DHCP
advertisement

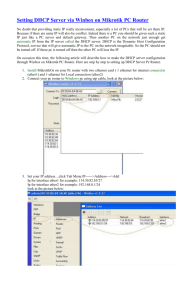
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Lab # 4 • DHCP is a client/server protocol that automatically provides an IP host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway. RFCs 2131 and 2132 define DHCP as an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard based on the Boot Protocol (BOOTP), with which it shares many implementation details. DHCP discovery “I NEED AN IP ADDRESS!” DHCP server offers “You can have 17.14.8.19 for 20 mins” “You can have 17.14.9.89 for 1 hr” : DHCP request “OK, let me have 17.14.8.19 for 20 mins” DHCP ACK “Your IP is now 17.14.8.19 for 20 mins” • Setup the first computer in every network as a DHCP server and have the other computers in the group point to it as DHCP clients. Thus computer 192.168.230.1 – which will be configured as DHCP server has static IP but all the clients get IP address from the Server. Configure DHCP client • Start->Control Panel->Network Connections. Right-click and select Open. Select anyone of the local area connections and click. Click Properties. Local Area connection properties window appears. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties. Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window appears. Select the radio button ‘obtain an IP address automatically’. Installing and Configuring DHCP Server • Start->Control Panel->Add/Remove Programs. Click on Add/Remove Windows Components. • Select Networking Services and check it. Then click Details button. Select DHCP and Simple TCP/IP Services. Click Ok. Click Next. Click Finish. • Start->Administrative Tools->DHCP. DHCP Manager appears. Click on the computer and right-click and select New Scope. New Scope Wizard appears Installing and Configuring DHCP Server Enter the name of scope and its description IP Range Click add exclusions Lease Duration Click Yes Add Default Gateway Click Next for DNS and WINS Servers Final Step Analysis Using Ethereal Network Analyzer Install Ethereal Software • Capture DHCP traffic We will use Ethereal software to capture DHCP traffic. In order to install this software, we need to install WinPCap software first. Then, we should install the Ethereal software. After installation, follow these steps. • 1. Run the Ethereal software. From the Capture Menu click Start. In the window that pops up choose the appropriate network interface and Click Ok. • 2. Generate DHCP traffic by using the commands ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew at the DHCP client. Stop the DHCP capture. Network Measurements • In this experiment, you are going to collect data about network parameters such as: • Bytes sent/second • Bytes received/second • Bytes Total/second • Current Bandwidth Real time performance chart • Creating a Real-Time Performance Monitor chart • Create a chart in Performance Monitor to display performance data real-time. • Note: For Windows 2003, you can find Network Monitor and Performance Monitor at: • Start ->Programs->Administrative Tools ->Network Monitor • Start-> Programs -> Administrative Tools -> Performance Network Monitor • • • • • Install the Network Monitor Click Start, click Control Panel. Double-click Add/Remove Programs. Click Add/Remove Windows Components. Click Management and Monitoring Tools, and then click Details. • Select the Network Monitor Tools check box, and then click OK. • Click Next. Configure the chart • Click the Start button, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Performance. • To see the Graph or Histogram or Report, you can click on the respective button available at the graphical part of the screen. • Select on Graph. To add entries to the chart, right-click on the graphical area and select Add Counters. • In the Performance Object box, select Network Interface. • Notice that Processor is the default object. In the Counter list, to know about an entry, select that entry and click on Explain. Configure the chart • Then select the Bytes Sent/second, Bytes Received/second, Bytes Total/sec, Current Bandwidth, Packets/second, Packets Sent/second, Packets sent unicast/second and Packets sent non-unicast/second. We can select them at the same time using Control key. • We have to select all the above entries for both the network cards. We can select both the network cards in the Instances list using Control key. • Click Close. • we need to generate some traffic. The implementation of this part depends on the available resources for network traffic generation in the lab. You can just use ping or view something from the server to generate some traffic. • Example of generating traffic: Use ping command and generate continuous [repetitive] traffic to the server [192.168.230.1] with the packet size of 65000. • ping –t –l 65000 192.168.230.1 Generate Alerts 1. On the left pane of the Performance Window, click on Performance Logs and Alerts. 2. Select Alert. To add an alert, right-click on it. 3. You can add an alert from a file or add a new one directly. 4. To add an alert directly, click New Alert Settings… 5. Enter the name for the alert in the Name text box. 6. Click on Add… to add counters. 7. Select the respective Performance Object, Counter and the instance. 8. In the Performance Object list, select Network Interface and 9. In the Counter box, select Bytes Total/sec along with one interface card at the Instances list.