Powerpoint

Safety and efficacy of maraviroc in
CCR5-tropic HIV-1-infected children aged 2 to <18 years
C Giaquinto, 1 L Keet, 2 C Fortuny, 3 A Fang, 4 M Vourvahis, 4
L McFadyen, 5 SR Valluri, 4 G Mukwaya, 4 J Heera 6
1 Clinica Pediatrica, Centro AIDS Pediatrico, Padova, Italy; 2 Department
Pediatrics, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa; 3 Hospital
Sant Joan de Deu, Barcelona, Spain; 4 Pfizer Inc, New York, NY, USA; 5 Pfizer Inc,
Sandwich, Kent, UK; 6 Pfizer Inc, Groton, CT, USA
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention
June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Country
Brazil
Italy
Portugal
Puerto
Rico
South
Africa
Spain
Study A4001031: participating sites (23 sites from 8 countries)
Investigator/institution
Marinella Della Negra, Instituto de Infectologia
Emilio Ribas, São Paulo
Carlo Giaquinto, Clinica Pediatrica, Centro AIDS
Pediatrico, Padova
José Gonçalo Marques, Centro Hospitalar de
Lisboa Norte, EPE, Hospital Santa Maria, Lisboa
Flora Candeias, Hospital D. Estefânia -Serviço de
Imunologia, Lisboa
Maria João Virtuoso, Hospital Distrital de Faro,
EPE, Faro
Midnela Acevedo-Flores, San Juan Research
Hospital, Puerto Rico Medical Center, Rio Piedras
Ismail Haroon Mitha, Benmed Clinic, Benoni,
Gauteng
Jan Fourie, Dr. J Fourie Medical Centre, Dundee,
KwaZulu Natal
Muthuhadini Patience Mawela, University of
Limpopo, Pretoria, Gauteng
Lizelle Keet, Iatros International, Westdene,
Bloemfontein
Claudia Fortuny, Hospital Sant Joan de Deu,
Barcelona
Daniel Blazquez Gamero, Hospital Universitario
12 de Octubre,
Country Investigator/institution
Thailand Kulkanya Chokephaibulkit, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol
University, Bangkok noi, Bangkok
USA
Virat Sirisanthana, Chiang Mai University, Muang, Chiang
Mai
Pope Kosalaraksa, Khon Kaen University, Muang, Khon
Kaen
Jintanat Ananworanich, The HIV Netherlands Australia
Thailand Research Collaboration, The Thai Red Cross AIDS
Research Centre, Bangkok
Carina Adriana Rodriguez, University of South Florida,
Children's Research Institute, St Petersburg, FL
Antonio Carlos Arrieta, Children's Hospital of Orange
County, Orange County, CA
Suzanne Renee Lavoie, Virginia Commonwealth University,
Richmond, VA
Joseph August Church, Children's Hospital Los Angeles, Los
Angeles, CA
Stephen Cole Eppes, Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for Children,
Wilmington, DE
Charles Debeaux Mitchell, University of Miami Miller
School of Medicine, Miami, FL
Natella Yurievna Rakhmanina, Children's National Medical
Center - Infectious Disease, Washington, D.C.
Introduction
•
Maraviroc (MVC) is a selective CCR5 antagonist and is the first of this class of oral agents approved for treatment of
CCR5-tropic HIV-1 in adults
•
Preliminary data from 31 children have previously been presented at IAS 2011
•
Here we present updated safety and efficacy findings from 94 subjects who received at least one dose of study medication with a data cut-off of March 12, 2013
– Efficacy data is reported until Week 48
– All safety data is included as of the cut-off date of March 12,
2013
•
Pharmacokinetic (PK) and dose-finding data from Stage 1 are presented in poster MOPE044, 1 also at this meeting
1. Vourvahis et al. IAS 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract #MOPE044.
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Study A4001031: Ongoing, open-label, two-stage, age-stratified, non-comparative study to evaluate PK, safety, and efficacy of MVC with optimized background therapy (OBT) in treatment-experienced children and adolescents infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1
Screening
Baseline
Day 1
Cohort 1: ≥2–<6 years (liquid)
Cohort 2: ≥6–<12 years (tablet)
Cohort 3: ≥6–<12 years (liquid)
Cohort 4: ≥12–<18 years (tablet)
End of study
Weeks
4–6 weeks
Screening S1
S2
S2
48 weeks 240 weeks (5 years)
Follow-up
5 years after initial MVC exposure
On or off MVC
S1, Stage 1 : intensive PK for dose finding (4-12 weeks): Minimum of 12 (cohort 1) and 10 children (in each of cohorts 2-4) to complete stage 1, prior to entering stage 2.
S2, Stage 2: safety/efficacy. Following the minimum numbers being reached for stage 1, all new patients then directly enter stage 2
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Methods
•
Subjects infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1 (as detected by
Phenotypic assay, ESTA) were enrolled into one of four age/formulation cohorts
•
Eligibility criteria included:
– HIV-1 RNA >1000 copies/mL at screening
– On stable or no pre-study antiretroviral (ARV) regimen for >4 weeks prior to screening visit
– Previous experience/intolerance >6 months (sequential or cumulative) with at least two ARV drug classes
•
OBT choice was guided by resistance test results and consisted of ≥3 ARVs in addition to MVC
•
MVC dose based on body surface area and co-medications 1
•
Safety, viral load and CD4 counts were evaluated at all study visits
•
Statistical analyses are descriptive in nature
1. Vourvahis et al. IAS 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Abstract #MOPE044.
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
<0.22
0.22
0.43
0.44
0.72
0.73
1.19
1.20
1.30
1.31
1.73
>1.73
BSA, m 2
MVC doses by BSA on entry and OBT
Dose in absence of potent
CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers
40 mg BID
100 mg BID
200 mg BID
300 mg BID
300 mg BID
300 mg BID
300 mg BID
Dose with potent
CYP3A4 inhibitors
10 mg BID
25 mg BID
50 mg BID
75 mg BID
100 mg BID
125 mg BID
150 mg BID
Dose with CYP3A4 inducers (in absence of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors)
40 mg BID
100 mg BID
200 mg BID
300 mg BID
375 mg BID
450 mg BID
600 mg BID
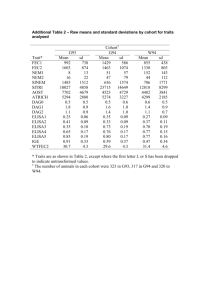
Subject baseline characteristics
(N=94)
Sex, males/females
Race,
White/Black/Asian/Other
Body surface area, m 2
(median [range])
Age, years
(median [range])
Median baseline plasma
HIV-1 RNA (log
10
, copies/mL [range])
Median baseline
CD4 counts (μ/L [range])
Median duration of study treatment (days)
[range]
Cohort 1
(N=13)
9/4
1/8/2/2
0.7
(0.5 – 0.7)
3.0
(2.0–5.0)
4.6
(3.9–5.6)
894.5
(131.5–1768.5)
226
(45 – 1321)
Cohort 2
(N=27)
13/14
5/18/3/1
1.0
(0.6–1.4)
10.0
(6.0–11.0)
4.3
(3.2–5.5)
467.8
(5.5–1120.5)
526
(92 – 1316)
Cohort 3
(N=12)
6/6
1/11/0/0
0.9
(0.6–1.6)
9.0
(6.0–11.0)
4.7
(3.5–5.3)
Cohort 4
(N=42)
16/26
9/26/6/1
1.3
(0.9–1.8)
14.0
(12.0–17.0)
4.4
(2.9–5.9)
414.0
(192.5–1341.0)
371.0
(29.0–847.5)
240
(2 – 1373)
261
(14 – 1234)
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Cohort 1
(N=13)
Study disposition through Week 48
75/94 children were followed up for 48 weeks
(26 discontinued MVC; 49 still on treatment)
Screened
(N=262)
Enrolled
(N=94)
Screen failure (N=164)
Viral load <1000 copies/mL (n=40)
PSGT was non-reportable (n=4)
Not CCR5-tropic (n=71)
Tropism not reportable (n=36)
Other (n=13)
In screening (N=4)
Cohort 2
(N=27)
Cohort 3
(N=12)
Cohort 4
(N=42)
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Study disposition through Week 48
75/94 children were followed up for 48 weeks
(26 discontinued MVC; 49 still on treatment)
Screened
(N=262)
Enrolled
(N=94)
Screen failure (N=164)
Viral load <1000 copies/mL (n=40)
PSGT was non-reportable (n=4)
Not CCR5-tropic (n=71)
Tropism not reportable (n=36)
Other (n=13)
In screening (N=4)
Cohort 1
(N=13)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=1)
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 2
(N=27)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=4)
• Virological failures (n=3)
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 3
(N=12)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=3)
• Virological failures (n=2)
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 4
(N=42)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=18)
• Virological failures (n=11)
• Adverse events (n=1)
• Other* (n=6)
*Other includes discontinuation (DC) due to withdrawal of consent, non-compliance, lost to follow-up; all virological failures had confirmed poor compliance with study medication; 3 virological failures had non-R5 tropism at failure
Study disposition through Week 48
75/94 children were followed up for 48 weeks
(26 discontinued MVC; 49 still on treatment)
Screened
(N=262)
Enrolled
(N=94)
Screen failure (N=164)
Viral load <1000 copies/mL (n=40)
PSGT was non-reportable (n=4)
Not CCR5-tropic (n=71)
Tropism not reportable (n=36)
Other (n=13)
In screening (N=4)
(n=1)
Cohort 1
(N=13)
DC prior to Week 48
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 2
(N=27)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=4)
• Virological failures (n=3)
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 3
(N=12)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=3)
• Virological failures (n=2)
• Other* (n=1)
Cohort 4
(N=42)
DC prior to Week 48
(n=18)
• Virological failures (n=11)
• Adverse events (n=1)
• Other* (n=6)
Ongoing Pre-Week 48
(n=4)
Ongoing Pre-Week 48
(n=7)
Ongoing Pre-Week 48
(n=4)
Ongoing Pre-Week 48
(n=4)
Completed Week 48
(n=5)
Completed Week 48
(n=19)
Completed Week 48
(n=5)
Completed Week 48
(n=20)
*Other includes discontinuation (DC) due to withdrawal of consent, non-compliance, lost to follow-up; all virological failures had confirmed poor compliance with study medication; 3 virological failures had non-R5 tropism at failure
Percentage of subjects with HIV-1 RNA
<400 copies/mL at 24 (N=84) and 48 weeks (N=75)*
67% at 24 weeks and 52% at 48 weeks had VL < 400c/mL
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
7/10
4/6
22/26
15/23
6/10 5/8
21/38
15/38
Week 24
Week 48
Cohort 1 Cohort 2 Cohort 3 Cohort 4
*Efficacy was evaluated using the missing/discontinuation = failure approach
Numerator=Number of responding subjects
Denominator=Includes all subjects who completed week 48 or discontinued prior to week 48
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Percentage of subjects with HIV-1 RNA
<48 copies/mL at 24 (N=84) and 48 weeks (N=75)*
46% at 24 weeks and 40% at 48 weeks had VL < 48 c/mL
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
2/10
3/6
14/26
10/23
6/10
4/8
17/38
13/38
Week 24
Week 48
Cohort 1 Cohort 2 Cohort 3 Cohort 4
*Efficacy was evaluated using the missing/discontinuation = failure approach
Numerator=Number of responding subjects
Denominator=Includes all subjects who completed week 48 or discontinued prior to week 48
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Median CD4% at baseline, Week 24, and Week 48
n = 11 6 4
Cohort 1
26 23 15
Cohort 2
11 9 5
Cohort 3
36 23 19
Cohort 4 n = children with available CD4 data at Week 24 and Week 48
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Summary of all-causality adverse events*
Subjects n (%)
With adverse events
Serious adverse events
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events
Death
Discontinued due to adverse events
60 (63.8)
16 (17)
10 (10.6)
0
3 (3.2)
Most frequently reported (>10%) adverse events by system organ class, n (%)
Gastrointestinal disorders
Infection and infestations
Nervous system disorders
Reproductive system and breast disorders
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
34 (36.2)
46 (48.9)
13 (13.8)
12 (12.8)
11 (11.7)
*All data included as of the cut-off date of March 12, 2013
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Adverse events (>Grade 2) in each cohort, n (grade)
None of these events were attributed to maraviroc by the study investigators
Cohort 1
(N=13)
Cohort 2
(N=27)
Gastritis (1, G3)
Vomiting (1, G3)
Cohort 3
(N=12)
Pneumonia (1, G3)
Cohort 4
(N=42)
TB drug-induced liver injury (1, G4)
Pneumonia (1, G3)
Otitis media (1, G3)
Transaminases increased (1, G4)
H1N1 influenza (1, G3)
Hepatic enzyme abnormal (1, G3)
Bipolar disorder (1, G3)
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Conclusions
•
These data suggest that in HIV-1-infected, treatmentexperienced children aged 2 − <18 years, MVC
(administered twice-daily) in addition to OBT was:
– Generally well-tolerated
– Effective at 48 wks, with 52% and 40% of subjects achieving
HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL and < 48 copies/mL, respectively
•
Virological failure was associated with non adherence and was more frequent in adolescents (Cohort 4)
•
Enrolment is continuing with collection of additional data, including OBT resistance, out to 5 years
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Acknowledgments
•
We would like to thank all study participants, caregivers, DMC members, and investigators
•
This ongoing study is being conducted by Pfizer Inc and is funded by ViiV Healthcare
•
Editorial support was provided by Complete
Medical Communications and was funded by ViiV
Healthcare
7th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; June 30-July 3, 2013; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia