Plant hormones - WordPress.com
advertisement

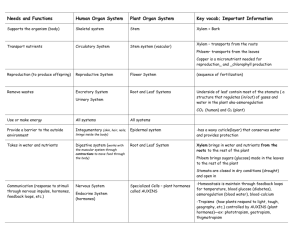
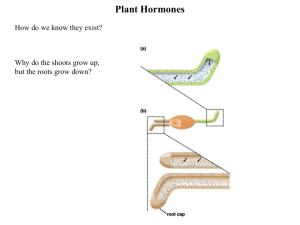
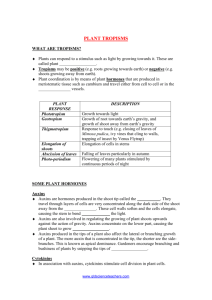
PLANT HORMONES PLANT HORMONES • All are produced in specific parts of the plant – eg shoot tip PLANT HORMONES • All are produced in specific parts of the plant – eg shoot tip • Transported to other parts of the plant – eg region of elongation PLANT HORMONES • All are produced in specific parts of the plant – eg shoot tip • Transported to other parts of the plant – eg region of elongation • Effective in very small amounts. TYPES OF HORMONES • Auxins - Produced in tips of roots and short and promote elongation and differentiation of the cells. TYPES OF HORMONES • Auxins - Produced in tips of roots and short and promote elongation and differentiation of the cells. - Responsible for apical dominance in which the main stem is the dominant growth site as growth of side stems is suppressed. TYPES OF HORMONES • Auxins - Produced in tips of roots and short and promote elongation and differentiation of the cells. - Responsible for apical dominance in which the main stem is the dominant growth site as growth of side stems is suppressed. - Main Auxin is Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) TYPES OF HORMONES • Gibberellins - Similar production sites and effects as Auxins. TYPES OF HORMONES • Gibberellins - Similar production sites and effects as Auxins. - Promotes growth by rapid elongation of cells, especially those of the stem between the nodes (where side branches and leaves come off). TYPES OF HORMONES • Gibberellins - Similar production sites and effects as Auxins. - Promotes growth by rapid elongation of cells, especially those of the stem between the nodes (where side branches and leaves come off). - Also known as ‘bolting hormone’ TYPES OF HORMONES • Gibberellins - Similar production sites and effects as Auxins. - Promotes growth by rapid elongation of cells, especially those of the stem between the nodes (where side branches and leaves come off). - Also known as ‘bolting hormone’ - Promotes cell differentiation of cambium. TYPES OF HORMONES • - Gibberellins Similar production sites and effects as Auxins. Promotes growth by rapid elongation of cells, especially those of the stem between the nodes (where side branches and leaves come off). - Also known as ‘bolting hormone’ - Promotes cell differentiation of cambium. - Breaks dormancy of seeds and buds. TYPES OF HORMONES • Cytokinins - Produced in the tips of roots and promotes cell division/mitosis. TYPES OF HORMONES • Cytokinins - Produced in the tips of roots and promotes cell division/mitosis. - Balance the growth in roots ad short, and also act to slow aging of tissues. TYPES OF HORMONES • Abscisic Acid - Promotes formation of abscission zone, the layer of cells where leaves and fruit fall from the tree. TYPES OF HORMONES • Abscisic Acid - Promotes formation of abscission zone, the layer of cells where leaves and fruit fall from the tree. - Promotes seed dormancy TYPES OF HORMONES • Abscisic Acid - Promotes formation of abscission zone, the layer of cells where leaves and fruit fall from the tree. - Promotes seed dormancy - Stimulates closing of stomata in most plants. TYPES OF HORMONES • Ethene - Produced and accumulates in aging fruit, promoting their ripening. TYPES OF HORMONES • Ethene - Produced and accumulates in aging fruit, promoting their ripening. - Produced in aging leaves, assisting in their fall.