QUALITY_OF_CARE_1_principles_of_quality
advertisement

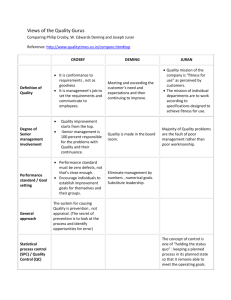
QUALITY OF CARE Sharon Gondodiputro, dr., MARS., MH Department of Public Health Faculty of Medicine Unpad References: 1. A.F. Al-Assaf, Mutu Pelayanan Kesehatan, Perspektif Internasional (Health Care Quality: An International Perspective), alih bahasa: Munaya Fauziah & Andri Lukman, Penerbit Buku Kedokteran-EGC, Jakarta, 2003, Bab 1 dan 2 2. Rakish,Longest & Kurt Darr, Managing Health Services Organizations, Health Professions Press, Inc. USA,1992, hlm.407-422 What is Quality? some definitions of quality PHILIP CROSBY , ’78 : Mutu adalah pencapaian kepada suatu keinginan atau spesifikasi tertentu (quality is conformance to requirements or specification) AL ASSAF, ’93 : Mutu adalah melakukan sesuatu dengan baik mulai dari pertama kali dan melakukan berikutnya lebih baik lagi (quality is doing the right thing the first time and doing it better the next) AMERICAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION,’91 : Mutu adalah pelayanan kesehatan mencapai tingkatan probabilitas dampak yang optimal bagi pasien (Quality is the degree to which care services influence the probability of optimal patient outcomes) IBM ’92 : Mutu adalah tercapainya keinginan dari pelanggan, baik internal maupun eksternal untuk suatu produk yang sempurna (quality is meeting the requirements of the customer , both internally and externally , for defect free products and services) Key words : Requirements or specification Doing the right thing the first time Defect free products and services Optimal patient outcomes : meeting the requirements of the customer , both internally and externally >> customer satisfaction Who are the customers? Who are the customers? Health workers Patients and their families INTERNAL CUSTOMERS Owners or third payers INTERMEDIATE CUSTOMERS EXTERNAL CUSTOMERS Principles of Quality DONABEDIAN DEMING JURAN CROSBY ISHIKAWA DONABEDIAN, BALANCE BENEFIT AND RISKS Components of quality Technical care Definition involves using medical knowledge and technology to maximize the benefits of care for the patient while minimizing the risks involved; Interpersonal involves paying attention to the psychosocial aspects of care, including the patient provider relationship, the larger social context in which care is provided and the social circumstances with which the patient must cope; Management/organ izational determines its accessibility, timeliness, the amenities provided and efficiency. Dr. Deming's philosophy Quality = Results of Work efforts Cost quality tends to increase and costs fall over time. However, when people and organizations focus primarily on costs, costs tend to rise and quality declines over time. DEMING’S WHEEL 1. PLAN: Design or revise business process components to improve results 2. DO: Implement the plan and measure its performance 3. CHECK/STUDY: Assess the measurements and report the results to decision makers 4. ACT: Decide on changes needed to improve the process JURAN 1. Determine who the customers are 2. Determine the needs of the customers 3. Develop product features that respond to the customer’s need 4. Develop the process that are able to produce those product features 5. Transfer the resulting plans to the operating forces 1. Evalaute “actual Quality performance” 2. Compare actual performanceto quality goals 3. Act on the differences 1. Establish the infrastructure needed to secure anually quality improvement 2. Identify spesific needs for improvement PHILIP B. CROSBY : 4 absoluts of quality (zero defect concept ) 1. Quality is conformance to requirements customer’s real need 2. PREVENTION Should have a system of detecting potential problem areas and identifying methods for preventing the occurrence of these problems cost savings 3. the performance standard is zero defect 4. the measurement of quality is the price of non conformance cost savings , because non quality causes problems and problems cost money ISHIKAWA CAUSE AND EFFECT DIAGRAM Quality Assurance is to demonstrate that a service or product fulfills or meets a set of requirements or criteria. Actual processes and/or outcomes are compared to predefined criteria or pre-selected requirements. Quality Control refers to the systematic use of methods to ensure that a service or product conforms to a desired standard. Primary emphasis is placed on monitoring processes and/or outcomes. Quality Improvement refers to the betterment or enhancement of a product or service. When enhancements are ongoing or occur repeatedly over time, the process is known as continuous quality improvement.