Unit N Review #2 KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement
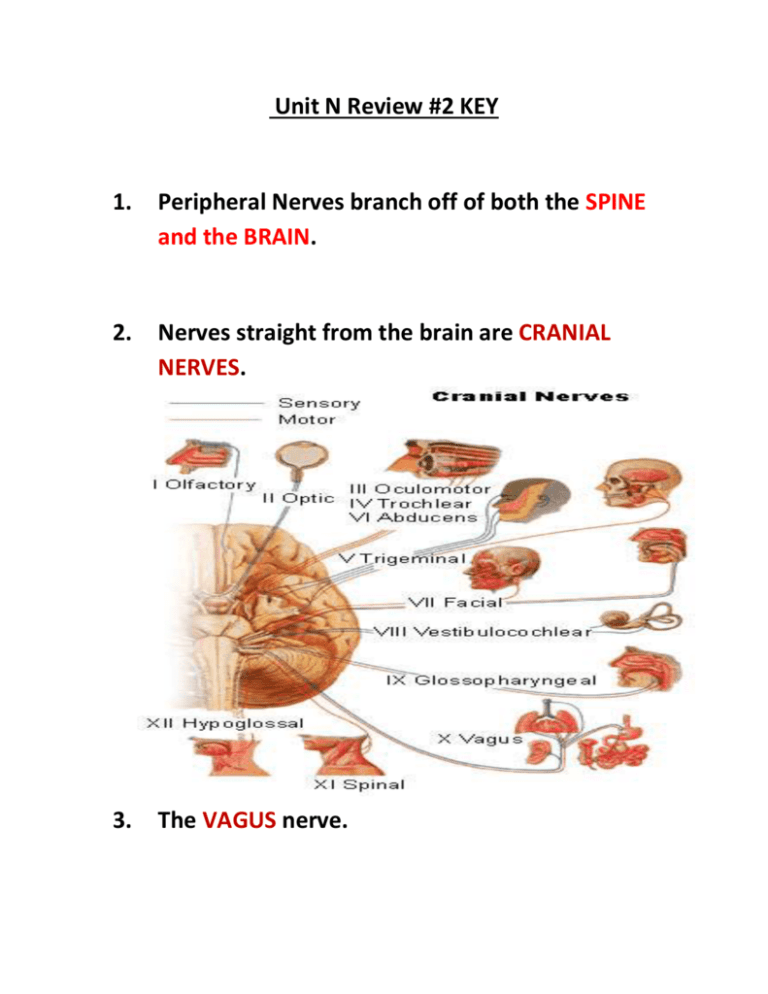
Unit N Review #2 KEY 1. Peripheral Nerves branch off of both the SPINE and the BRAIN. 2. Nerves straight from the brain are CRANIAL NERVES. 3. The VAGUS nerve. 4. The Vagus nerve serves the Heart (blood pressure, heart rate) also it stimulates the Digestive Organs. 5. Spinal Nerves are classified as mixed nerves as about half of their neurons are Sensory carrying information toward the spine, while the other half are motor neurons carrying information out from spine toward effectors. 6. Three main types of nerves are: 1.Motor Nerves 2. Sensory Nerves 3. Mixed Nerves. 7. Spinal nerves come into the spine and branch dorsally and ventrally, the dorsal root consists of SENSORY (afferent) neurons. 8. A dorsal root ganglion consists of a cluster of many, many, afferent neuron cell bodies. (See Diagram Below) 9. Motor neuron axons make up the ventral portion of a spinal nerve. 10. The Peripheral Nervous System consists of two subsystems they are the SOMATIC (mostly voluntary motor control and incoming sensory) and the AUTONOMIC (involuntary control of vital organs). 11. SOMATIC 12. SOMATIC 13. AUTONOMIC 14. The ANS is divided into two subdivisions/modes the PARASYMPATHETIC and the SYMPATHETIC. 15. NO ! LO N-2 1. Whatever works for you. Parasympathetic Parallel = Straight and Steady Parachute = Slow you down. Sympathetic – I sympathize with what you went through. 2. Both divisions use two motor neurons (a short one joined to a long one) to bridge the gap between the CNS and the appropriate effector. - Both divisions are involuntary (automatic). - Both divisions operate the same internal effectors. (heart, gut, blood vessels etc.) 3. For both divisions the Cell Body of Neuron #1 is in the CNS (brain or spinal cord). 4. A GANGLION 5. The long nerve fiber that runs from the CNS out to the ganglion is called the PREGANGLIONIC Fiber. 6. The nerve fiber that runs from the Ganglion and then lands on the effector is called the POSTGANGLIONIC Fiber. 7. In the Sympathetic system the Preganglionic is very SHORT and the Postganglionic is very LONG. 8. In the Parasympathetic system the Preganglionic is very LONG and the Postganglionic is very SHORT. 9. In the Sympathetic system the Ganglion is found FAR from the effector, more near the CNS. 10. In the Parasympathetic system the Ganglion is found very NEAR the effector. 11. The Sympathetic system is activated during times of emergency/excitation (“Fight or Flight” for survival) 12. Reactions that get you away from danger or help you fight for your survival. 13. When Sympathetic kicks in the following occurs: - Heart Rate goes up -Blood pressure goes up - Pupils dilate to allow more light in - Airways open up to allow more oxygen in - Liver starts to break down glycogen into glucose to bring up blood sugar for energy. - Blood directed to skeletal muscles. - (digestive function inhibited) 14. The Sympathetic system uses NOREPINEPHRINE (Noradrenalin). 15. The nerves that run the Parasympathetic mode stem from the CRANIAL and SACRAL regions of the CNS 16. The nerves the run the Sympathetic mode stem from the THORACIC and LUMBAR regions of the CNS. 17. The function of the Parasympathetic system is for NORMAL ACTIVITY of those effectors. 18. The Parasympathetic system will: - bring the Heart back to normal heart rate. - cause pupils to return to normal dilation. - cause airways of lungs to return to normal diameter. - trigger liver to start converting extra blood sugar into glycogen, releasing bile. - increase activity and blood flow to gut for digestion 19. The Parasympathetic system uses ACETYLCHOLINE neurotransmitter. Para S C A N N A R C O E C A E R A R N T M R A I Y A L A L L L C Holine Nor Sypa F E E L T A P M U H R I E M O N R B R E G A A P E R C H N I R C C I N E Y Practice Quiz: 1. A – Medulla Oblongata has many vital réflex arcs 2. C – To allow for better vision for survival 3. A 4. D – Need to bring things back to normal level. 5. C – Hypothalamus = Homeostasis. 6. D 7. A – Thalamus is the Gatekeeper. 8. C 9. C – Found in dorsal root ganglion. 10. D 11. D 12. D – As constriction of iris causes pupils to become smaller. 13. B 14. D – Thalamus (Gatekeeper) 15. B – Hypothalamus 16. A 17. D – Cerebellum 18. C – Sensory neurons have very long dendrites. 19. D 20. C – Somatic is incoming sensory and outgoing voluntary motor. 21. B 22. A – When the gut is being stimulated, the parasympathetic system is at work. This system uses Acetylcholine neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine will work to pace the heart at a slower more relaxed pace than if it were being stimulated by Norepinephrine. Practice Quiz Question: 1. A) B) C) D) What is the function of the PARASYMPATHETIC System? Cause the pupils to dilate Increase blood flow to the digestive system Open up airways and increase breathing rate. To stimulate a “Fight or Flight” response. 2. A) B) C) D) When norepinephrine hit an effector, it is released from... The axon bulbs of a long post-ganglionic fiber. The axon bulbs of a short post-ganglionic fiber. The axon bulbs of a long pre-ganglionic fiber. The axon bulbs of a short preganglionic fiber.