Diffusion & Osmosis
advertisement

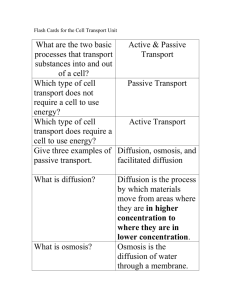
In a few sentences write about what you think would happen to a food factory if its power were to shut off and there is no way to get rid of its garbage. SCIENCE STARTER Based on your observations and prior knowledge write in your journal what you think will happen when an egg is put into vinegar for one day. Give reasons for your hypothesis. Do the same thing for what would happen for two days? Will it be destroyed? Will is grow larger, smaller, stay the same size? Will the egg shell resist the vinegar? After a couple of minutes you will discuss with your neighbors and then we will discuss as a group. EGGSPERT IN DIFFUSION DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS SPI 0707.1.5 (Diffusion) After this lesson you will be able to: Explain how materials move through simple diffusion. Cell division allows organisms to grow and repair injuries. Think of an organism like a factory. Just like a factory an organism needs to be able to obtain energy, get material in, and get rid of waste. So the cells of an organism performs these functions. These functions keep a cell healthy so they can divide. CELLULAR GROWTH AND DIVISION So we know that cells need to get material into them and also remove waste, but how do they do this? By Diffusion! The movement of molecules from an area in which they are highly concentrated to an area in which they are less concentrated. WHAT IS DIFFUSION? DIFFUSION molecules move from areas of HIGH concentration to areas of LOW concentration Diffusion does NOT require any energy BrainPop DIFFUSION OF WATER The cells or organisms are surrounded by and filled with fluids that are made mostly of water The diffusion of water is so important to life processes that it has been given a special name- Osmosis Observation Hypothesis – Write in your science journal what you think will happen to the egg by tomorrow. Will water diffuse from the vinegar into the egg or will it diffuse out of the egg into the vinegar? Why? SCIENCE STARTER The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. Semipermeable means that only certain substances can pass through Semipermeable is sometimes called selectively permeable Osmosis requires NO ENERGY. OSMOSIS A membrane that allows only certain materials to cross it Materials pass through pores in the membrane SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE OSMOSIS WATER molecules move from areas of HIGH concentration to areas of LOW concentration Through a membrane! ONLY WATER!!!! Osmosis Hypertonic- a solution that causes a cell to shrink because of Osmosis. Hypotonic- a solution that causes a cell to swell because of Osmosis. Isotonic- a solution that causes no change in the size of the cell OSMOSIS In this picture a red blood cell is put in a glass of distilled water. Because there is a higher concentration of water outside the cell, water enters the cell by OSMOSIS. In this case too much water enters and the cell swells to the point of bursting open. EQUILIBRIUM = molecules are evenly distributed WHEN DO THE MOLECULES STOP MOVING? Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Osmosis is the movement of water thru a semi permeable membrane. Active transport requires energy. (molecules move from an area of lesser to higher concentration) Passive transport needs NO ENERGY! (molecules move from an area of higher to lesser concentration). SUMMARY All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive – maintain homeostasis These include exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), taking in water, minerals, and food, and eliminating wastes. These tasks happen at the cellular level. Molecules move through the cell membrane by diffusion A balance, or EQUILIBRIUM, must be maintained. WHY ARE OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION IMPORTANT?