the Ch. 13 Study Guide

Coyle/Tang-Johnson Chemistry Study Guide
Chapter 13 Study Guide – States of Matter
TEST: Thursday 4/7/11
13.1 The Nature of Gases
Define the following terms:
kinetic energy (KE = 1/2 mv 2 )
kinetic theory
gas pressure
vacuum
atmospheric pressure
barometer/manometer
pascal (Pa)
standard atmosphere (atm)
1. What is STP in… a) atm?
2. 0
◦
C = ____ K b) mmHg (torr)? c) kPa? d) lbs/in 2
3. What is the formula for pressure?
4. What are the 4 fundamental assumptions about gases in the kinetic molecular theory for ideal gases?
?
1
Coyle/Tang-Johnson Chemistry Study Guide
13.2 The Nature of Liquids
Define the following terms:
vaporization
evaporation
vapor pressure
boiling point
normal boiling point
1. Why do liquids have a definite volume?
2. Where does evaporation occur?
3. As evaporation occurs, which particles tend to escape the liquid first?
4. Circle the correct word: As evaporation takes place, the liquid’s temperature
(increases/decreases), therefore, evaporation is a (heating/cooling) process and is
(exothermic/endothermic).
5. What happens to the rate of evaporation as liquid is heated?
6. In a closed container or system at constant vapor pressure, how does the rate of evaporation of liquid compare to the rate of condensation of vapor?
7. What is boiling?
8. True or False? When the external pressure is greater than the vapor pressure of the bubbles in the liquid, boiling does not happen.
9. Why does water boil at a lower temperature at high altitudes?
2
Coyle/Tang-Johnson
13.3 The Nature of Solids
Define the following terms:
melting point
crystal
Chemistry Study Guide
unit cell
allotropes
amorphous solid
glass
1. True or False? The melting point is a different temperature than the freezing point.
2. Why do ionic solids have high melting points?
3. What’s the difference between a crystal lattice and a unit cell?
4. What are the three types of unit cells that can make up a cubic crystal system?
Sketch a diagram of each.
5. Give three examples of amorphous solids:
3
Coyle/Tang-Johnson Chemistry Study Guide
13.4 Changes of States
Define the following terms:
sublimation
phase diagram
triple point
1. At what temperature does sublimation occur?
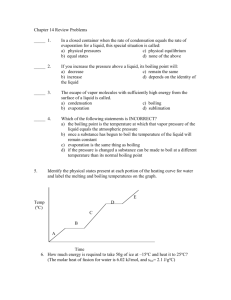
2. What do the lines separating the phases in a phase diagram represent?
4
Coyle/Tang-Johnson Chemistry Study Guide
The common phase or state changes are listed in the table below:
Condensed state
Process Less condensed state
Heat effect
Name for heat effect
Solid melting
→ Liquid endothermic
Heat of fusion
Liquid boiling
→
Gas endothermic Heat of vaporization
Solid sublimation
→
Gas endothermic Heat of sublimation
Gas
Gas condensation
→
Liquid exothermic Heat of condensation deposition
→
Solid exothermic Heat of deposition
Liquid crystallization
→
Solid exothermic Heat of crystallization
Note that the changes are endothermic when the system goes from a condensed state to a less condensed state. This results from the fact that energy is needed to
"pry' apart a condensed state. The particles are attracted to one another in the condensed state by intermolecular forces. The stronger the forces the bigger the energy change. The reverse process has the opposite sign.
5
Coyle/Tang-Johnson Chemistry Study Guide
6