Student Presentation
advertisement

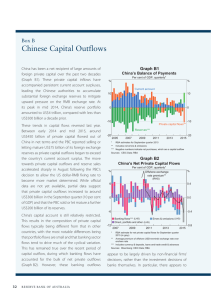
Financial Market of China --- Chinese Capital Account and Current Account Introduction Concept and Relationships between current account, capital account and official reserves Present Capital Account and Current Account Reasons, Advantages and Disadvantages from the data Forecasted Capital Account and Current Account Reasons, Advantages and Disadvantages from the Forecasted Results Conclusion: Good Expectations for the Development of China Part I Current Account: It is the sum of net sales from trade in goods and services, net factor income (such as interest payments from abroad), and net unilateral transfers from abroad. Capital Account: (Financial account) It is the net change in foreign ownership of domestic assets. KA account deficit: domestic ownership of foreign assets has increased more quickly than foreign ownership of domestic assets KA account surplus: foreign ownership of domestic assets has increased more quickly than domestic ownership of foreign assets Official reserve: It records the government's current stock of reserves. Reserves include official gold reserves, foreign exchange reserves, and IMF Special Drawing Rights (SDRS). Relationships between: current account, capital account and official reserve Current Account + Capital Account = Change in Official Reserve Account (Total) Figure 1 Factors that affect Capital Flows Capital Inflows Capital Outflows Export Import Supply Labor to foreign Foreign supply Labor to domestic Obtain Offer Investment Get foreign capital Foreign get domestic capital Loans Foreign in debt Domestic in debt Official Reserve Decreasing Increasing Export and Import Labor Return of Investment Part II Present Current account and capital account prevailing in China China’s Balance of Payments Components,1994-2004 (USD billion) 1. Current Account Surplus 2001.11.10 China's accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) Export is booming faster 2005.07.21 Bank of China declared 2% appreciation of RMB Exchange rate US dollar/ China RMB decreased from 8.27 to 8.10 2001~2007 The increase rate of current account = (160.6-17.4)/17.4 = 824.1% 2. Capital Account Surplus Capital flows (1996-2002) capital flow amount ($100 million) 600 400 200 0 -200 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 -400 -600 Year Capital inflows Capital outflows Net differences • Figure2: • China’s International Direct investment of capital inflows and outflows (1997-2003) Unit: $100million Year 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 Capital Inflows 417.3 452.6 454.6 403.2 407.2 468.8 535.05 2.7 28.2 23.8 22.4 70.9 20.87 Capital Outflows 21.1 Net Differences -396.1 -449.9 -426.4 -379.4 -384.8 -397.9 -514.18 •Source from: According to 2003 Chinese foreign economical trade yearbook 2004 Chinese commerce yearbook computation 3. Official Reserve Why this “Double surplus” ? 1. Increasing in FDI: (1)FDI need to balance the resources settles around the globe. (2) Chinese economic characters strengthen the capability to absorb capital in: Cheap- Labour => Low Cost Cumulative FDI 1980 1980 1990 1990 2000 2000 2003 2003 In Out In Out In Out In Out China 1.1 0 20.7 2.5 348.3 25.8 501.5 37 Japan 3.3 19.6 9.9 201.4 50.3 278 89.7 336 UK 63 80.4 204 229.3 438.6 898 627 1129 US 83 215 395 430.5 1214 1293 1554 2069 2. Less domestic invest abroad: 1. China’s stage of development: 2. China’s macro policy: (1) Aim to enlarge the export, lack of independency. (2) The examination and approval system is too complex. 3. The enterprises in China have problems themselves. 4. China has a relative higher return of interest on saving. Figure 3:International Direct Investment flows and its growth rate (1997-2002) Unit: $100milli on All country Developed country Developing country Year Inflows Outflows Inflows Outflows Inflows Outflows 1997 4819.11 4769.34 2696.54 3960.57 1932.24 766.62 Flows Growth rate 24.80 20.74 22.62 9.15 26.55 25.04 1998 6860.28 6832.11 722.65 6308.91 912.84 Flows Growth rate 42.36 43.25 75.14 59.29 -1.O 498.37 -34.99 Flows 10790.83 10965.54 8246.42 10213.07 2292.95 727.86 1999 Growth rate 45.26 44.31 80.72 59.82 -1.79 -32,81 2000 Flows 13929.57 12007.83 11205.28 10977.96 460.57 Growth rate 29.09 9.51 35.88 7.49 7.31 990.52 36.09 2001 8238.25 7114.45 893.79 6605.58 2094.31 473.82 Flows Growth rate -40.86 -40.75 -47.40 -39.83 -14.89 -52.16 2002 6511.88 6473.63 4603.34 6000.63 1621.45 430.95 Flows Growth rate -20.96 -9.1 -21.90 -9.16 -22.58 -9.05 Source from: According to 2004 Chinese comm erce yearbook reorganization Advantages for this surplus in capital account 1. Balance the international profit. 2. Having more money to boost up domestic economy. 3. Lower unemployment Rate Disadvantages for this surplus in capital account 1. Means that the domestic market is occupied by foreign investors. 2. Since foreign investor will gain from investment, the profit as a financial capital massive will backflow to developed country. 3. The domestic economical industrial structural adjustment may be affected. 4. Financial foreign exchange crisis: more pressure in appreciation of RMB Part III Forecast Capital Account Reasons for Our Forecasts Advantages of Our Forecasts Results Disadvantages of Our Forecasts Results The Volume of International Trade between China with UK, USA and Mongolia (Source: World Trade Organization) Import and Export in the 10th Five-year Plan Period (www.stats.gov.cn/.../ t20060302_402308116.htm) RMB exchange rate to USD 2005/07/21 to 2007/03/12 Source from: The People’s Bank Of China From the data and Charts above, there is big pressure for RMB to appreciate, and let’s look at what would happen for the capital account. The appreciation of Chinese Currency will make investment less attractive because of the speculation reasons. Adding… Our Theoretical Prove Recall: Current Account + Capital Account = Change in Official Reserve Account From the data above, China is now experiencing a “Double Surplus” in both current account and capital account. =>If a government runs a current account surplus and has no change in official reserves, then the current account surplus must be balanced by a capital account deficit. As there will be a Capital account deficit… Advantages: 1. Avoid Repeat Investment 2. Balance the Payment of domestic without increasing Official reserve. 3. Increasing the demand of foreign currency, which will less the pressure of evaluated domestic currency. Advantages: 4. Stop borrowing useless capital from foreign countries and lending to foreign countries. 5. Having more influence in global market. 6. Gain good money from investing abroad. Explanation I : Solow Model there is a decrease on saving rate the saving line shifted from L1 to L2 the capital per worker (k) decreases from K1 to K2 the output decreases from y1 to y2 Worse off Explanation Ⅱ : Disappear of Speculation Short Run: There is a difference between actual exchange rate and market exchange rate Investors have the motivation to get the profit from speculation If there is an appreciation on Exchange rate, there will be a decrease on capital inflow Long-Run: The attractive points on investing foreign assets still exist There will be a capital outflow In total: KA will have a negative sign in the long term. Explanation Ⅲ : Output Function Y = C + I + G + Export - Import d Y/Y = d C / C * C / Y + d I / I * I / Y + d G / G * G / Y + d NX / NX * NX / Y There will be a decrease on economic growth. Explanation Ⅳ : Labour Market the cost of labour will increase. the opportunities provided will decrease. the unemployment rate will increase due to the above reasons. Explanation Ⅴ : Aggregate Demand Foreign investment decreases Domestic interest rate decreases Saving rate decreases Domestic investment decreases Less motivation for economic growth R LM R1 IS1 R2 IS2 Y2 Y1 Y Nowadays, China runs surplus on both Current Account and Capital Account. Under the pressure of International Trade Partner, Chinese Currency has the tendency to appreciate. After the adjustment of Chinese Currency, Speculation Investment will be withdrew. China now is experiencing the specific development period and there will be some problems. Group Members: Stella, Xu Tony, Chen Lucy, Zhang