Minerals Definition of a Mineral
advertisement

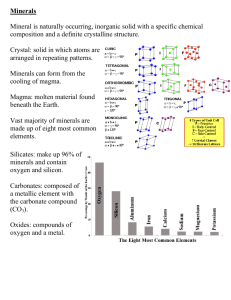
Matter and Minerals ____________________ are the basic building blocks of minerals. Over 100 elements are known. Atoms Smallest particles of matter Have all the characteristics of an element The nucleus is the central part of an atom and contains: _____________________________________________________________. _____________________________________________________________. ________________, or shells: surround the nucleus, contain electrons— negatively charged particles The ___________ ______________is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. ________________ of an element have the same number of protons but varying numbers of neutrons. Have different mass numbers: the sum of the neutrons plus protons Many isotopes are radioactive and emit energy and particles. The _____________ ____________ is the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Why Atoms Bond When an atom’s outermost energy level does not contain the maximum number of electrons, the atom is likely to form a ______________ _______ with one or more atoms. A ________________ consists of two or more elements that are chemically combined in specific proportions. An ___________ is an atom that gains or losses electrons. Types of Chemical Bonds 1. ____________ ______________form between positive and negative ions. 2. ____________ ______________ form when atoms share electrons. 3. _______________ ____________ form when metal ions share electrons. Minerals • Definition of a Mineral: _______________________________ _______________________________ _______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Identifying Minerals • Physical properties: _______________ _______________ _______________ _____________________________ ________________ _____________________________ ________________ Color: EX: ______________________________________ 1._________________________________________________________________ 2._________________________________________________________________ Color: EX: ________________________________________ ____________ - ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________. Obtained by scratching a mineral on a piece of unglazed porcelain. • Streak: Red chalk on a chalk board makes red marks. White chalk makes white marks. • _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________. Gold - When gold is run across a streak plate it makes a ____________________ Color. Pyrite or Fool’s Gold - When pyrite is run across a streak plate, it has a _________________________________________________________. Pyrite is not worth much money, while gold is worth a lot. They look alike, so miners call it fool’s gold. Hematite -_________________________________________________________. • Hema means_______________. • The mineral was named hematite because it looked like it was bleeding when it was taken across a streak plate. Luster: EX: _____________________, ____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Two Major Types: _______________________, ______________________ Hardness: _____________________________________________________________ ____________ ______________ of Hardness. o _______________________________ o ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________. Hardest (10) ____________________ Softest (1) __________________________ Common Objects: _______________________, __________________________, ____________________, ___________________, __________________________ Crystal Shape (or Form): EX: _____________, __________________ External expression of a mineral’s internal atomic structure Planar surfaces are called _______________ _________________. Angles between crystal faces are __________________________________. Cleavage vs. Fracture: _____________________________________________________________ ______________: tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weakness Minerals that do not exhibit cleavage are said to _____________________. Do not confuse cleavage planes with crystal faces! Crystal faces are just on the surface and may not repeat when the mineral is broken. Cleavage is described by: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Cleavage (1 Direction) EX: ___________________________ Cleavage (2 Directions) EX: ______________________, _____________________ Cleavage (3 Directions) EX: ______________________, _____________________ Cleavage (4 Directions) EX: _______________________ Fracture: EX: ___________________________ minerals that do not exhibit cleavage are said to fracture smooth, curved surfaces when minerals break in a glass-like manner: ____________________ _________________________ Specific Gravity: EX: ________________________, _________________________ weight of a mineral divided by weight of an equal volume of water _____________ minerals tend to have ___________ specific gravity than non-metallic minerals Other Properties: 1. 2. 3. 4. __________________________________________________ (calcite fizzes) ___________________ (halite tastes salty) ___________________ (talc feels soapy, graphite feels greasy) _________________________ (magnetite attracts a magnet) Rock Forming Minerals: ~_______________________________ make up most rocks in Earth’s crust Composed mainly of the ___ elements that make up over ____ of the crust Mineral Groups: ____________________________ (Most Abundant) ________________________________ (~8% of Earth’s crust) o ___________________________ O2o ___________________________ (CO3)2o ___________________________ S2o ___________________________ (SO4)2o ___________________________ Cl-, F-, Bro _____________________________ (single elements; e.g., Au) 1. Silicates: ___________________________ o fundamental building block o 4 oxygen ions surrounding a much smaller silicon ion Joining Silicate Structures How tetrahedra may be linked: o ___________________________________________________ o ___________________________________________________ o ______________________________________________________ o ______________________________________________________ o ______________________________________________________ Olivine Group dark silicates (Fe-Mg): _____________________________________ Single ______________________, _________________________________. Pyroxene Group: Ferromagnesian / dark silicates (Fe-Mg) EX: _________________ Single ______________________, _________________________________ Amphibole Group: Ferromagnesian / dark silicates (Ca, Fe-Mg) EX: ________________ Double _____________________, _________________________________ Mica Group and Clay Minerals: light silicates (K, Al):_________________________ EX: _______________________ _______________________,______________________________________ Feldspar Group: light silicates (K-Na-Ca, Al): _______________________________ EX: ___________________________, _______________________________ Three- _________________________________,______________________ Quartz: light silicates (pure SiO2) EX: ______________________________ Three-__________________________________, _____________________ 2. ___________________ - Minerals that contain the elements carbon, oxygen, and one or more other metallic elements. 3. ____________________- Minerals that contain oxygen and one or more other elements, which are usually metals. 4. __________________, __________________ - Minerals that contain the element sulfur. 5. __________________- Minerals that contain a halogen ion plus one or more other elements. 6. ______________ _______________ Minerals that exist in relatively pure form.