Af Am Aw BW, BS,
advertisement
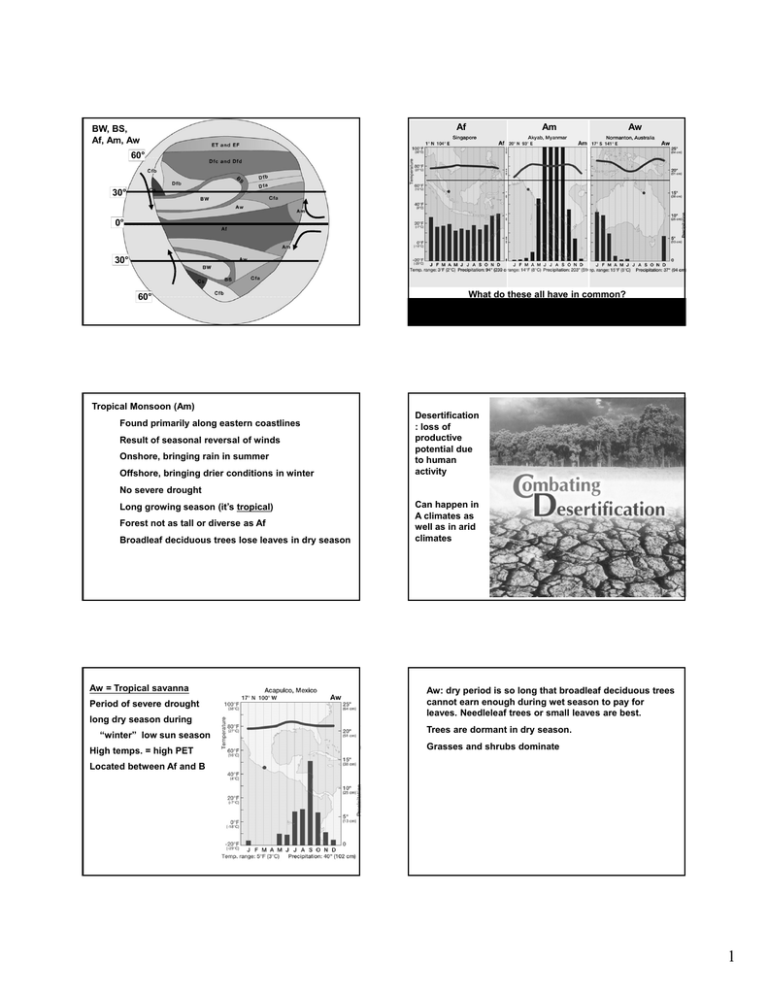
BW, BS, Af, Am, Aw Af Am Aw 60° 30° 0° 30° 60° What do these all have in common? Small group question: What leaf shape/shedding habit do you expect to find in each of these and why? Tropical Monsoon (Am) Found primarily along eastern coastlines Result of seasonal reversal of winds Onshore, bringing rain in summer Offshore, bringing drier conditions in winter Desertification : loss of productive potential due to human activity No severe drought Long growing season (it’s tropical) Forest not as tall or diverse as Af Broadleaf deciduous trees lose leaves in dry season Aw = Tropical savanna Period of severe drought long dry season during “winter” low sun season High temps. = high PET Can happen in A climates as well as in arid climates Aw: dry period is so long that broadleaf deciduous trees cannot earn enough during wet season to pay for leaves. Needleleaf trees or small leaves are best. Trees are dormant in dry season. Grasses and shrubs dominate Located between Af and B 1 Baobab or Upside-Down Tree grows in Africa and Australia. The legend says that after it was planted by God it kept moving, so God replanted it upside down Aw Biomes: Plant formations associated with major climate types. Where is Aw located ? What causes it to be predictably wet and dry? Pressure belts follow direct vertical rays of sun. In July, when sun is north of Equator, ITCZ affects Aw rain in summer. In January, when sun is south of Equator, Subtropical High affects Aw dry in winter. EF ET Df Cs B Aw Af Aw B Cs Df Where is Aw located ? What causes it to be predictably wet and dry? Pressure belts follow direct vertical rays of sun. In July, when sun is north of Equator, STH affects Aw dry in S. Hemis. winter. In January, when sun is south of Equator, ITCZ affects Aw rain in S. Hemis. summer. EF ET Df Cs B Aw Af Aw B Cs Df EF Tropical savanna Desert Temperate grassland Temperate forest Mediterranean scrub Boreal forest Tundra Ice ET Tropical rainforest EF ET Df Cs B Aw Af Aw B Cs Df ET ET EF EF 2 Biome: Biological community associated with major climate region. Changes in vegetation along precipitation gradient in “A” E A D Af Am Aw B C Decreasing precipitation B A Decreasing precipitation Mangrove: tropical, low energy coastal, woody plants, tolerate saltwater Mangrove Global mangrove distribution Environmental issues associated with A climates Mangrove destruction for aquaculture/wood chips Rainforest clearing for agriculture / ranching Honduras Shrimp ponds, Indonesia 3 Climate Parameters: “A” and “E” ET: “Tundra” Northern Alaska, Canada, Russia, Arctic Ocean shores EF: “Frost” Greenland and Antarctica, ice caps Tropical: never below 64° average Notice difference in temperature scales Never freezes Too cold Polar: for trees never above 50° average Tundra in orange Frost in white Polar Climates: too cold for trees! ET: Tundra Climate at least one month above freezing (but below 50ºF) permafrost – frozen ground around Arctic Ocean – coastal location moderates temperature low vegetation – shrubs and grasses fauna migrate in for summer some can freeze What happens when water changes state from liquid to solid? EF: Frost Climate never thaws out water always locked up as ice Antarctica and Greenland ice caps World’s coldest temperatures −89.2 °C (−128.6 °F) - Antarctica too cold for any vegetation penguins, polar bears, etc. Tundra: Hrafntinnusker, Iceland 4 Biome: Biological community associated with major climate region. Frost climate: Antarctica E D C B A Decreasing precipitation C and D: the inbetween climates. EF E A C How are C and D alike? D ET E Decreasing precipitation Characteristics of both C and D climates E, C & D Great variability 60° Week to week…frontal passage Seasonal…air mass dominance 30° Zone of air mass contrasts Lack constant heat of tropics or constant cold of polar climates 0° 30° 60° 5 Worldwide Distribution of Climates “C” and “D” “C” Mesothermal (Mild mid-latitude) climates: summer dominated but can freeze Cfa: Subtropical = Mobile, almost (but not) tropical moist all year (small “f”) warmest of C climates = “a” dominated by mT air mass warm with high humidity, long summer tropical storms in summer SE U.S., SE China dominated by temperate deciduous forest southern pines southern deepwater swamps drier part is tall-grass prairie In Cfa, enough water for vines In Cfa, enough light gets to forest floor for growth Pines common on sandy soils of coastal plain 6 Cfa wetlands: Distribution of cypress in SE U.S. Typical cypress trees in southern deepwater swamps High stress, needleleaf deciduous, knees Baldcypress versus Spruce pine In coastal saltwater “C” environments, trees cannot survive dual strees of salt and freezes. Marsh “grasses” and “reeds” dominate Needleleaf deciduous versus needleleaf evergreen Marine West Coast: Temperate rain forest Cfb: Marine West Coast “f” = moist all year “b” = cooler than Cfa (shorter growing season) dominated by mP air masses and relatively warm ocean currents rainy, drizzly, highest annual % cloud cover Pacific northwest, western Europe temperate marine conifer forest (temp. rain forest) large needleleaf evergreens large sized spruce & fir, redwoods (N. Amer.) 7 Cfa “subtropical”, mT airmass, eastern side of continent Cfb “Marine West Coast”, mP airmass, western side of continent Big needleleaf evergreens Broadleaf deciduous Pacific Coast Redwoods Csa: Mediterranean “s” = summer dry drought during growing season fire common scrub, stunted woodlands, grass, bulbs most near water bodies that moderate temperatures around Mediterranean, southern California influenced by subtropical high and polar front Where is Cs located ? What causes it to be predictably wet and dry? Pressure belts follow direct vertical rays of sun. In July, when sun is north of Equator, Subtropical High affects Cs dry in summer. In January, when sun is south of Equator, Polar Front affects Cs wet in winter. EF ET Df Cs B Aw Af Aw B Cs Df ET EF Where is Cs located ? What causes it to be predictably wet and dry? Pressure belts follow direct vertical rays of sun. In July (winter in S. Hemis.), when sun is north of Equator, Polar Front affects Cs wet in winter. In January (summer in S. Hemis), when sun is south of Equator, Subtropical High affects Cs dry in summer. EF ET Df Cs B “Mediterranean” Cs s= summer dry Aw Af Aw B Cs Df ET EF 8 Chaparral, Mediterranean scrub-shrub (leathery leaves, coppice sprouting common) Fires in San Bernadino, California after dry summer, landslides occur during winter rains Grasslands and large herbivores North American Grasslands Drier parts of “C” and “D” climates, transitional to “B” climates. Ecotone Biome: Biological community associated with major climate region. E Cfb D C Cfb C Cfa B A drier B Decreasing precipitation Decreasing precipitation 9