) – Invalidated segregation laws, as separate facilities were inherently unequal. Brown v. Board of Education II (1954) – Ordered desegregation of public facilities with “all deliberate speed.” Roth v. United States (1957) – Publications deemed “obscene” are not protected by Freedom of Speech. Engel v. Vitale (1962) – Laws authorizing prayers at the start of school, even if they are voluntary and non-denominational, are unconstitutional. T Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) – The court has a responsibility to appoint a lawyer to defend people who cannot afford to pay for one. Miranda v. Arizona (1966) – Suspects must be informed of their rights before interrogation can begin. Furman v. Georgia (1972) – The death penalty is a cruel and unusual punishment in some circumstances. Roe v. Wade (1973) – Established that women have the right to get an abortion during the first trimester of their pregnancy.