Exercise Physiology
advertisement

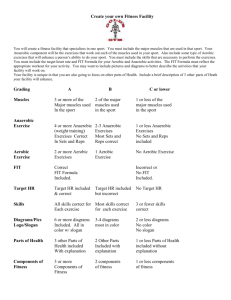
Exercise Physiology Year 11 Physical Education AS 1.2 Credits: 5 Miss Sandri CALENDAR AUGUST 2013 MONDAY HOSE 16 x Lessons TUESDAY No Lesson WEDNESDAY Hose- Theory 12 13 19 20 Biomechanics Summary/ Short term responses of exercise No Lesson 26 15 21 28 16 PracticalVolleyball Projectile Motion/ Leavers Practical Lesson (speedball) 27 Force Summation *Practical* Force Summation 14 Practical- Cross Country OR Frisbee Golf FRIDAY BIOMECANICS Hose- Practical Newton’s Laws Theory No Lesson THURSDAY 22 Long Term Responses of Exercise 23 29 Anaerobic Energy Systems Revision- Exercise Physiology Practical Lesson 30 CALENDAR SEPTEMBER 2013 SummaryEnergy systems No Lesson 2 Practical Lesson3 RevisionAnatomy No Lesson 9 16 4 5 6 11 12 13 18 19 RevisionBiomechanics 10 17 EXAM 1.20pm Study Leave CALENDAR AUGUST 2013 MONDAY BRADLEY 14 x Lessons TUESDAY Bradley- Anatomy WEDNESDAY Bradley- Anatomy 12 Stability/ Force Summation 13 Force SummationFrisbee Golf 19 Biomechanics Revision & Short term responses 20 Practical Lesson (netball) 26 BradleyCross Country Newton's Laws of Motion THURSDAY No Lesson 14 15 21 22 16 23 Cross CountryNo class No Lesson 28 Force Summation/ Practical Practical SessionVolleyball No Lesson Long term responses of exercise 27 FRIDAY 29 30 CALENDAR SEPTEMBER 2013 Anaerobic & aerobic energy systems Summary- Energy Systems Practical Lesson 2 Revision Exercise Physiology 3 RevisionAnatomy 9 16 4 5 6 11 12 13 18 19 RevisionBiomechanics 10 17 EXAM 1.20pm Practical Lesson No Lesson Study Leave Biomechanics Revision: 5 Quick Questions: 1. Name the BOS, COG and LOG. 2. Key points- to maximise stability you should… ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Lower the _____ Increase the size of the ____ Keep the ____ within the ____ The _____ passes within the ____ 3. Define force summation. 4. What are the three principles of force summation? 5. Name Newton’s 3 laws of motion. 5 Quick Questions: 1. Name the BOS, COG and LOG. Base of support (BOS); Centre of Gravity (COG); Line of Gravity (LOG). 2. Key points- to maximise stability you should… ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ (COG) Lower the _____ (BOS) Increase the size of the ____ (BOS) (LOG) within the ____ Keep the ____ (LOG) passes within the (COG) The _____ ____ 3. Define force summation. The sum of all forces generated by each body part. 4. What are the three principles of force summation? Timing, using the greatest number of body parts and sequence. 5. Name Newton’s 3 laws of motion. Law 1: Inertia Law 2: Acceleration Law 3: Action/ Reaction Exercise Physiology 1. Short Term Physiological Responses to Exercise 2. Long Term Physiological Responses to Exercise 3. Anaerobic Energy Systems 4. Aerobic Energy Systems Body Systems • Muscular system • Cardiovascular/ Circulatory system • Respiratory system Short Term (Acute) Physiological Responses to Exercise Effects that take place while we are exercising… Short Term Physiological Responses to Exercise Immediate or acute effects of exercise on the body. TASK: Measure your ‘resting’ heart rate (15 seconds then x4) 1 minute of strenuous exercise (star jumps, squat jumps, press ups, lunge jumps). Measure heart rate (15 seconds then x4) Listen to my instructions for timing Thinking about the 1 minute of exercise you just did- What effects did you feel taking place within your body? BRAINSTORM Short Term Physiological Responses to Exercise Immediate or acute effects of exercise on the body. Simplified answers: ▫ Increased temperature ▫ Increased heart rate ▫ Increased respiration ACHIEVED !! Muscular System- Increased Temperature • Muscles receive more blood and oxygen ▫ Working harder • Muscles increase in temperature ▫ Bi-product of energy production ▫ Blood moves to surface of the skin (heat regulation) ▫ Sweating (heat regulation) Cardiovascular- Cardiac Output Increases “The heart beats faster and stronger” • The heart rate increases to ensure that more oxygen is delivered to the working muscles. • This also allows Co2 to be removed from the body. • Stroke volume also increases so the amount of blood processed each beat increases. • (Cardiac output (Q) = SV x HR) Respiratory System- Increased Ventilation “Breathing quickens and deepens” • Increase in the number of breaths per minute (respiratory rate) • Increase in the amount of air taken in each breath. (tidal volume) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fy hYHlA7bZw Short Term Effects of Exercise- Summary • Muscular System ▫ Increased temperature Sweating • Cardiovascular System ▫ Increased cardiac output Heart rate & stroke volume Deliver O2 and remove Co2 from muscles • Respiratory System ▫ Increased ventilation Respiratory rate and tidal volume Word List respiratory oxygen muscles heart heart transported increasing cardiovascular working breathing oxygen exercise lungs energy draws The ___________ and lungs are responsible for moving ___________ around the body. The _________________________ system inhales oxygen into the _______________ where it is ____________ into the blood. The ____________ system pumps _____________filled blood around the body where it provides the ________________ with the ______________ it needs to perform work. The cardio respiratory system _______________ more oxygen into the body as a response to ______________. It does this by _____________ both its _________________ and _______________ rate to deliver an increased quality of oxygen to _________________ muscles. Word List respiratory oxygen muscles heart heart transported increasing cardiovascular working breathing oxygen exercise lungs energy draws The ___heart___ and lungs are responsible for moving __oxygen___ around the body. The ______respiratory____ system inhales oxygen into the _____lungs____ where it is______transported______ into the blood. The __cardiovascular_ system pumps ___oxygen__filled blood around the body where it provides the ____muscles_____ with the ___energy___ it needs to perform work. The cardio respiratory system ____draws ___ more oxygen into the body as a response to ___exercise___. It does this by ____increasing____ both its _____heart_____ and ___breathing___ rate to deliver an increased quality of oxygen to ______working_____ muscles. Speedball • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zi3NqQ34oQI Long Term (Chronic) Physiological Responses to Exercise Effects that take place following exercise weeks, months, years later… Body Systems • Muscular system • Cardiovascular/ Circulatory system • Respiratory system Think about the effects of training on the body. Try to link your answer to the three energy systems. BRAINSTORM Long Term Physiological Responses to Exercise Effect of training on the body. Simplified answers: ▫ Muscles increase in size and strength. ▫ Size of the heart increases. ▫ The heart pumps more blood per beat (stroke volume). ▫ The cardiovascular system becomes more efficient. ▫ The recovery rate becomes quicker. ▫ Resting heart rate becomes lower. ACHIEVED !! Muscular System • Muscles increase in size and strength Hypertrophy Receiving more O2 Working harder • Muscles become more flexible Subject to training • Muscles receive more O2 From increases in the cardio respiratory system Cardiovascular System • Increased heart size Because the heart is a muscle too! The heart is pumping much more blood around the body to produce O2 and remove CO2. Exercising heart rate becomes lower • Because the heart is larger (more blood pumped through per beat) Increased stroke volume • Because the heart is larger (more blood pumped through per beat) Decreased resting heart rate Heart is bigger, therefore it doesn’t need to pump as often Respiratory System • The lungs can breathe in and out a greater volume of air, and with it oxygen. ▫ Increased efficiency for exchange in the lungs and muscles. ▫ This means more O2 being delivered to muscles and more Co2 being removed from the muscles. The Interconnection between the 3 Energy Systems • Muscular system • Cardiovascular/ Circulatory system • Respiratory system None of these effects are possible unless all three energy systems work together to increase O2 and remove Co2. Body system Muscular Short term response to exercise Long term response to exercise • Muscles receive more blood and oxygen • Muscles increase in temperature • Muscles become more flexible • Muscles get larger and stronger • Muscles become more flexible • Muscles get more blood • Vessels can receive more oxygen • The blood is able to carry more oxygen • Heart beat increases • More blood pumped around body • The blood is able to carry more oxygen • The heart gets larger • Resting heart rate gets lower • Heart rate returns to normal faster • Exercise heart rate gets lower Cardiovascular Respiratory • Breathing rate increases • The lungs can breathe in and out • Amount of air taken in each a greater volume of air, and with breath increases it oxygen Sticky Notes 1. One thing you do not understand fully from the last two lessons (short term & long term effects of exercise). 2. The aspect/ aspects that are the most difficult to understand from the whole content anatomy (bones/muscles/movements), biomechanics (stability/force summation/Netwon’s laws), physiology- be specific- what parts in particular?) 3. One sport that you would like to play for practical lessons. Don’t forget- lunch time tutorial Energy Systems Anaerobic & Aerobic Energy Systems • Three pathways provide energy for physical activity. ▫ Two are anaerobic (without oxygen) and the other is aerobic (with oxygen). Energy Systems • The type of energy pathway used is dependent on the type of activity performed. 1.Activity that is longer in duration and of low intensity is fuelled by the aerobic energy system 2.Activity that is shorter in duration and of higher intensity is fuelled by the anaerobic energy systems Energy Systems 0-10 seconds: ATP-PC system 10 seconds- 2 minutes- Lactic acid system 2 minutes + Oxygen system Anaerobic - Aerobic The Energy Systems Overlap ATP-PC Aerobic Anaerobic • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5G8cVpXpsL8 Anaerobic Energy Systems- Sports • Sports and activities that use this energy system include team sports such as; ▫ Rugby ▫ Netball ▫ Soccer • where high intensity activity is performed for short periods of time. Anaerobic Exercise • Anaerobic exercise is defined as exercise performed at an intensity where a persons cardiovascular system cannot supply enough oxygen to keep up with demand and therefore energy is produced without the presence of O2. Lactic Acid • Lactic acid is a bi-product of this energy production resulting in muscle soreness and will lead to a decrease in work intensity or a build up of lactate to the point where exercise can no longer continue. Anaerobic Energy System- Key Points • An – aerobic. • Anti- oxygen • Exercise performed without oxygen. • Usually lasts for around 0-2 minutes. • First 10 seconds include the ATP- CP system. Aerobic Exercise • Aerobic exercise is defined as exercise performed at intensity when a persons cardiovascular system can supply enough oxygen to keep up with demand. • Examples include running, swimming and biking long distances. Activity 1: Identify which energy system is used the most in each sport. EVENT 100m Sprint Marathon Triple Jump 400m Long Jump 800m Javelin High Jump Shot Put 3000m AEROBIC ANAEROBIC LACTIC ATP-PC Activity 1: Identify which energy system is used the most in each sport. EVENT AEROBIC ANAEROBIC LACTIC 100m Sprint Marathon ATP-PC X X Triple Jump X 400m X Long Jump X 800m X Javelin X High Jump X Shot Put X 3000m X 5 Quick Questions: 1. True or false- The aerobic energy system does not use oxygen. 2. True or false- The anaerobic energy system comes into effect at 2 minutes + 3. Describe the anaerobic energy system. 4. What energy system would be most predominant in these sports? a) b) c) d) e) Football/soccer 400m run Shot put 3000m run Marathon 5. Draw the energy systems graph 5 Quick Questions: 1. True or false- The aerobic energy system does not use oxygen. FALSE (the anaerobic energy system doesn’t use oxygen) 2. True or false- The anaerobic energy system comes into effect at 2 minutes + FALSE (the aerobic energy system comes into effect at 2 minutes + 3. Describe the anaerobic energy system. Short duration, high intensity, ATP-PC (0-20seconds), lactic acid (20seconds-2minutes) 4. What energy system would be most predominant in these sports (anaerobic or aerobic)? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Football/soccer 400m run Shot put 3000m run Marathon Anaerobic Anaerobic Anaerobic Aerobic Aerobic 5. Draw the energy systems graph Hurdles vs. Marathon • See if you can complete this worksheet without looking at your notes. Simon Says: Paragraph Format- Energy Systems Explain in detail anaerobic and aerobic energy systems. Finished? Come and get a puzzle worksheet. CALENDAR AUGUST 2013 MONDAY HOSE 16 x Lessons TUESDAY No Lesson WEDNESDAY Hose- Theory 12 13 19 20 Biomechanics Summary/ Short term responses of exercise No Lesson 26 15 21 28 16 PracticalVolleyball Projectile Motion/ Leavers Practical Lesson (speedball) 27 Force Summation *Practical* Force Summation 14 Practical- Cross Country OR Frisbee Golf FRIDAY BIOMECANICS Hose- Practical Newton’s Laws Theory No Lesson THURSDAY 22 Long Term Responses of Exercise 23 29 Anaerobic Energy Systems Revision- Exercise Physiology Practical Lesson 30 CALENDAR SEPTEMBER 2013 SummaryEnergy systems No Lesson 2 Practical Lesson3 RevisionAnatomy No Lesson 9 16 4 5 6 11 12 13 18 19 RevisionBiomechanics 10 17 EXAM 1.20pm Study Leave CALENDAR AUGUST 2013 MONDAY BRADLEY 14 x Lessons TUESDAY Bradley- Anatomy WEDNESDAY Bradley- Anatomy 12 Stability/ Force Summation 13 Force SummationFrisbee Golf 19 Biomechanics Revision & Short term responses 20 Practical Lesson (netball) 26 BradleyCross Country Newton's Laws of Motion THURSDAY No Lesson 14 15 21 22 16 23 Cross CountryNo class No Lesson 28 Force Summation/ Practical Practical SessionVolleyball No Lesson Long term responses of exercise 27 FRIDAY 29 30 CALENDAR SEPTEMBER 2013 Anaerobic & aerobic energy systems Summary- Energy Systems Practical Lesson 2 Revision Exercise Physiology 3 RevisionAnatomy 9 16 4 5 6 11 12 13 18 19 RevisionBiomechanics 10 17 EXAM 1.20pm Practical Lesson No Lesson Study Leave Summary of Physiology 5 Quick Questions: 1. List 3 short term effects of exercise on the body. 2. List 3 long term effects of training/exercise on the body. 3. What are the two energy systems? 4. Give 5 key points for each system. 5. Draw the energy systems graph.