Carbon Changing Costumes
advertisement
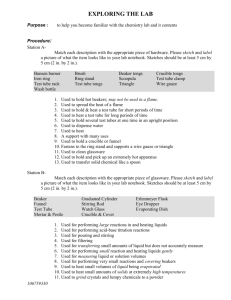
CH 11 Explore Activity: Carbon Changing Costumes p. 550 Keep these overarching questions in mind as you go through the activity…… 1. How do these chemical reactions relate to the real world? 2. How has the carbon changed? In the engage activity, you saw that carbon can take different forms. You also saw carbon taking part in different chemical reactions. In natural systems, carbon takes part in many, many reactions. During this Explore, you will investigate several of these reactions. Investigative Question: In nature, what CHEMICAL REACTIONS does carbon participate in? In nature, what FORMS does carbon take? Replicate fig 11.4 in your lab note book. Make it large (fill the page), neat and colorful. You may enhance it as you wish. (ex: add some critters!) Station 1 • Read Intro….. • Sketch bottles; describe them; indicate how they might be different. • Observe! Record your observations! • Make a graph showing CO2 solubility on the Y-axis and temperature on the X-axis. Station 1 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 8 on p. 552) 4. Use a number 1to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 2 • What happens to rainwater as it percolates through organic soil? (focus question-discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) • Complete steps 1-5 on p. 553 (*Use 200ml of H2O and 2 tsp of soil). Draw and describe “before” and “after”. • Clean up after yourselves…..dirty water, used filters, used paper towels and etc. Station 2 Q’s 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What does percolate mean? What does organic mean? What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 6 on p. 553) WHERE WOULD THIS STATION HAPPEN IN NATURE? Use a #2 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 3 • Carbonate rocks contain carbon . What happens to these rocks when rain (which is weak carbonic acid ) weathers them? (focus question-discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) 1. Obtain two test tubes. Place 3 inches of acetic acid (CH3COOH) in one test tube and 3 inches of water in another test tube. 2. Add ½ of an antacid table (Alka Selzter) to each tube and compare what happens in each. Record your observations in words and pictures. 3. The reaction you are observing is shown below……. Please copy this into your lab notebook. Name the reactants and products. CaCO3+(CH3COOH) Ca + CH3COO +H2O + CO2 4. What do you think the gas bubbles are? • In the real world, this reaction happens much, much slower and the resulting gas gradually dissolves rather than furiously bubbling off. • Imagine how the reaction would change if the CO2 dissolved into surrounding water rather than bubbling off into the atmosphere. Station 3 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 8 on p. 554) WHERE WOULD THIS STATION HAPPEN IN NATURE? 4. Use a #3 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 4 Limestone (CaCO3) is a rock that contains a lot of carbon. The earth’s metamorphic activity pushes these rocks deep inside the earth where it is very hot. What happens to the limestone as it is heated up? (focus question-discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) 1. Measure the mass of the test tube. (be careful….test tubes can roll!) 2. Use the plastic weigh boat to mass out between 1.5 and 2 grams of NaHCO3 (this is used in place of the CaCO3). Add mass of test tube and record this initial mass. 3. Put NaHCO3 in test tube and heat for about 3 minutes. (wear goggles and always keep open end of tube pointed away from people’s faces!) 4. Observe any changes you see. Record your observations in words and pictures. 5. After heating, cover your test tube with a small piece of foil to prevent any water from being absorbed from the atmosphere. 6. Let the test tube cool for 1 minute. After 1 minute you can immerse it in water to speed cooling. 7. Make sure the test tube is dry, remove foil and weigh it again. Record. Compare the before weight with the final weight. What accounts for the different in weight? Station 4 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. Dissolve the residue in the test tube in some water. Add 5 drops of universal indicator. Dissolve a similar amount of in a test tube. Add 5 drops of universal indicator. What do you notice? 4. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 7 on p. 556) WHERE WOULD THIS STATION HAPPEN IN NATURE? 5. Use a #4 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 5 What do you think the seafloor looks like at a depth of 1-2 kilometers? In this station you will simulate how carbon changes forms inside the ocean. How can carbon move from the shallow ocean to greater depths? (focus question-discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) 1. Place 100 mL of water into one beaker. Add a spoonful of baking soda (NaHCO3) and stir until the solution is clear. 2. In a different beaker add 100 mL of water. Add 1 large spoonful of calcium chloride (CaCl2) and stir until the solution is completely clear. 3. Add 8 drops of universal indicator to each beaker. Record your observations in words and pictures. 4. Pour the contents of the beakers together. Describe what you see. 1. What color? 2. What pH? (refer back to your color chart in the Engage activity) 5. What evidence do you have that a solid has formed? You may have to wait several minutes for the solution to settle. You may even have to come back to this station later. The solid is Calcium Carbonate. Look at your original two reactants from the separate beakers. Where did the calcium come from? Where did the carbonate come from? Station 5 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 9 on p. 557) WHERE WOULD THIS STATION HAPPEN IN NATURE? 4. Use a #5 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 6 • What do you remember about PHOTOSYNTHESIS??? (focus question- discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) • Carry out step 1 on pg. 558 by making a careful, detailed, labeled sketch of the plant. • Under the plant, neatly write out the balanced equation for photosynthesis. Station 6 Q’s 1. What form or forms does carbon take in the reactants and in the products? 2. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 4 on p. 558) 3. Where does photosynthesis happen in nature? List several places. 4. Use a #6 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur. Station 7 What would you see if you dug into this compost pile? Where does all the carbon go that is in this decaying vegetation? (focus question – discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) Carefully read Station 7 on p 559-560. 1. Illustrate, using words, pictures and chemical equations the 3 ways that microbes break down organic matter. (Hint….you should discuss the following: aerobic respiration, anerobic respiration, aerobes, anerobes, glucose, methane, carbon dioxide, ethanol, swamps) Station 7 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after these reactions? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. Why do people like Mrs. Nance encourage you to collect food scraps and yard waste? Why not just throw this “yucky” stuff away??? 4. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 5 on p. 560) 5. Use a #7 to show where on the diagram these chemical reactions might occur. Station 8 • What do you remember about CELLULAR RESPIRATION?? (focus question – discuss this with your lab mates before you begin) • Neatly write out the balanced equation for cellular respiration. • Follow steps 2-3 on page 560. One inch of water is enough. (make sure you blow gently into the test tube or you’ll end up with a BTB and water facial!!) • Rinse out the test tube and throw away the straw when you are finished. Clean up any mess you’ve made. Station 8 Q’s 1. What form or forms did carbon take before and after this reaction? 2. How did carbon change? Why did carbon change? 3. How do you know that CO2 was produced? 4. WHAT’S THE BIG IDEA????? (copy and answer question 6 on p. 561) 5. Use a #8 to show where on the diagram this chemical reaction might occur.