Animal Nutrition
advertisement

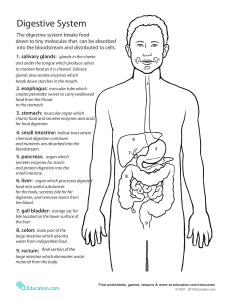
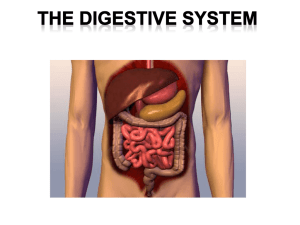
Animal Nutrition With a side bar on the animal kingdom! Animal Phylogeny P.640 32.8 Why Digest? Makes food available to cells May be intracellular-within each individual cell May be extracellularenzymes are released and food is prepared for all cells. Intracellular is primitive Porifera Picture Phylum Porifera Extracellular with one body opening and gastrovascular cavity Cnidaria cross section Phylum Cnidaria Planaria cross section Phylum Platyhelminthes Extracellular with one way digestive tract (have mouth and anus) Nematode Pix Phylum Nematoda Annelids Annelid cross section Phylum Annelida Animals are group based on food source Carnivores- eat meatshorter intestine, pointed teeth. Omnivores- eat meat and plants, teeth like carnivore in front and herbivore in back. Herbivores- eat plants, longer intestine, large flat teeth to break up plant tissue. Long very specialized digestive tract. Bear Pix Herbivore modifications 41.22 Specialized Actions Mechanical-teeth, grinding(pebbles in bird and earthworm gizzards), churning. Chemical-hydrolysis by enzymes • Ex:Salivary amylase • Source-salivary gland • Substrate-starch-a polysaccaride • Product-maltose- a disaccaride Human Digestive System Digestive System Pix Food moves by peristalsis Accessory Organs Liver-produces bile Gallbladder-stores and concentrates bile Pancreas-produces pancreatic juice (both enzymes and bicarbonate) 41.16 Stomach-Site of Protein Digestion •Convoluted •Secretes Gastric Juice-acidic secretions of gastric glands of mucosa •Two cell types•Parietal-HCl •Chief-pepsinogenactivated in low pH-to form pepsin •Low pH denatures proteins •Protein digestion finished in small intestine •Output from stomach-chyme 41.15 Protein Digestion 41.18 Pepsin Source-chief cells as pepsinogen Substrate-protein Product-polypeptides Optimum pH-2 Trypsin Source-pancreas as trypsinogen Substratepolypeptide Product-amino acids Optimum pH-neutral Small Intestine Carbohydrate, lipid, protein digestion finished. Everything absorbed (exceptions-aspirin, alcohol, water absorbed in stomach) First 25 cm-duodenumreceives secretions from pancreas, gall bladder. Then jejunum Then ileum 41.21 Structure of the GI Tract 41.19 Inner mucosaepithelium Submucosaconnective Muscularis-double layer of smooth muscle Serosa-more connective tissue SI Absorption Brush Border-where a.a’s and monosac’s are transported into the epithelial cells, across membranes and into blood capillaries within the villi. From here carried to the liver Fat-hydrolyzed, absorbed, reassembled into triglycerides. Triglycerides combine with protein to form chylomicronsabsorbed into lymphatic system-empties into veins near the neck. 41.19 Large Intestine Large in diameter Joins SI near two vestigial organs • Appendix and cecum Vitamin K made by microorganism here and absorbed. Bacteria ferment here- produce gas Low fiber diets-food moves slowlyassociated with high colon cancer rates Pancreas Secretes Pancreatic juice-enters duodenum through the pancreatic duct. Contains • • • • • Trypsin-protein Chymotrypsin-protein Pancreatic amylase-starch Lipase-fat Bicarbonate-neutralizes HCl makes alkaline Secreted as zymogens-inactive enzymes Activated by brush border enzymes Digestion is completed by brush border enzymes Liver •Largest internal organ •Secretes bile •Bile pigment-from RBC’s-no digestive role-too much jaundice •Bile salts-work like detergent to emulsify •Stored in gall bladder-fatty food triggers release •Regulatory •Metabolizes drugs, alcohol •Removes steroid hormones •Produces most blood proteins •Regulates blood glucose-stored in liver as glycogen, used up-does gluconeogenesis Regulation of digestion Coordinated by nervous/endocrine Sight/smell-nervous Food in stomach-release of gastrin-causes release of gastric juices Hormones control passage of food into duodenum-high fat slows passage Duodenum secretes CCK in response to fat-causes bile release Secretin-causes pancreas to release bicarbonate