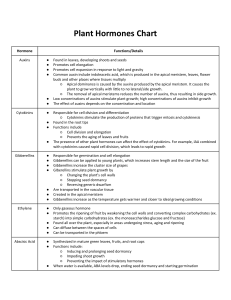
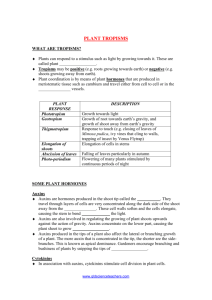
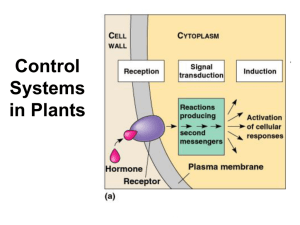
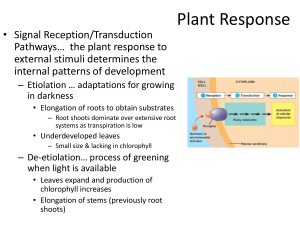
Plant Hormone Quiz Key
1. Name 3 processes which are regulated or influenced by gibberellins.
Possible answers include cell elongation, seed germination, dormancy, flowering , sex expression,
enzyme induction, and/or leaf and fruit senescence.
2. What are the 2 structural types of gibberellins?
C-19 Gibberelins (19 carbon) and C-20 Gibberelins (20 carbon)
3. Where are cytokinins synthesized?
Cytokinins are synthesized in meristematic tissues in roots.
4. Name one process that is regulated by cytokinins.
Possible answers include: apical dominance and lateral root initiation, senescence and chlorophyll
degradation in aging leaves, growth of dicot seedlings in the dark (in combination with ethylene),
and/or development of sex organs and male sterility
5. How does ethylene affect growth?
Promotes root growth and root hair growth, can cause asymmetric growth in stems and leaves,
regulates seedlings’ horizontal growth & apical hook formation (“Triple response” of seedlings grown
in dark).
6. What is the triple response due to ethylene?
Seedlings’ horizontal growth & apical hook formation, specifically ‘short, thick and curled’ growth.
7. What about the structure of ethylene makes it unique among plant hormones?
Ethylene is a very small, simple molecule compared to other plant hormones.
8. Name 3 important processes affected by abscisic acid.
Possible answers include: plant development, bud & seed dormancy, germination, cell division, leaf
senescence, abscission, and/or cellular response to stress
9. How does abscisic acid help protect against drought?
In a drought, ABA increases in some plants, causing the stomata to close, preventing water loss and
ABA can also produces osmolytes that protect cell membranes from dehydration
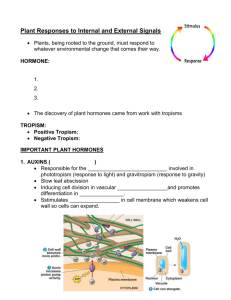
10. What is the primary function of auxins?
Auxins are essential for cell growth.
11. Why are auxins considered the ‘Master Hormones’?
Auxins are responsible for the coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in the plant life
cycle, stimulate or inhibit the expression of specific genes, and coordinate development at all levels in
plants, from the cellular level through organs and ultimately the whole plant.
12. Name a process that is affected by cytokinins and auxins working in harmony.
Possible answers include: stimulates cell division; when applied to callus, rooting can be generated;
xylem tissues can be generated; stimulate cell division in the cambium and in tissue culture.
13. Name 3 functions which are regulated by auxins.
Possible answers include: stimulate cell elongation; stimulate differentiation of phloem and xylem;
stimulate root initiation on stem cuttings and lateral root development in tissue culture; mediate the
tropistic response of bending in response to gravity and light; suppresses growth of lateral buds; delay
leaf senescence; can induce fruit setting and growth in some plants; involved in assimilate movement
toward auxin; delay fruit ripening; promote flowering in Bromeliads; stimulate growth of flower parts;
stimulate the production of ethylene at high concentrations; and/or inhibit growth by closing the
stoma during water stress.
14. What is unique regarding the structure of synthetic auxins?
Ether linkage