Asia Business Forum Jan 2013 Presentation
advertisement

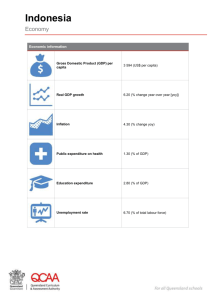
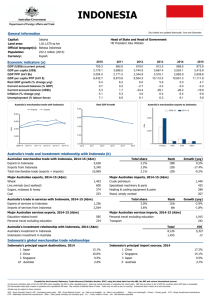
ASIA BUSINESS FORUM Asia Economic Outlook: What to Expect in 2013 January 23, 2013 Washington State Export Destinations 2011 Top 25 Markets and % Share of State Total Value (Millions) % Share $56,669 87.5 11,233 17.3 1 China 2 Canada 8,547 13.2 3 Japan 6,468 10.0 4 Korea, South 3,261 5.0 5 United Arab Emirates 2,753 4.3 6 Hong Kong 2,079 3.2 7 United Kingdom 2,017 3.1 8 Turkey 1,760 2.7 9 Australia 1,718 2.7 10 Taiwan 1,715 2.6 11 Indonesia 1,587 2.5 16. Singapore, 1.5% 19. Malaysia, 1.3% 22. Philippines, 1.2% 24. India, 1% Source: US Census Bureau Asian Markets as Share of Washington State Exports = 46 % Worth over $26 billion in 2011 UPDATE ON JAPAN’S ECONOMY IN 2012 AND PROSPECTS FOR 2013 Marie Anchordoguy, Professor and Chair, Japan Studies Program, University of Washington I. HOW HAS JAPAN’S ECONOMY PERFORMED IN 2012 AND WHAT ARE ITS PROSPECTS FOR 2013? WHAT ARE KEY FACTORS IMPACTING PERFORMANCE? A. GDP Growth --2012: 0.7%-1%, Forecast for 2013: 0.9%1.2% --Japan’s 2012 GDP is still 3% below the peak it reached in early 2008. B. KEY REASONS FOR SLOW GROWTH IN 2012 AND 2013 i) Heavy dependence on exports and Health of other Economies ii)High Yen iii)Aftermath of 3-11-11 Triple Disasters iv) Political Instability a. Former PM Noda pushed through controversial increase in consumption tax b. Lower House Election in mid-December 2012. Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) won and Democratic Party of Japan (DPJ) lost, but this was a vote against the DPJ not for the LDP. LDP President Shinzo Abe become Prime Minister again (also 2006-07) c. Instability of policies toward nuclear power v)Consumer Electronics makers confront serious problems vi) Japan-China Dispute over Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands a. Right-wing Mayor of Tokyo decides to buy the islands in 2012; Japanese government decides it would be best for them to buy them instead. Leads to anti-Japanese demonstrations and vandalism, and plummeting Japanese exports to China. II. WHAT ARE GROWTH AREAS IN 2013 AND WHAT IS NEW IN 2013? Growth Areas: --Auto industry, opportunities related to Japan’s strong M&A activities, employment and investment opportunities for foreigners. What’s New: --New leadership in Japan, China, and Korea provides more political stability and an opportunity for a new beginning in Japan-China and Japan-Korea Relations --Decision about joining TPP (Trans Pacific Partnership) free-trade agreement talks III. WHAT ARE THE RISK AREAS IN 2013 THAT WILL LIKELY AFFECT PERFORMANCE? --Japan-China Relations --Upper House Election in July 2013; if the LDP loses, there would be a split in the two houses of parliament, leading to further gridlock. --Health of the Global Economy IV CONCLUSION --Japan will continue to muddle through --Citizens are very unhappy. Leadership vacuum --Distrust of government has grown sharply since the triple disasters --The high cost of importing energy will continue to be a drag on the economy Still, many positive trends; Japan is not doing so poorly when placed in context of economic, political and social problems in the EU and US UPDATE ON CHINA’S ECONOMY IN 2012 AND PROSPECTS FOR 2013 JANUARY 23, 2013 Fraser Mendel, Partner Davis Wright Tremaine LLP CHINA – 2012 IN REVIEW Leadership Transition Slowing economic growth Local government debt situation Falling real estate prices Debt problems, slower growth, weak export demand Increased outbound investment Continued friction in the South China Sea CHINA – 2012 ECONOMIC GROWTH NEW POLITBURO STANDING COMMITTEE President Xi Jinping Premier Li Keqiang Zhang Dejiang Yu Zhengsheng Liu Yunshang Wang Qishan Zhang Gaoli CHINA – 2013 OUTLOOK Economic growth stable Exports remain depressed Real estate prices declining Debt problems slow growth Continued emphasis on innovation Increased outbound investment Continued friction in the South China Sea OVERALL SLOWING ECONOMIC GROWTH 8 Percent growth, y-o-y 2013-2018 7 2019-2025 6 Total Factor Productivity Capital Contribution 5 Labor Composition 4 Labor Quantity 3 2 1 0 -1 Optimistic Base Pessimistic Optimistic Base Pessimistic Sources: The Conference Board Global Economic Outlook 2013, https://www.conference-board.org/data/globaloutlook.cfm? CHINA – GROWTH AREAS IN 2013 Planning for Demographic changes Renewable energy Online retailing Infrastructure Construction / real estate Pollution mitigation and control Clean and green food products + investment in overseas agriculture Expanded acquisition of overseas resources CHINA – 2013 RISK FACTORS Diaoyutai / Senkaku Conflict Pollution Corruption & Anti-corruption efforts Rising costs Economic inequality Bankruptcy of some smaller cities Growth of unregulated lending sector ASIA BUSINESS FORUM January 23, 2013 Indonesia: 2012 – 2013 Economy & Business Climate Anita Sulaiman, Country Adviser – Singapore & Indonesia INDONESIA’S PERFORMANCE: 2012 IN REVIEW Source: Bank of Indonesia 2012 HIGHLIGHTS February September Largest contract in commercial & Boeing history: Lion Air order of 230 Boeing 737 airplanes worth $22.4 billion McKinsey releases “Unleashing Indonesia’s Potential Report”: Now 16th. 2030, could be world’s 7th largest economy, surpassing Germany & UK) January Indonesia Financial Services Authority (OJK) formed January April 23 S&P affirms sovereign credit rating at BB+ (Outlook: Positive) Garuda named “Best International Airline” Moody’s upgrades sovereign credit rating to investment grade: Baa3 from Ba1 (Outlook: Stable) Central Bank lowers BI rate to 5.75% (from 6%) February Foreign exchange reserves hits highest level (2012) of $114.93 billion Jakarta elects new Governor Joko (Jokowi) Widodo (snubs political establishment) September November 21 Fitch affirmed sovereign credit rating at BBB(Outlook: Stable) Indonesia tops Nielson Global Consumer Confidence Survey (Q3 2012) with score of 119, (alongside India). January 18 April November Indonesia, as next APEC Chair, announces 2013 logo & theme: Resilient AsiaPacific – Engine of Global Growth December GOOD BUT LOWER PERFORMANCE: WHY? Global economic uncertainty • • • • Crisis in Europe & recession in US Instability in Middle East & Africa Slower economic growth in emerging countries esp. China & India Trade imbalance with declining exports (& burgeoning imports) Weak infrastructure & high logistics costs • • • • • Overburdened airports: Jakarta’s CGK at beyond capacity past 6 years Poor condition of ports: Unable to keep up with economic growth Bad roadways, bad traffic; floods Poor connectivity between towns/cities/regions Policies & regulations deemed as hindrance to businesses Government initiatives Strong domestic consumption driven by emerging middle class Influx of investments • Master Plan MP3EI (2011- 2025): Economic development • Master Plan MP3KI (2011- 2025): Poverty reduction • Tax incentives • • • • Highest contributor to economy: ≅ 2/3 of GDP 240 million (World’s 4th most populous nation) 45 million consuming class (to to 135 million in 2030) Robust consumer confidence with surge in government & private sector projects • • • • Second biggest contributor: ≅ 30% of GDP Regaining of investment grade: Fitch in Dec. 2011 & Moody’s in Jan. 2012 AT Kearney FDICI: Ranked #9 in the world (from 19 in 2010) 2012 realization may top $31 billion (Rp. 300 trillion), a record OUTLOOK FOR 2013 POSITIVE Annual GDP growth target set at 6.8 % (BI forecast: 6.3% - 6.8%) Domestic consumer demand 65% of GDP = less vulnerable to Europe & US drag Fitch: Affirmed RI’s investment grade at BBB- (stable outlook); boost joining BRICS Investment realization targeted to increase to Rp. 390.3 trillion (FDI $29 billion) Govt set inflation rate assumption at 3.5% - 5.5% Government to hold BI rate steady at 5.75% (since March 2012) Household consumption (to 5.8 – 6.3%) & investment (to 10%) will continue to drive growth Per capita income rising & middle class growing (to expand to > ½ total population) Oil & gas investment to increase: $26.2 billion: 274 work plans & budgets approved Exploding gas demand = efforts to reduce exports + expand downstream capacity Sales of capital goods, including machine tools, will rise 8% to $27 billion RISKS & CONCERNS Endemic corruption/Judiciary a problem: 118 in list of 176 countries Rising inflation from domestic fuel subsidies & power tariff hike (Transparency International) Weak institutions & bureaucratic inefficiencies: 128 out of 185 globally (World Bank’s Doing Business) Political uncertainty: 2014 elections Infrastructure congested & inadequate to support growth; respond to natural disasters Lack of institutions with strong capital structure to finance planned projects Crisis in developed world: Threaten exports, foreign liquidity, investment growth Emerging trend of trade deficits fueling current account deficits & hurting the Rupiah Under-developed HR: Low-skilled workforce + Minimum pay increase not matched with increase in productivity REASONS TO BE OPTIMISTIC + OPPORTUNITIES Master plans to guide development & growth: Impetus for change Relative political & economic stability: Conducive to business Strong & growing domestic demand: Fuel growth, limit exposure to external shocks Poverty reduction means growing middle class Growing middle class means better qualified workforce & bigger market Positive investment outlook thanks to strong economic fundamentals Abundance of fertile land & natural resources Financial markets poised for volatility: Stock market to maintain good performance Financial stability: Investor confidence evident in influx of capital investment THANK YOU | TERIMA KASIH Anita Sulaiman anitasulaiman@aol.com PUBLIC DEBT BURDENS (% OF GDP) AT KEARNEY 2012 FDICI Son Michael Pham, Principal U.S – Asia Gateway VIET NAM ECONOMIC OUTLOOK For 2013 VIET NAM Son Michael Pham, Principal U.S – Asia Gateway smp@usasiagateway.com