CTE - Transition to Common Core
advertisement

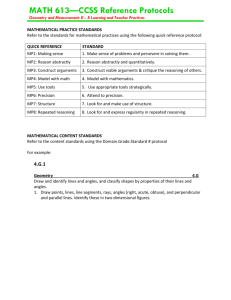
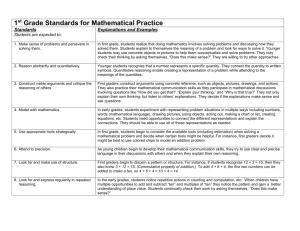
Standards for Mathematical Practice and Career and Technology Education (CTE) Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically 6. Attend to precision 7. Look for and make use of structure 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Accounting Academy Business Management Academy Marketing Academy Examples of activities from Business which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice •Reason abstractly and quantitatively-determine the cost of the transaction based on standard billable hours formulas, tax reform, and government restructuring strategies. •Model with mathematics-compare the prices of a car purchased within a simple interest, compound interest or price rebate model of payment. •Attend to precision- enter data into an accounts receivable file during an accounting simulation and correct any errors. •Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning- compare and contrast the bond market, commodities market, international currency markets and precious metals as investments. Explain how these markets respond interdependently to changes among each other. Computer Science Examples of activities from Computer Science which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice • Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them - design, test, and debug JAVA programs to solve problems. • Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others - propose, write and defend your software engineering design for a program that will enable a Mindstorm programmable Lego robot to sort marbles. • Use appropriate tools strategically – read a case study and determine which SQL database management tools software will require the least training time to learn. • Look for and make use of structure - determine the type of array structures that might be useful in storing a specific set of data. Career Research And Development CRD Examples of activities from Career Research & Development (CRD) which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them Conduct a class-wide month long home budgeting simulation using local salary, housing and cost of living research data. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively Make a long term financial plan that includes projected salary, housing and cost of living, retirement costs, and college costs. 7. Look for and make use of structure Using data from your Myers Briggs Temperament Indicator (MBTI), assemble a team you would love to work with and one that would be your worst nightmare. Culinary Science Examples of activities from Culinary Science which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice • Make sense of problems – convert the yield of a recipe from six to fifty using the appropriate mathematical operations. • Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of otherscalculate unit prices in order to cost a banquet menu and justify the budget needed. • Attend to precision-calculate the yield percent from the aspurchased weight and edible portion quantity of a fruit or vegetable. • Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning-use kitchen ratios to calculate ingredient quantities for standard recipes. Technology Education Examples of activities from Technology Education which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice • Reason abstractly and quantitatively - select the right materials that can withstand the shear and bending load limits on structural elements and buildings. • Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others - design a process to make a cooling system more energy efficient. • Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning troubleshoot a design problem. Teacher & Child Development Academies Examples of activities from the Teacher Academy and Child Development Academy which support the Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. • Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others – use research data to support an argument against a specific educational practice. • Model with mathematics –think aloud when using mathematical reasoning to create an equitable distribution of toys in the classroom. Make Sense of developmental Problems and Persevere in solving them by monitoring vital signs and milestone data. • Look for and make use of structure – incorporate math manipulatives when creating a lesson plan introducing fractions. • Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning – match students’ answers to expected responses in Piaget’s Concrete Operations stage.