Nomenclature - Naming compounds

Nomenclature -
Naming compounds - chpt 4
•
Extra-Credit - Chpt. 4 pg. 118-122,
#1, 3, 6, 10, 13, 17, 18, 24-29, 36
How/Why are compounds made?
Groups in Periodic Table have similar properties
Because same number of valence electrons (outer electrons)
Group 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A outer e1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 filled
When elements make compounds - they want to be like
Noble gases.... so Ionic Compounds gain or lose electrons
(become ions) - see Figure 3.15 on page 79.
Ionic Compounds
for single elements...
Group 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A
Charge +1 +2 +3 +/-4 -3 -2 -1 0
Metal ions (positive ions) keep their name
Nonmetal ions (negative ions) Keep 1st syllable add -ide oxygen becomes oxide ion nitrogen becomes nitride ion chlorine becomes chloride ion iodine becomes iodide ion
Compounds are neutral (have no charge)
Use your ion sheet!!!!!
Ionic Compoundformula to name
Formula to name:
1st: look up element or group of elements on ion sheet - find name of that ion, ignore charge.
NOTE: Once you find the metal (positive ion) or NH
4
+1 everything else is the negative ion.
2nd: Write the name of each ion (positive cation and negative anion) as given from the ion sheet.
Write names for these compounds:
LiBr
MgCl
2
K
2
O
Ionic Compound-
Name to formula
Name to formula:
1st: look up name on ion sheet - find symbol and charge
2nd: use the charges to make the compound neutral, put a subscript if you need more than 1 of them.
Do NOT put charges in final formula.
Write Formulas for these compounds: sodium bromide calcium oxide lithium nitride cesium fluoride
Ionic Compound-
Polyatomic ions
Polyatomic ions:
A group of atoms that are chemically bonded and have a charge.
The method is the same as single atoms with that charge... just treat them as a group with the charge on the ion sheet.
If you need more than 1 of them, use parentheses and subscript.
Write Formulas for these compounds: potassium nitrate calcium bicarbonate ammonium oxide sodium oxalate magnesium phosphate barium hydroxide
Molecules
Molecules are made from only nonmetals, so we recognize them by a nonmetal listed 1st.
Nonmetals all want to gain electrons!!! Molecules are NOT made from ions.
They have to share... the nonmetals can share in many ways.
Both CO and CO
2 exist... can ’ t just say carbon oxide!!! not unique... so we have to use prefixes to tell how many of each atom. Naming is similar 1st element keeps name, 2nd element root +ide. nitrogen dioxide O
2
Cl dibromine tetraflouride N
3
F
6 trisulfur pentaoxide Se
2
O
5
Elements that are molecules: Br
2
I
2
N
2
Cl
2
H
2
O
2
F
2
Acids
Acids produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in solution.
H +1 is the hydrogen ion (a proton !).
Acids all have Hydrogen listed 1st. Only the hydrogens listed 1st are dissolved in water.
Most Common Acids (know these).
Notice they have different numbers of hydrogens
HCl
H
2
SO
4
HNO
3
HC
2
H
3
O
2
H
3
PO
4 hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid nitric acid acetic acid phosphoric acid
Acids -
3 types of naming
Formula to name: from the ion sheet, if the negative ion has no oxygen
(ends with -ide) use root (usually 1st syllable)
-ide hydro_____ic acid if it has oxygen, then it ends either -ate or -ite
-ate _____ic acid
-ite _____ous acid
HBr
HNO
3
HNO
2
H
2
CrO
4
Acids name to formula
Name to formula:
1st: change hydro___ ic back to -ide or
-ic acid back to -ate or -ous back to -ite
2nd: find the name on the ion sheet and its charge,
3rd: add enough H +1 to make neutral
Remember write formula without charges!
hydroiodic acid sulfuric acid oxalic acid nitrous acid
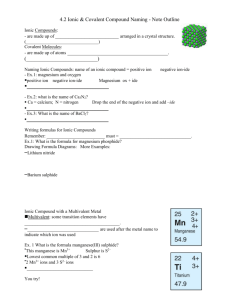
Ionic Compounds revisited
Transition metals can have multiple oxidation states
(more than one common charge)
Each of the common ions is listed on the ion sheet. We just use roman numerals after the metal name to
PbSO4 distinguish the charge.
Fe+2 iron(II) Fe+3 iron(III)
Cu+1 copper(I) Cu+2 copper(II)
PbCl4 cobalt(II) nitrate iron(III) dichromate
Nomenclature
Summary
H 1st - Acid, 3 types of naming H +1 and Nonmetal -x
-ide hydro______ic acid
-ate ______ic acid
-ite ______ous acid
Metal 1st - Ionic compound - use ion sheets
Metal is positive ion, the rest is the negative ion
Make the compound neutral
Nonmetal 1st - Molecule (not ions!!!)
Use prefixes (memorize them!)
1st element keeps its name, 2nd element ending is ide
If use mono , only on the second atom