General - Newcastle University Staff Publishing
advertisement

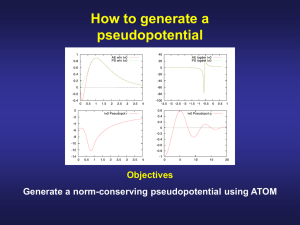
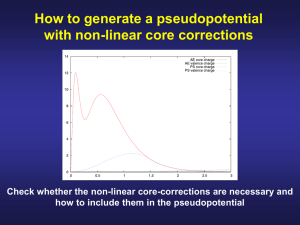
Introduction to the Theory of Pseudopotentials Patrick Briddon Materials Modelling Group EECE, University of Newcastle, UK. Contents Pseudopotential theory. – The concept – Transferability – Norm conservation – Non-locality – Separable form – Non-linear core corrections Pseudopotentials • A second main plank of modern calculations • Key idea - only valence electrons involved in chemical reactions • e.g. Si = [1s22s22p6 ]3s23p2 • Chemical bonding controlled by overlap of 3s23p2 electrons with neighbouring atoms. • Idea: avoid calculating the core states altogether. The problem with core states Core states are very hard to describe accurately. They: • vary rapidly. This makes – plane wave expansions impossible. – Gaussian expansions difficult • Expensive and hard to do. • oscillate - positions of nodes is important. Core states contd. Core states: • make the valence states oscillate. • require relativistic treatment. • make the energy very large. This makes calculations of small changes (e.g. binding energies) very hard. Empirical Pseudopotentials Main idea is to look for a form for the potential Vps(r) so that the solutions to: ps ˆ T V r E for a reference system agree with expt. E.g. get band structures of bulk Si, Ge. Then, use the potentials to look at SiGe or SiGe microstructures. Transferability • Problem: these pseudopotentials cannot be transferred from one system to another. • e.g. diamond pseudopotential no good for graphite, C60 or CH4. Transferability Why is this? • the valence charge density is very different in different chemical situations - only the core is frozen. • We should not try to transfer the potential from the valence shell. Ionic Pseudopotentials We descreen the pseudopotential: Split charge density into core and valence contributions: nr n r n r c v n r core charge density c n r valence charge density v Ionic Pseudopotentials Then construct the transferrable ionic pseudopotential: n r dr v V r V r Vxc n r r r v ps ion ps We have subtracted the potential from the valence density. The remaining ionic pseudopotential is more transferrable. Ab Initio pseudopotentials • This approach allows us to generate pseudopotentials from atomic calculations. • These should transfer to solid state or molecular environment. • ab initio approach possible. • Look at some schemes for this. • “Pseudopotentials that work from H to Pu” by Bachelet, Hamann and Schluter (1982) Norm Conservation • A key idea introduced in 1980s. • Peviously defined a cutoff radius rc: – if r > rc, Vps = Vtrue. • Now require ps = true if r > rc. • Typically match ps and first two (HSC) or four (TM) derivatives at rc Cutoff Radius • rc is a quality parameter NOT an adjustable parameter. • We do not “fit” it! • Small rc means ps = true for greater range of r more accurate. Cutoff Radius • BUT, small r will lead to rapidly varying ps (eventually it will have nodes). • Use biggest rc that leaves results unchanged. • Generall somewhere between outermost maximum and node. Schemes • Kerker (1980) – not widely used • Hamann, Schlüter, Chiang, 1982 – basis of much future work • Bachelet, Hamann, Schlüter, 1982 – fitted HSC procedure for all elements Schemes Troullier, Martins (1993) – An improvement on BHS – refinement to HSC procedure – widely used today • Vanderbilt (1990) – ultrasoft pseudopotentials – Important for plane waves – widely used today Schemes Troullier, Martins (1993) – An improvement on BHS – refinement to HSC procedure – widely used today • Vanderbilt (1990) – ultrasoft pseudopotentials – Important for plane waves – widely used today Schemes Hartwigsen, Goedecker, Hutter (1998) – Separable – Extended norm conservation – The AIMPRO standard choice BUT ... ALL LOOK COMPLETELY DIFFERENT! Accuracy • Look at atoms in different reference configuation. • E.g. C[2s22p2] and C[2s12p3]. • E = 8.23 eV (all electron) • E = 8.25 eV (pseudopotential) Silicon Pseudopotential Silicon Pseudopotential Some things to note: • Asymptotic behaviour correct, r>rc • Non-singular at origin (i.e. NOT 1/r) • Very different s, p, d forms Pseudo and All electron Wavefunctions (Si) Silicon Wavefunctions Some things to note: • Nodeless pseudo wavefunction, r>rc • Agree for r>rc. Cutoff is around 2. • Smooth – not rapidly varying Log derivative d ln R dr rc Non-locality • Norm conserving pseudopotentials are non-local (semi-local). • This means we canot write the action of potential thus: V V r r Non-locality Instead we have different potentials for different atomic states : Vˆ s Vs r s r Vˆ p V p r p r This is the action of an operator which my thus be written as Non-locality ps ˆ V Vl r l l l 0 or Vˆ V r, r r dr ps * ˆ V r, r Vl r, r Ylm Ylm lm with Vl r, r Vl r r r Kleinman Bylander Form Problem: Take matrix elements in the basis set i(r), i=1, N: ps ˆ r V r d r r V r , r r d r d r i j i j 4r F r F 2 where i lm j* lm lm F r i r Ylm , d d i lm r Vl r dr Kleinman-Bylander Form • Problem is: There are N2 integrals per atom is the basis set is not localised. • A disaster for plane waves. • Not the best for Gaussians • Recall there is no such things as “the pseudopotential”. • Can we chose a form that helps us out? Kleinman Bylander Form contd Kleinman and Bylander wrote Vl r, r Vl r Vl r So that this time where Vij F F i lm j* lm lm F i r Vl r Ylm , dr i lm N integrals per atom. Improvement crucial for plane wave calculations to do 100 atoms Kleinman Bylander Form contd The Kleinman and Bylander form Vl r, r Vl r Vl r Is called SEPARABLE or sometimes FULLY NON-LOCAL They: 1. Developed a standard pptl – e.g. BHS 2. Modified it to make it separable. The HGH pseudopotentials HGH pseudopotentials are also fully separable. They proposed a scheme to generate in this way directly (i.e. Not a two stage process). Thus they avoided issues with “ghost states” that were initially encountered when trying to modifuy a previously generated pptl. The HGH pseudopotentials HGH pseudopotentials are also fully separable. They proposed a scheme to generate in this way directly (i.e. Not a two stage process). Thus they avoided issues with “ghost states” that were initially encountered when trying to modifuy a previously generated pptl. Non-Linear Core Corrections An issue arises when constructing ionic pseudopotentials: v n r dr ps ps v Vion r V r Vxc n r r r We have subtracted the potential coming from valence charge density. Non-Linear Core Corrections contd OK for Hartree potential as: n r dr n r dr V n r r r r c v H However: V n Vxc n r Vxc n r xc clearly c v n n n n c v 13 c 13 v 13 Non-Linear Core Corrections contd This is true if valence and core densities do not overlap spatially. i.e. Core states vanish before valence states significant. Problem: this just does not always happen. NLCC contd Is a problem when it is difficult to decide what is a core electron and what is a valence electron. e.g. Cu: 1s22p22p63s23p64s23d10 The issue is the 3d electrons – a filled shell. Largely do not participate in bonding. Are they core ot not? NLCC contd What about e.g. Zn: 1s22p22p63s23p64s13d10 The same question. What happens if we look at ZnSe using “3d in the core”? What about ZnO? Effect of large core core a0 Val AlAs [1s22s22p6] 3s23p1 0% 2 6 10 2 4s 4p 1 -2% 2 6 10 2 5s 5p 1 -4% 2 6 10 2 GaAs 3s 3p 3d InAs 4s 4p 4d ZnSe 3s 3p 3d 4s -10% Non-Linear Core Corrections contd A solution is to use a NLCC Descreen with the potential from the total density, not just the valence density: n r dr tot V r V r Vxc n r r r v ps ion ps Non-Linear Core Corrections contd Fixes lattice constant completely for GaAs, InAs. Good for GaN, ZnSe. Band structure still be affected. CARE. NLCC will not work if the states change shape when moving from atom to solid. Other properties ma Summary • The concept of a pseudopotential • A norm conserving pseudopotential • A non-local pseudopotential • A separable pseudopotential. • A nonlinear core correction. Reading... • Kerker paper • BHS paper •Troullier Martin paper • HGH papers • Louie-Froyen-Cohen paper