Chapters_5_old
advertisement

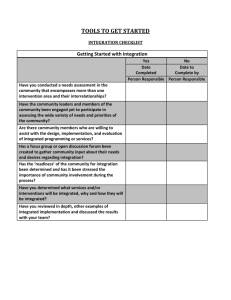
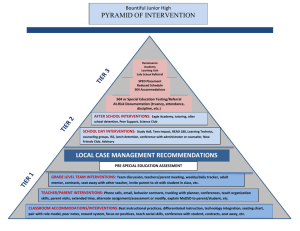
Chapter V: Implementation Stage “The Action Stage” Various Models • Mental Health – Possible interventions are based on whether the problem is due to the client or consultee. • Behavioral – Which types of reinforcement are most effective with a given client. • Organizational – Determine at what level of the organization to intervene and then select an intervention appropriate to that level. Stage III: Implementation • Phase One: Choosing an Intervention • Phase Two: Formulating a Plan • Phase Three: Implementing the Plan • Phase Four: Evaluating the Plan Stages Entry Diagnosis Implementation Choosing an Intervention Formulating a Plan Implementing the Plan Evaluating the Plan Disengagement Stage 3: Implementation Choosing an Intervention • “What are we going to do? Formulating a Plan • How are we going to do it? Implementing the Plan • Actively try to solve the problem. Evaluating the Plan • How did we do? The Implementation Phase is Critical! An Error Here = Wrong Solution but Right Problem Right Plan but Wrong Intervention Phase One: Choosing an Intervention • The client (system) is ready for some form of direct assistance from the consultee or indirect service from the consultant. • Select one or two interventions that have a high probability of being successful – Evidence-based? –Social Factors? – Costs/Benefits? –Fit? The Stump Approaching a problem with your mind already made up is like plowing a field full of stumps. Decision Consultation: To what degree has the consultee … • developed a wide range of alternative interventions? • considered the objectives & related values of the possible interventions? • weighed the potential negative consequences risks & potential payoffs of each intervention? • searched for new information relative to each interventions? • processed the consultant’s comments about potential positive and negative factors related to the interventions? • made a final determination of the interventions’ potential positive and negative consequences as well as the driving & inhibiting forces that affect their implementation? • does the consultee have the capacity to successfully execute the chosen intervention? • Which interventions have been set aside for use in contingency Imagine that!! • Consultees do not always follow through on the implementation of the intervention they are supposed to implement. • Relates to – perception of the “Fit” – Difficulty level – Quality of the relationship – Consultees values – Routines in the setting To avoid the “D’Oh! (failure to follow through) consider the following together • Do we believe that the intervention will really work? • Can the consultee implement with high levels of treatment integrity? • Does the consultee see it as a part of their duties to carry out the intervention? • Is the intervention in line with the consultee’s perception of what needs to be done? • Does the intervention fit relatively easily with the consultee’s routine? Obstacles • A large amount of data to process in section • Outcomes are difficult to predict – Keep a list of alternatives • Support needed (e.g. $, staff, time, etc) Guidlines • Try to use positive interventions 1st • Avoid the complex • Fit skill learning into daily routine • Promote the less time-costly Types of Interventions “When your only tool is a hammer, everything looks like a nail.” • Individual Interventions – Academic – Behavioral • Consultee-Centered Case Consultation (Ch 9) • Dyadic & Triadic Interventions – 3rd Party Peacemaking – conflict resolution Types of Group Interventions • Interventions for Groups & Teams – Team Building – Nominal Group Technique – Quality Circles – Work Teams Types of Group Interventions • Interventions for use between groups – Intergroup Team Building – Organizational Mirroring • Interventions for the entire organization – Total Quality Management (TQM or TQI) – Survey Feedback/Action Research – Parallel Learning Structures – Strategic Planning Phase Two: Formulating the Plan • Plan- a detailed step-by-step method, formulated before hand, for doing something. • Considerations– What (objective) – Where (locale of implementation) – When (time frame) – How (methods, procedures, sequence) – Who (who is responsible for what) Egan’s pitfalls • • • • • • • Trying to accomplish too much Formulating too large a plan Overanalyzig the plan Under-analyzing Failing to consider system-wide impact Poorly defined desired outcomes Failure to consider human-side factors Phase Three: Implementing the Plan • Help consultee be flexible • Reassure and prepare consultee –stuff happens • Offer technical assistance during this time – be available & monitor in brief bites • Exercise caution toward dependency Treatment Integrity • The degree to which the intervention is implemented as intended. – Why? Objective and subjective costs – Assessment methods • Functional Outcome Analysis (FOA) • Interviews, observations, training, scripted plans Treatment Integrity • Treatment Integrity is enhanced by – High Probability Interventions – Promotion of Correct Implementation – Social Validity – Treatment Acceptability – Social Importance Phase Four: Evaluating the Plan • Evaluation- the collection of data/information about the implementation to determine its effectiveness in meeting the specified goal – implementation evaluation – outcome evaluation Techniques used in outcome evaluation • Individualized goal attainment measures • Standardized outcome assessment devices • Consumer satisfaction survey Multicultural Implications: Implementation Stage • Cultural differences can impact the perception of the type of intervention selected and these differences should be taken into account when selecting and implementing an intervention • The question of responsibility during implementation may be based on cultural differences • During evaluation it is important to have multicultural input Application for Multicultural Implications during Implementation • Some cultural groups choose to focus on using groups rather than focusing on time factors • Some cultural groups may see the efficiency of the plan as most beneficial during evaluation; whereas, other groups may evaluate the social impact of the plan