LEARNING PRINCIPLES
advertisement

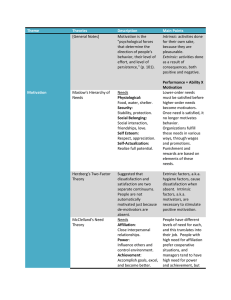
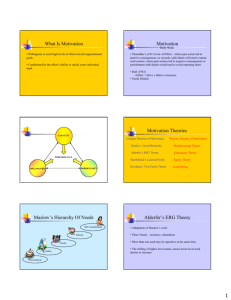
MOTIVATION MOTIVATION DEFINED Willingness to exert high levels of effort to reach organizational goals. BASIC ASSUMPTIONS Everyone is motivated Key? Two types of motivation Intrinsic Extrinsic TYPES OF MOTIVATION Extrinsic Motivation: "What gets rewarded gets done" Based on extrinsic/tangible rewards Intrinsic Motivation: "What is rewarding gets done" Based on intrinsic/intangible rewards Motivation Theories Equity Reinforcement Expectancy Theory TODAY’S TOPIC Motivation EQUITY THEORY People compare their outcome/input ratio to that of others Conclusions Ratios are equal (equity exists) Ratios are unequal (inequity exists) RESPONSES TO EQUITY/INEQUITY Equity: Maintenance Inequity: Change Inputs Change Outcomes Quit Forms of Justice REINFORCEMENT THEORY Behavior is a function of consequences Behavior that is rewarded persists To increase behavior Positive reinforcement negative reinforcement REINFORCEMENT THEORY To reduce behavior Extinction Punishment Immediacy is crucial Implications? REWARDING B WE HOPE FOR: Long-term growth Setting challenging goals Total Quality Candor BUT WE REWARD: Teamwork EXPECTANCY THEORY People are motivated to do that which they believe is possible and valuable Expectancy: Belief that you can perform Instrumentality: Belief that performance will lead to an outcome Valence: Value of the outcome EXPECTANCY THEORY According to expectancy theory, what must managers do to motivate their employees? Effective Rewards & Incentive Systems: HERZBERG Movement vs. Motivation KITA What’s wrong with KITA? With movement? TYPES OF MOTIVATION Extrinsic Motivation: "What gets rewarded gets done" Based on extrinsic/tangible rewards Intrinsic Motivation: "What is rewarding gets done" Based on intrinsic/intangible rewards Job design Job enrichment (Herzberg) Hygienes Dissatisfied (salary, relationships, setting...) Motivators (responsibility, achievement, recognition…) Neutral Motivated Job Characteristics Model Core Job Dimensions Skill Variety Task Identity Task Significance Critical Psychological States Experienced Meaningfulness of Work Autonomy Experienced Responsibility for Outcomes of Work Feedback Knowledge of Actual Results of Work Activities Personal & Work Outcomes High Internal Work Motivation High-quality Work Performance High Satisfaction with Work Low Absenteeism & Turnover IMPLEMENTING CONCEPTS CORE JOB DIMENSIONS Combining Tasks Skill Variety Forming Natural Work Units Task Identity CRITICAL PSYCHOLOGICAL STATES Experienced Meaningfulness PERSONAL WORK OUTCOMES High Internal Work Motivation Task Significance Establishing Client Relationships Autonomy Experienced Responsibility for Outcomes of Work High Satisfaction with the Work Vertical Loading Opening Feedback Channels High Quality Work Performance Feedback Knowledge of the Actual Results of Work activities - STRENGTH OF EMPLOYEE’S GROWTH NEEDS - KNOWLEDGE & SKILLS - CONTEXT SATISFACTION Low Absenteeism and turnover Intrinsic Motivation: From Theory to Application Provide Intrinsic Rewards Survey of 1,500 employees found that recognition is the most powerful workplace motivator Build intrinsic motivators into employee’s jobs Employee Participation and Empowerment