Plant Hormones - Langdon Biology
advertisement

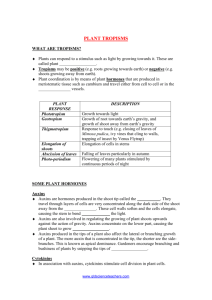
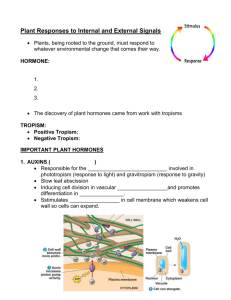
Plant Hormones • Plant hormones – – – – Organic compounds produced in low concentrations Produced in one part of plant (i.e. source) Transported to another part of plant (i.e. target) Cause physiological or developmental responses (stimulatory or inhibitory) • Also called plant growth regulators or phytohormones Plant Hormones • Major types of plant hormones: – – – – – Auxins- most common is IAA or indole –acetic acid Gibberellins Abscisic acid ABA Cytokinins Ethylene Plant Hormones • Auxins – Types of auxins used in horticulture • Natural auxin is indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) – IAA is broken down in sunlight • Synthetic auxins used in horticulture: • 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) – Site of auxin production in plants: • Shoot and root tips (apical meristems) • Young, expanding leaves • Young seeds Plant Hormones • Auxins – Action of auxins in plants: • Stimulate cell elongation – Auxins increase the length of most plant cells and thereby contribute to the growth and elongation of the plant. Also cause a bend toward light - positive phototropism- because more auxin remains in cells on opposite side of light source • Promotes apical dominance – Pinching bud removes source of auxin and releases axillary buds from apical dominance • Promotes growth of adventitious roots- roots in uncommon – Eg. geranium cuttings, transplanting. place Plant Hormones • Auxins – Actions of auxins in plants • Promotes or inhibits abscission of leaves, flowers and fruit – NAA (synthetic auxin) applied shortly after bloom is used to thin apples – NAA applied during fruit development inhibits abscission of apples • Auxin concentration determines if action is stimulatory or inhibitory – Low concentration promotes adventitious root growth, but high concentration inhibits root growth of cuttings – 2, 4-D is used as herbicide by applying at high concentrations Plant Hormones • Gibberellins • Several different gibberellins (GA) produced by plants – Large, complicated molecules not synthesized – Commercial gibberellins produced by fungus – Site of gibberellin production in plants: • • • • • Shoot and root tips (apical meristems) Young, expanding leaves Embryos Fruits Tubers Plant Hormones • Gibberellins – Action of gibberellins in plants: • Stimulate cell elongation – Dwarf plants treated with gibberellins produce normal growth – Applied to grapes to elongate the peduncle (stem of flower cluster) and pedicels (stem of single flower), making looser cluster • Promotes cell division in vascular cambium • Promotes seed germination – causes production of amylase enzyme that breaks down starch into energy needed for growth – Used by beer brewers to stimulate sugar production in barley malt (sugar is converted into alcohol during fermentation) • Influences flower and fruit development Plant Hormones • Abscisic Acid (ABA) – Similar structure as gibberellins – Site of abscisic acid production in plants: • All organs (e.g. roots, leaves, stems, fruits) – Actions of abscisic acid in plants • Counteracts effects of auxins and gibberellins • Maintains dormancy in seeds and buds • Stimulates guard cells to close stomates (to conserve water) source of ABA are the spongy mesophyll cells Plant Hormones • Ethylene has been used in practice since the ancient Egyptians, who would gas figs in order to stimulate ripening. – Site of ethylene production in plants: • Throughout plants – Actions of ethylene in plants • Inhibits root and shoot elongation by blocking transport of auxins from apical meristems • In addition to causing fruit to ripen, it can cause plants to die. It can be produced when plants are injured, either mechanically or by disease. Ethylene will cause a wide range of effects in plants, depending on the age of the plant and how sensitive the plant is to ethylene. Plant Hormones • Cytokinins – Types of cytokinins used in horticulture • Several natural forms • Synthetic cytokinins used in horticulture: – Benzyladenine (BA) – Site of cytokinin production in plants: • Embryos • Young leaves and fruit • Apical meristems of roots Plant Hormones • Cytokinins – Actions of cytokinins in plants • Promotes cell division (cytokinesis) • Contributes to cell enlargement (in leaves) • Stimulates differentiation of cells (with auxins) – High cytokinin and low auxin promotes shoot initiation in tissue culture, whereas reverse combination promotes root formation – Moderate levels of both hormones promotes callus growth • Delays senescence =changing of colour in leaves (maintains and promotes synthesis of chlorophyll) Plant Hormones • Ethylene – Actions of ethylene in plants • Induces adventitious root formation by blocking (and accumulating) auxin at tip of stem cutting • Enhances flow of latex in rubber trees • Enhances flowering in pineapples • Stimulates abscission of leaves and fruit – Used as a harvest aid for cherries • Promotes fruit ripening (apple, tomato, citrus, coffee) • Promotes senescence (aging) of flowers