The Integumentary System
advertisement

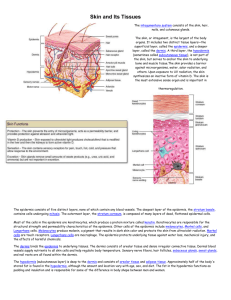
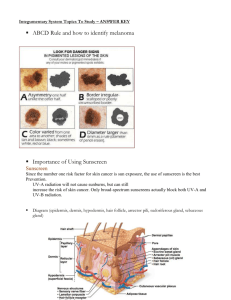
Chapter 5 Introduction to Skin Most accessible but often least appreciated organ system. The skin, or simply integument, accounts for approximately 16% of your total body weight. The skin’s surface, 1.5 - 2.0 m2, is constantly worn away, attacked by micro-organisms, irradiated by sunlight, and exposed to environmental chemicals. Skin is composed of two major components: Two Components of Skin Functions of Skin The epidermis is composed primarily of keratinocytes arranged into layers called strata. Thin Skin versus Thick Skin Thin Skin versus Thick Skin Thin skin, which covers most of the body surface, contains four strata and is about as thick as the wall of a plastic sandwich bag (roughly 0.08 mm). Thick skin, which occurs on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, possesses five strata. It is about as thick as a standard paper towel (roughly 0.50 mm). Note that the terms “thick” and “thin” refer to the relative thickness of the epidermis, not the integument as a whole. Strata of the Epidermis Stratum Basale = the “basement layer”; innermost layer Stratum Spinosum = the “spiny layer” Stratum Granulosum = the “grainy layer” Stratum Lucidum = the “clear layer” Stratum Corneum = the “horny layer”; outermost layer Strata of the Epidermis Ridges of the Skin Dermal Papillae The dermis supports the epidermis and the hypodermis connects the dermis to the rest of the body. Layers of the Dermis Dermis versus Hypodermis Cleavage Lines Factors influencing skin color include epidermal pigmentation and dermal circulation. Pigmentation Dermal Circulation Skin Cancers Nerve fibers and corpuscles Hair follicles, hair shafts, and arrector pili muscles Oil glands and sweat glands Arteries, veins, and lymph vessels Accessory Organs of Skin Sensory Receptors in the Skin Hairs and their Associated Structures Hair Structure Sebaceous Glands Sweat Glands Nails and their Associated Structures Nail Changes The integumentary system is physically and functionally tied to all other body systems and as a result, the state of the skin can be an indication of the health of an individual. Hormones and Endocrine Functions of Skin Vitamin D Vitamin D Age-Related Changes in Skin