MEDICAL PARASITOLOGY
advertisement
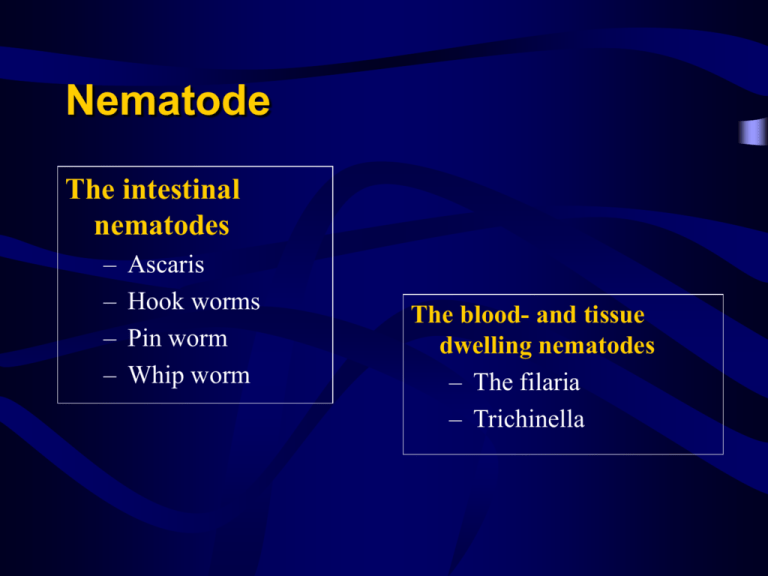
Nematode The intestinal nematodes – – – – Ascaris Hook worms Pin worm Whip worm The blood- and tissue dwelling nematodes – The filaria – Trichinella Ascaris 蛔虫 Ascaris lumbricoides 似蚓蛔线虫 Introduction • The first representative and the most common intestinal parasite • Cosmopolitan in distribution • Rural > urban • Children > adults Morphology Adult Looks like an earthworm Female (20-35 cm); Male (12-30 cm) 3 lips which carry minute teeth A pair of female and male worms of A. lumbricoides. Notice the vulvar waist(arrow)of the female worm and the coiled end of the male worm. Ascaris female worm A scanning electron micrograph of Ascaris showing the three prominent “lips” Egg • Fertilized egg • Unfertilized egg Egg shell Ovum Albuminous layer A. lumbricoides, fertilized egg (6050 micrometer) A. lumbricoides, fertilized egg A. lumbricoides unfertilized egg The life cycle of A. lumbricoides Living site Adults in small intestine Migration Larvae migrate though the lungs HOST MAN Diagnostic stage Undeveloped eggs in feces Method of infection Infective stage Infective eggs are ingested Eggs embryonate in soil by 2-3 wks Symptomatology Larva Pneumonitis Asthma attacks Loeffler’s syndrome Adult • The presence of few worms may be asymptomatic (85%) • The most common symptoms are vague abdominal pain • Large numbers of worms may cause malnutrition and present signs and symptoms of obstruction • Migration of adult worms may cause signs and symptoms of perforation, peritonitis, appendicitis or extrahepatic biliary obstruction. A.lumbricoides in common bile duct Cross section of a liver specimen contains many adult worms of A.lumbricoides obstructing the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. Ascarid chronic pancreatitis A large mass of Ascaris lumbricoides that was passed from the intestinal tract. The ruler at the bottom of the image is 4 cm (about 1.5 inches) in length. An autopsy specimen shows intestinal obstruction by many adult worms of A.lumbricoides. Notice the markedly distended intestinal loop, the thin intestinal wall with hemorrhage and worms protruding from the perforated wound. Peritonitis caused by intestinal perforation due to Ascaris Resected bowel and the adult female from the peritoneal cavity Diagnosis • Microscopic identification eggs in the stool a direct wet mount examination of the specimen (200,000 eggs/female/day) • Macroscopic identification of adults passed in stool or through the mouth or nose Epidemiology • Worldwide distribution, throughout the temperate and tropical areas • 1,000,000,000 people in the world • 40% population in Africa and Asia • 600,000,000 in China (1992) Treatment • Albendazole a single oral dose of 400 mg • Mebenazole 100 mg orally twice daily for 3 days Prevention • Avoid contacting soil that may be contaminated with human feces • Do not defecate outdoors • Dispose of diapers properly • Wash hands with soap and water before handling food • When traveling to areas where sanitation and hygiene are poor, avoid water or food that may be contaminated • Wash, peel or cook all raw vegetables and fruits before eating Hook worms 钩虫 Ancylostoma duodenale 十二指肠钩口线虫 Necator americanus 美洲板口线虫 Pinworm 蛲虫 Enterobius vermicularis 蠕形住肠线虫 Whip worm 鞭虫 Trichuris trichiura 毛首鞭形线虫 Adult worms of Ancylostoma duodenale Adult worms of Necator americanus Morphology • Adult – Cylindrical with the head bent sharply backwards – Males are smaller than the females and possess a bursa at their posterior end Scanning electron micrograph of the oral opening of Ancylostoma duodenale, another species of human hookworm. Note the presence of four cutting "teeth," two on each side. Adult mouthpart of Necator americanus Note : The large buccal capsule is open dorsally with one pair of cutting plate teeth. Bursa of hookworms Lift A. duodenale; Right N. americanus A.d N.a Larger Smaller “C” “S” 4 hooklets 2 plates Spicules Round Tridigitate at the terminus Separated Broader Bidigitate at the base Fused at terminal Mucron Present Absence Size Shape Buccal capsule Bursa Dorsal ray Enterobius vermicularis adult female 0.8-1.3cm.in length , spindle-shaped with a long thin sharply tail. The greater part of the body is occupied by the uterus filled with eggs. Trichuris trichiura adults. • Egg (indistinguishable between the 2 species) – Median size (like the ascaris egg) – Elliptical – Transparent – Thin shell – 4-cell stage when discharge Enterobius vermicularis egg. Note the thick shell and characteristic shape; approximate length = 55 µm. Egg < Ascaris egg Non-symmetrical ellipse; D shaped Transparent Thick transparent shell Tadpole-like embryo when discharged Trichuris vulpis egg Life Cycle • Host -man • No intermediate host 钩虫: Egg Larva (free-living) Larvae migrate from skin to the lungs 蛲虫:Egg takes 6 hours to be infective stage 鞭虫: Similar to Ascaris but no pulmonary migration . There are reservoir hosts. Parasitic site: 蛔虫: small intestinal 钩虫: upper small intestine; Duodenum, jejunum 蛲虫: colon Gravid female adult deposits its eggs on the anus and perianal skin. 鞭虫: ileo-caecal region Infection stage 蛔虫: infective egg 钩虫: infective larva 蛲虫: infective egg ( Egg takes 6 hours to be infective stage) infective mode: Anus-Hand-Mouth Auto-infection/Cross-infection 鞭虫: infective egg Pathogenic stage: 蛔虫: adult worm /larva 钩虫:adult worm Digestive disturbances /Allotriophagy Microcytic hypochromic anemia (sucking, oozing, discharging) A.d. 0.15-0.4ml/d; N.a. 0.02-0.1ml/d larva:Dermatitis ‘ground itch’ Pneumonitis and Bronchitis Pathogenic stage: 蛲虫:adult worm Anal itching (migration of gravid females) Ectopic infection Digestive disturbances 鞭虫:adult worm Digestive disturbances Anemia Trichuris trichiura in the large intestine. Many worms are present, each with its anterior end embedded in the intestinal mucosa, resulting in the erythema. Etiologic dignosis: 蛔虫:fecal direct smear 钩虫:Brine floatation Larva cultivation Egg counting(to estimate infection intensity) 蛲虫: Collect eggs from perianal region by anal swab on the cellophane tape. Search adult female in the perianal region when the child is sleeping. 鞭虫: Brine floatation Prevention and Control 钩虫:Distribution Cosmopolitan 0.4 billion humans are infected in China • Natural factors – Soil contamination – Night soil as fertilizer – Suitable climate dry-land vegetable- raising & mine Prevention and Control 蛲虫 • Readily endemic in children concentrated units • Should put the prevention in first • Mebendazole (100mg repeated after 2 weeks) 鞭虫 Principles same as for ascaris Drug: Albendazole 400mg/d 阿苯达唑/丙硫咪唑/肠虫清 Mebendazole 100mg/次 2次/d 连服3天 (600mg repeated after 2 weeks)






