كبير السن - TAMAM Oman
advertisement

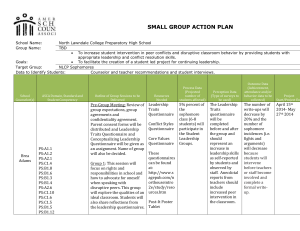
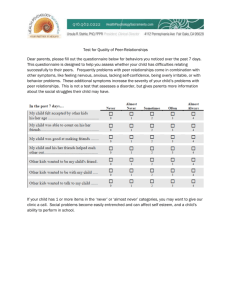
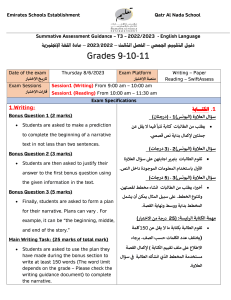
TAMAM PROJECT WORKSHOP USING QUESTIONNAIRES FOR DATA COLLECTION Dr. Ali AlBulushi WHAT IS A QUESTIONNAIRE? • A research tool for data collection • It is a tool used to collect information/data from usually large population about a specific phenomenon under investigation. • The term ‘questionnaire’ used in different ways: – often refers to self-administered and postal questionnaires (mail surveys) – some authors also use the term to describe structured interview schedules (telephone or faceto-face) WHY A QUESTIONNAIRE • Target large amount of people • Use to describe, compare or explain a phenomenon • Can cover a wide range of activities and behaviour, knowledge, attitudes, preferences • Specific objectives, standardised and highly structured questions • Used to collect quantitative data – information that can be counted or measured. What are the strengths and limitations of questionnaires? Let’s get some from you! STRENGTHS OF QUESTIONNAIRES • • • • • • • • • Helps to collect background and baseline information easily Can target large number of people Reach respondents in widely dispersed locations Can be relatively low cost in time and money Relatively easy to get information from people quickly Standardised questions Analysis can be straight-forward and responses pre-coded Low pressure for respondents Lack of interviewer bias (possibility of ‘ghost interviewer’ effect) LIMITATIONS OF QUESTIONNAIRES • Low response rate and consequent bias and confidence in results • Unsuitable for some people (e.g. poor literacy, visually impaired, young children) • Question wording can have major effect on answers • Misunderstandings cannot be corrected • No opportunities to probe and develop answers • No control over the context and order questions are answered • No check on incomplete responses • Seeks information only by asking, can we trust what people say? e.g. issues with over-reporting QUESTIONNAIRE PREPARATION • Establish the purpose and/or guiding question of the questionnaire • Construct the questionnaire – Plan for the questions in light of your purpose – Develop the questions • Plan for the administration DEVELOP THE QUESTIONS • Types of Questions 1. Dichotomous questions (YES/NO) 2. MCQ 3. Scaled response (Likert scale) 4. Ranking 5. Checklist It’s not necessary to have the same type of 6. Open-ended questions all through the questionnaire • Dichotomous Question – Have you taught the ENGLISH basic education curriculum to grade grade 8? ☐ YES ☐ NO • Multiple Choice Question – The new Basic Education Curriculum of English is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A waste of time; An extra burden on teachers Not appropriate to our school A useful complementary curriculum Well-presented-and practicable • Scale responses (Likert scale) Strongly disagree The teacher is the only one who should be held accountable for students academic achievement The teacher should address students’ deviant behavior when it is observed outside the school The teacher should discuss the students’ progress with their parents There are many factors that influence students’ academic achievement Disagree Undecided Agree Strongly agree • Ranking – Please indicate your priorities by placing numbers in the boxes to indicate the ordering of your views, 1=the highest priority, 2=the second highest, and so on. – The proposed amendments to the English basic education curriculum might e successful if the following factors are addressed: • • • • • The appropriate material resources are in schools ☐ The amendments are made clear to all teachers ☐ The amendments are supported by the English team ☐ The necessary staff development is assured ☐ There are improvements to students achievement ☐ • Checklist – Do you have a scheduled time outside class to assist your students? ☐ YES ☐ NO – How many students do you assist outside class time on an average teaching day? _____ students • Open-ended – What are the difficulties that you personally face in managing the interaction between your students in the classroom? OPEN VS. CLOSED QUESTIONS (OPPENHEIM, 1992) Strength OPEN CLOSE D Limitation Freedom & spontaneity of answer Time-consuming Opportunity to probe Coding more problematic Useful for testing hypothesis about ideas or awareness More effort from respondents Requires little time Loss of spontaneous responses No extended writing Bias in answer categories Low costs Sometimes too crude Easy to process May irritate respondents Make group comparisons easy Useful for testing specific hypothesis TASK 1 Please see the handout about the questionnaire pitfalls task prepared in Arabic. هل تفضل المواد الدراسية الفلسفية والنظرية وأكاديمة الطابع أم المواد العملية البسيطة والتي لها صلة مباشرة بالواقع العملي لك كطالب؟ مو ّجه يقود المستجيب الى أجابة معينة دون سؤال َ أخرى ما هي الجوانب المحددة لوضع المناظرة الميتافيزيقية التي تود أن تراها معكوسة في مادة دراسية كالمهارات الحياتية والتي تستهدف طالب الصف ١١ إناث في بيئة ساحلية؟ سؤال رفيع الثقافة حتى وإن تم توجيهه للمثفقين جدا تدرس مقررا بدون وزن أكاديمي (٣ هل تفضل أن ّ أو ٤أو ٥حصص) لطالب غير متفرغين (األربعاء ظهرا فقط) ومساءا واحدا فقط في األسبوع ويشمل تعويضا ماليا عن المواصالت ،أم مقررا أطول بدون وزن أكاديمي ( ٦أو ٧أو ٨حصص) لطالب متفرغين ،أم مقررا كامال مصمم للمتفرغين في جزء يوم محدد ولكن بدون حضور حصص مسائية؟ من ٍ سؤال معقد أن كان عمرك أكثر من ٤٥عاما ولم تحضر أي دورة تدريبية خالل الخدمة ،ضع عالمة ✓ في خانة (أبداً) وعالمة ✓ أخرى في خانة (كبيرًالسن) سؤال أو تعليمات مثيرة للحساسية ما مدى شعورك بعدم تسجيل معلمين في دورات تدريبية بدون وزن أكاديمي خالل الخدمة من المعلمين الذين لم يكملوا عامين في سلك التدريس؟ سؤال بصياغة نفي مزدوجة أجب في الصفحات ٥و ٦و ٧عن كل سؤال يتعلق بأراءك عن الدورات التدريبية أثناء الخدمة بشكل عام ومعتقداتك عن قيمتها في الحياة المهنية للمعلمين على رأس عملهم؟ سؤال مفتوح جدا في أستبانة تكمل ذاتيا من المستجيب وتتطلب وقتا كبيرا أيضا هل يقوم طفلك بأنجاز واجباته بإنتظام؟ كم يبلغ عدد الطالب في المدرسة؟ كم عدد أجهزة الحاسب األلي في المدرسة؟ جزء منها .ما معنى تعددية التفسير للعبارة أو ٍ (بإنتظام)؟ كم عدد الطالب جميعها مع المتغيبين بعذر (كرحلة مدرسية) أو بدون عذر؟ كل أجهزة الحاسب اآللي بما فيها العاطلة عن العمل أو مع الخاضغة للتصليح خارج المدرسة؟ ؟ SNDPأم PGKLMأيهما تفضل ال وجود أختصارات غير مفهومة كم عمرك؟ ٦٠-٥٠ ،٥٠-٤٠ ،٤٠-٣٠ ،٣٠-٢٠ ،٢٠-١٥ فئات غير منفردة /منفصلة يجب ان تدرس مادة المهارات الحياتية للطالب الغير مجيدين فقط ولكن يمكن أن تقدم لجميع الطالب في المراحل العليا. سؤال مزدوج TASK 1 FEEDBACK: AVOIDING PITFALLS IN QUESTION WRITING 1. Abbreviations 2. Ambiguity and vague wording (fairly, generally, you – the respondent, household, family?) 3. Doubled barrelled – ‘do you speak English or French?’ 4. Double negatives – ‘Do not you de-emphasize corporal punishment?’ 5. Inappropriate categories 6. Leading questions – ‘do you like indoor confined individualistic sports or outdoor open team-based sports in the fresh air?’ 7. Memory issues – ‘list at least 5 of your best subjects at schools and the teachers who taught them.’ 8. Social desirability 9. Question complexity TASK 2 Each school should have brought a questionnaire drafted to be used in TAMAM project. Exchange your questionnaires and try to give feedback to the questionnaire you received. Focus on the design, layout, questions, purpose, instructions, length, userfriendliness, etc. If you were sending out a questionnaire, what would you do to maximise the response rate and minimize non-response? TECHNIQUES FOR MINIMIZING NONRESPONSE • Good design: thoughtful layout, easy to follow, simple questions, appearance, length, degree of interest and importance, thank people for taking part • Pre-notification • Explanation of selection • Cover letter • Incentives – Small future incentives, e.g. prize draw – Understanding why their input is important • Reminders • Confidentiality • Anonymity • Pre-paid return envelopes