No Slide Title
advertisement

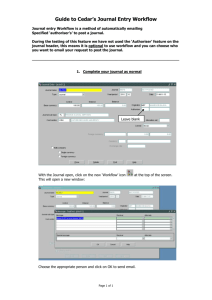
Planning and Scheduling for Dynamic Workflow Management Dr Nikolay Mehandjiev Department of Computation, UMIST, Manchester, U.K. E-mail: mehandjiev@acm.org WWW: www.co.umist.ac.uk/~ndm Aim: Promoting the effective application of AI P&S techniques to WM Roadmap: • similarities between P&S and WM • areas where P&S can provide substantial input to dynamic WM Some related projects Motivation Workflow Management – Growing need for • Business Process Modelling • Supply Chain Execution – Rapidly changing processes – Static tools incapable of dynamic optimisation AI Planning and Scheduling – Applied to a range of real work problems – Mostly linked with materials and production – Potential for Workflow Management A simple workflow process 1. Customer selects laptop 2. Customer sends specs to purchasing 3. Purchasing requests quote from supplier 4. Supplier sends quote to purchasing 5. Purchasing confirm quote with customer 6. Purchasing send purchase order 7. Supplier sends laptop to customer 8. Supplier sends invoice to purchasing 9. Purchasing send cheque to supplier Workflow Management Semi-automatic composition Effective monitoring and prediction Optimisation Re-planning Conflict identification and resolution Role for Planning and Scheduling Mapping similarities Highlighting differences Terminology Design-time work WM: humans assisted by simple tools P&S: mainly automatic by software Representations WM: domain-oriented and user-friendly but vague P&S: mathematically formal and semantically precise Languages WM: scripting languages for coordination of activities P&S: AI plan languages are higher level Requirements Short-term Integration of scheduling and resource allocation in WM tools Re-planning Generating workflow definitions from process models Process mining Medium-term WM support for skilled work User empowerment Visualising work Long-term Flexibility Evolvability and Adaptiveness Decentralised management Roadmap themes Human factors State-of-art WM: tailorable workflow systems P&S: mixed-initiative planning Research issues User empowerment versus centralised control Balance human and software effort at different stages Visualising the way planners work Recommended actions Trans-disciplinary workshops Prototype supporting user control Infrastructure State-of-art WM: WfMC reference architecture P&S: PDDL and ADL Research goals From objects through components to agents Developing planning and scheduling servers Recommended actions Draw up a reference architecture Interface standards Domain and business modelling State-of-art Process management: ARIS, iThink, IDEF, PIF, PSL, WPDL Knowledge engineering: CommonKADS, CoRE Ontologies: CYC, Enterprise, TOVE, DAML-OIL/OWL AI planning: ADL, PDDL, STRIPS/PDDL, GIPO Research goals How to synthesise BPM, P&S and ontology modelling languages into a language which is: •Useable by domain experts; •Has rigorous semantics and mathematicall formal; •Executable •Translateable into other formalisms •Suitable for planning Recommended actions Taxonomy of languages and tools Organise a hands-on workshop on modelling Planning and scheduling State-of-art Many planning techniques available, current trends to: • integrated planning and scheduling • mixed initiative planning • constraint-based approaches Some tools to support these, eg ILOG Scheduler, but expert-oriented Successful industrial applications but not in WM Research goals How to best combine human capabilities with P&S? Create interfaces so that planners are easily used by domain experts. Recommended actions Definition of graduated reference problems Enactment / execution State-of-art Conditional planning Reactive planning Research goals flexible working with overall plan use of plan repair or re-planning techniques for exception handling combination of plans for multiple actors Requirements Techniques for monitoring execution Techniques for exception handling Adaptation, optimisation & metrics State-of-art Mature optimisation techniques coming from AI and OR Using multiple criteria for planning and scheduling Research goals Appropriate metrics for WM – time and cost only? Languages for providing metrics to the system Combination of metrics Requirements User-definable metrics and optimisation parameters Integration with process design and enhancement tools Interaction with the user Main recommendations • To raise awareness of real challenges and constraints in workflow domain; • To make application and tool developers aware of what AI planning and scheduling research has to offer; • To address practical issues of integrating planning and scheduling technology into suites of application software, and of making the techniques usable by typical software engineers, analysts, etc. • To form a consensus on medium and long term research goals. • The RoadMap should be seen as a living document and be extended and updated regularly. Related work at UMIST 1. Tailorable workflow systems and EUD - ECHOES 2. Allocating tasks in distributed teams – SAMBA, BT Exact 3. Semi-automatic allocation of tasks to agents - RAMASD 4. Agent-based workflow support systems – Agentcities & IntLog 5. Supporting the automatic formation of Virtual Enterprises ECHOES workflow description organisational taxonomy Application Achievements • Users can change workflow during execution under an “intelligent guardian” • Highly responsive mode of interaction • Multi-aspect visual language that can evolve • Architecture to support all this SAMBA visualisation and monitoring agent control viewpoint 1 control viewpoint 2 business process layer agent workflow support software layer (a) (b) BT Short Term Fellowship (1998) Aim: Provide work coordination software that: • Allows workers to control their work • Allows managers to modify local business rules • Informates people about the work process • Supports team building and social interaction processes control viewpoint n RAMASD Funded by BT Exact as a PhD studentship (June 1999 – June 2002) Allocate behaviour to agents using • Roles • Role models • Role algebra Method • Use synthesis-based design process • Allocated by constraint satisfaction algorithm • Incorporated in the agent-building toolkit Zeuss Application •Currently for the design of agent systems •Can be used to allocate tasks to performers Agentcities.ORG network snapshot taken from http://www.agentcities.org/Network/ IntLog Co-optimise production and logistics services. Agents allocate work using extensions to Contract Net protocol. An Agentcities prototype related to EC-funded project MaBE (www.mabe-project.com) Summary Workflow Management TCU produced a Roadmap on the use of AI P&S techniques to Workflow Management. This presentation summarised findings of the Roadmap regarding: • Similarities and differences between the two areas; • Open research issues and actions in the area of P&S application to Workflow Management. • Requirements for applying P&S techniques to Workflow Management. Several projects were then described briefly as an example of activities relevant to the Roadmap. For further information regarding this presentation, please e-mail me on mehandjiev@acm.org