WVSSS Integration in Middle and High School
advertisement

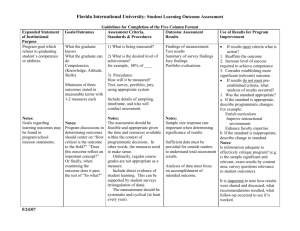
WV Student Success Standards Math Integration Dr. Barb Brady School Counseling Coordinator & Office of Secondary Programs Staff College and Career and Citizenship Ready means that students exit high school qualified to enroll in highquality postsecondary opportunities in college and career, including the U.S. Military, without need for remediation and equipped with the knowledge, skills and dispositions to make that transition successfully. This means that all students must graduate having mastered rigorous content knowledge and demonstrated their ability to apply that knowledge through higher-order skills including but not limited to critical thinking and complex problem solving, working collaboratively, communicating effectively, and learning how to learn. Students must also be prepared to navigate the pathways and systems that will allow them to gain access to positive postsecondary opportunities. School Success – College and Career Ready Core Skills Beyond academics Key skills and dispositions supported by research as strongly predictive of academic and lifelong success. (Pk-12 school success, college retention, graduation, etc.) Initiative Intellectual Curiosity Social & Personal Responsibility Self–Control Adaptability Study Skills Problem Solving Collaboration Time and Goal Management Critical Thinking Communication Leadership Self–Awareness Self–Control Applied Knowledge Integrity Self-Efficacy Social & Personal Responsibility Knowledge, Skills, and Dispositions: The Innovation Lab Network State Framework for College, Career, and Citizenship Readiness, and Implications for State Policy Beyond academics School Success – College and Career Ready Knowledge, Skills, and Dispositions: The Innovation Lab Network State Framework for College, Career, and Citizenship Readiness, and Implications for State Policy Chief Council of State School Officers – Feb 2013 School Success: College and Career Ready Knowledge, Skills, and Dispositions: The Innovation Lab Network State Framework for College, Career, and Citizenship Readiness, and Implications for State Policy Chief Council of State School Officers – Feb 2013 Global Competence Global competence is the capacity and disposition to understand and act on issues of global significance. Educating for Global Competence: Preparing Our Youth to Engage the World Council of Chief State School Officers’ EdSteps Initiative & Asia Society Partnership for Global Learning (2011) Global Competence • Recognize perspectives and communicating with diverse audiences • Understand the work individuals in society carry out, civic participation, self-expression, social life, and health unfold in a global scenario. • Appreciate cultural diversity and the importance of intercultural understanding and acceptance of differences of opinion • Investigate the world beyond their immediate environment, framing significant problems and conducting well-crafted and age-appropriate research. • Take action to improve conditions, viewing themselves as players in the world and participating reflectively. Educating for Global Competence: Preparing Our Youth to Engage the World CCSSO Delivery Systems 5.1.b. Integrated Delivery of WV Student Success Standards – The WVSSS (see incorporated documents) describe the attitudes, knowledge, skills and behaviors all students shall develop in relation to academic and learning development; career and life planning; personal and social development; and global citizenship. The WVSSS are critical to the holistic development of all students and require integration into all aspects of each student’s educational experience utilizing a variety of delivery modalities. The WVSSS are the foundational standards for each CSCP. The integrated delivery of these standards is coordinated by the school leadership team, the school counselor and teachers. CSCP Four Student Standards areas: – ACADEMIC and LEARNING DEVELOPMENT – CAREER DEVELOPMENT and LIFE PLANNING – PERSONAL and SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT – GLOBAL CITIZENSHIP Programmatic Level Competencies (Elementary [3 levels], Middle and High School) – Competencies grouped by overarching Learner Outcomes How the Student Success Standards were Developed • Reviewed the current standards in Policy 2315 and the revised version from the Model Task Force. • Reviewed other state and national standards and documents including: • ASCA National Standards (same as 2001 Policy 2315) • Utah Office of Education Comprehensive Counseling and Guidance Program (global citizenship) • Connecticut State Board of Education Comprehensive School Counseling Program (programmatic levels) • Council of Chief State School Officers (Global Competence Matrix) • National Association of School Psychologists (School Mental Health) • National Association for the Education of Young Children (developmentally appropriate practices) • National Endowment for Financial Education • College Board: National Office for School Counselor Advocacy • National High School Center - College and Career Readiness Mapping the Landscape West Virginia Student Success Standards • REPLACE school counseling program standards • Identify programmatic level competencies • Everyone owns the responsibility to ensure student success and college and career readiness West Virginia Student Success Standards • Course Integration – Cross walk tools – NxtGen Standards • Standards-based advisory systems (6-12) • Course Integration • coordinated by the school leadership team, the school counselor and teachers WVSSS Integration • School leadership team determines priorities and delivery schedule (who, what, when, how) – Student data (Middle and high school needs assessments, discipline referrals, bullying incidences, dropout rate, culture survey, etc.) – Community data (crime, violence, poverty rate, disasters – Systemically embedded in early learning framework – Programmatic level indicators designed to be purposefully within each programmatic level Student Success Standards (continued) Composite Cross-Walk Cross-walk Integration Guide SAMPLE – English/Language Arts West Virginia Student Success Standards (WVSSS) for Adolescent Level Programming (Grades 9-12) Competency 3.2 - Goal Setting and Attainment: ALP.SS.3.2.1 • analyze the relationship between behaviors, choices and consequences and apply a decision making model to achieve desired goals. • HE.HS.5.01: apply a decision-making process for various life situations Some mathematical content lends itself will to SSS Learning Outcomes For example: Learning Outcome: Practice Financial Responsibility Middle School Objectives Related to “Practice Financial Responsibility” • M.7.RP2 represent proportional relationships by equations. For example, if total cost t is proportional to the number n of items purchased at a constant price p, the relationship between the total cost and the number of items can be expressed as t = pn. • M.8.EE.5 graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare the cost of a cell phone plan represented by a graph to the cost of another represented by an equation. WV School Counseling Model and Implementation Tools GROUP DIALOGUE • Give examples of how the WVSSS are being integrated in your schools. • Discuss your role in coordinating integrated delivery of the standards • Describe your leadership team and the process for ensuring integrated delivery of the WVSSS within your programmatic level Questions Dr. Barb Brady barbbrady@k12.wv.us S