Peripheral Nervous System
advertisement

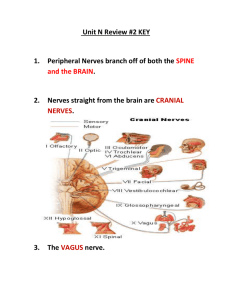
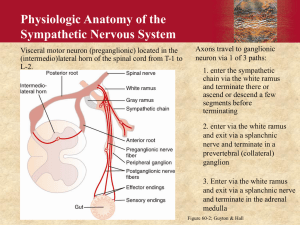
Peripheral Nervous System What do you see? CNS AND PNS Characteristics of the P.N.S. Nerves that branch out from brain, spinal column Not covered w/ meninges No CSF Divided into somatic and autonomic branches 2 Divisions: Somatic Nervous System CRANIAL & SPINAL nerves Afferent Sensory nerves Efferent, VOLUNTARY Motor nerves Autonomic Nervous System Parasympathetic & Sympathetic Systems INVOLUNTARY motor nerves Maintains homeostasis Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System: Cranial & Spinal Nerves Sensory Nerves Motor Nerves (send impulses to the brain/spinal cord) (Send impulses away from brain/spinal cord) Autonomic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System (Rest & Digest) Sympathetic Nervous System (Fight or Flight) PNS: Cranial & Spinal Nerves You’ve got a lot of nerve! (Cranial Nerves, that is!) Twelve total Arise from brain, passing through various foramina Specialized tasks – some sensory, motor, or both Some with multiple branches Identified by Roman numeral and anatomical name Mnemonic time! “Oh, Oh, Oh, To Touch And Feel Very Green Vegetables… Aah, Heaven” …there are more out there… They help you remember… Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharangeal, Vagus, Accessory, Hypoglossal Functions! Sammy Sosa Made Money, But My Brother Says Barry Bonds Made More S = sensory M = motor B = both Spinal nerves have their ups and downs… Sensory and motor PNS: Autonomic Nervous System Can you explain each of these? Autonomic Nervous System Regulates internal environment Controls glands, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle Homeostasis! Integrated with endocrine system Digestion, sexual functions, stress responses No conscious thought… A nervous system divided… Parasympathetic Cranial nerves, sacral spinal nerves Promotes relaxation, digestion “Post-stress”, P.S. Sympathetic Thoracic, lumbar spinal nerves Prepares body to react to stress “Fight or Flight” “S for stress” It’s all about connections… Somatic nerves: Full length of nerve connects spinal cord to body component Cell body in gray matter… terminus contacts effector Autonomic nerves: Two neurons working together Preganglionic originates in brain/spinal cord Myelinated Synapses with postganglionic neuron (non-myelinated) Form follows function… In parasympathetic nervous system… Preganglionic neurons long, terminate close to effector (short postganglionic neuron) Allows specific, targeted control In sympathetic nervous system… Preganglionic neurons short, terminate close to spinal cord (sympathetic ganglion chain) Postganglionic neurons long, travel from ganglion to effector Allows widespread activation of body systems Double agents? Effectors receptive to both systems… how? Preganglionic nerves of Symp, Parasymp NS secrete acetylcholine… Postganglionic nerves secrete different NT’s Parasympathetic NS acetylcholine Sympathetic NS norepinephrine Cause antagonistic effects in effector Antagonistic effects… Effector Sympathetic Action Parasympathetic Action Iris Opens pupil Closes pupil Salivary glands Reduces saliva production Increases saliva production Oral/nasal mucosa Reduces mucus production Increases mucus production Heart Increases activity Decreases activity Lung Relaxes respiratory muscles Constricts respiratory tree muscles Stomach Reduces digestive action Increases digestive action Small intestine Reduces digestive action Increases digestive action Large intestine Reduces digestive action Increases digestive action Kidney Decreases urine prod. Increases urine prod. Bladder Relaxes bladder Contracts bladder