Price of Ice-Cream Cone (Rp)
advertisement

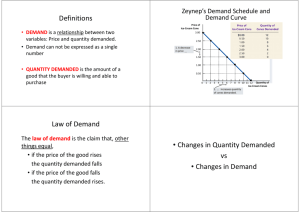
Subject : Economics Class :X Time Aloccation : 2 x 45 Minute Today's Lesson Standar Kompetensi dan Kompetensi Dasar STANDAR KOMPETENSI : 3. Memahami konsep ekonomi dalam kaitannya dengan permintaan, penawaran, harga keseimbangan, dan pasar Kompetensi Dasar 3.2. Menjelaskan hukum permintaan dan hukum penawaran serta asumsi yang mendasarinya. 1. Menginterpretasikan hukum permintaan dan penawaran. 2. Menginterpretasikan asumsi yang mendasari hukum permintaan dan penawaran. 3. Menggambar kurva permintaan dan penawaran yang bergerak dan bergeser. 4. Membuat fungsi permintaan dan fungsi penawaran berdasarkan hukum permintaan dan penawaran. The Law of Demand The law of demand says: “If price increases, the demand for goods or services will decrease. On the contrary, when price decreases, the demand for goods or services will increase, ceteris paribus”. Price Quantity Demand Price Quantity Demand P ↑ Qd ↓ or P ↓ Qd ↑ “relationship between price and demand is inversely” Example: Kartini’s Demand Schedule Price of Ice-Cream Cone (Rp) Quantity of Cones Demanded 12.000 10.000 8.000 6.000 4.000 2.000 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Copyright © 2004 South-Western Demand Curve Price of Ice-Cream Cone Rp. 12.000 10.000 1. A decrease in price ... 8.000 Price of IceCream Cone (Rp) Quantity of Cones Demanded 12.000 10.000 8.000 6.000 4.000 2.000 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 6.000 4.000 2.000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 2. ... increases quantity of cones demanded. Copyright © 2004 South-Western The Law of Supply The law of supply says: “If the price of goods or services increases, the quantity of goods or services supplied also increase, and on the contrary, if the price of goods or services decreases, the quantity of goods or services supplied also decreases, ceteris paribus”. Price Quantity Supply Price Quantity Supply P ↑ Qs ↑ or P ↓ Qs ↓ “relationship between price and supply is directly proportional” Example: Krisna’s Supply Schedule Price of Ice-Cream Cone (Rp) Quantity of Cones Supplied 2.000 4.000 6.000 8.000 10.000 12.000 0 1 2 3 4 5 Copyright © 2004 South-Western Supply Curve Price of Ice-Cream Cone Rp.12.000 1. An increase in price ... 10.000 Price of IceCream Cone (Rp) Quantity of Cones Supplied 2.000 4.000 6.000 8.000 10.000 12.000 0 1 2 3 4 5 8.000 6.000 4.000 2.000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 2. ... increases quantity of cones supplied. Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Assumption of the law of demand and supply Assumptions underlying the law of demand and supply of other factors being equal that changes only the price of the goods themselves. This condition is known as “Ceteris paribus” Factors - Factors That Affect Demand Level of Income Population People’s Taste People’s Prediction Price of Subtitutive and Complementary Goods Factors - Factors That Affect Supply Production Cost Number of Producers Natural Disasters Technology Price of Other Goods and Services Demand Curve Shifts Price of Ice-Cream Cone Increase in demand Decrease in demand Demand curve, D2 Demand curve, D1 Demand curve, D3 0 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Example: If Income Increase Price of IceCream Cone $3.00 An increase in income... 2.50 Increase in demand 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 D1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 D2 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Example: If Income Decrease Price of IceCream Cone $3.00 2.50 An increase in income... 2.00 Decrease in demand 1.50 1.00 0.50 D2 0 1 D1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Supply Curve Shifts Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply curve, S3 Decrease in supply Supply curve, S1 Supply curve, S2 Increase in supply 0 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Determine The Demand And Supply Functions Formula: Initial Quantity Product Initial Price P – P1 P2 – P1 Prices After The Change Q – Q1 = Q2 – Q1 Quantity After The Change Demand and Supply Functions Demand Function: PD = a - bQ PD = 8.000 – 0,02 Q Supply Function: PD = a + bQ Ps = 8.000 + 0,02 Q Demand Function Coefficient Price P = a - bQ constants Quantity The Law of Demand Supply Function Coefficient Price P = a + bQ Quantity constants The Law of Supply Example Price Quantity 4500 175.000 3500 225.000 how its function P – 4.500 3.500 – 4.500 P – 4.500 = = Q – 175.000 225.000 – 175.000 Q – 175.000 50.000 1000 50.000 P – 225.000.000 = –1.000 Q + 175.000.000 50.000 P = –1.000 Q + 400.000.000 PD = 8.000 – 0,02 Q Sekian • Semoga Bermanfaat • Terima kasih